字节流分类总览
- 字节流的方向分类
- InputStream 抽象输入类
- OutputStream() 抽象输出类
- 字节节点流
- FileInputStream
- FileOutputStream
- 字节过滤流
- BufferedOutputStream
- BufferedInputStream
- 提供了IO效率,减少访问磁盘的次数。数据存放在缓冲区中。flush()刷新缓冲区,提交数据
- 序列化和反序列化
- 对象流
- ObjectInputStream
- ObjectOutputStream
- 增强读写8中基本数据类型和字符串功能
- 读写对象,可以实现对象的持久化存储
字节流的分类
字节流分为两大类
输入字节流
- InputStream 抽象输入类 是输入类字顶级抽象类
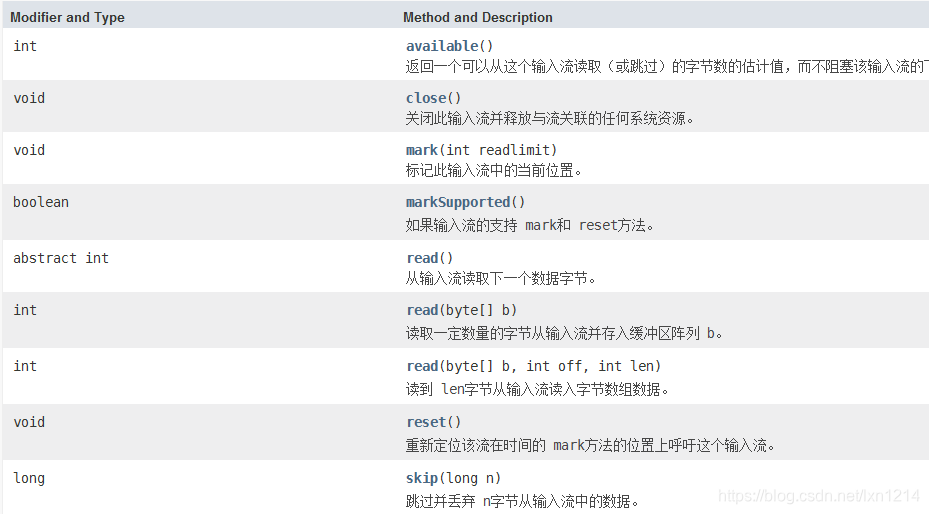
以上是JDK1.8文档提供的该抽象类的方法
其中常用的有以下几种
void close()
关闭此输入流并释放与流关联的任何系统资源。
abstract int read()
从输入流读取下一个数据字节。
int read(byte[] b)
读取一定数量的字节从输入流并存入缓冲区阵列 b。
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) (不常用但是要知道)
读到 len字节从输入流读入字节数组数据。
输出字节流
- OutputStream() 抽象输出类 是输出类顶级抽象类
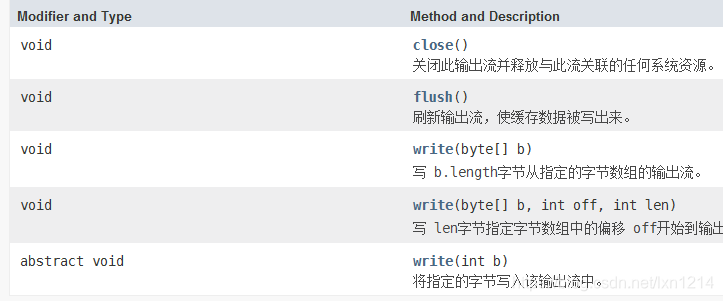
以上是JDK1.8文档提供的该抽象类的方法基本都是常用的除了write(byte[] b, int off, int len)
字节节点流
FileInputStream输入字节节点流
- 是InputStream子类
- 构造函数如下
public FileInputStream(String name)
throws FileNotFoundException
// 系统相关的文件名称
public FileInputStream(File file)
throws FileNotFoundException
// file代表传递一个File对象指向打开连接的地址
public FileInputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj)
//通过使用文件描述符 fdObj创建一个 FileInputStream,它代表一个现有连接到文件系统中的一个实际的文件。
- 具有的方法
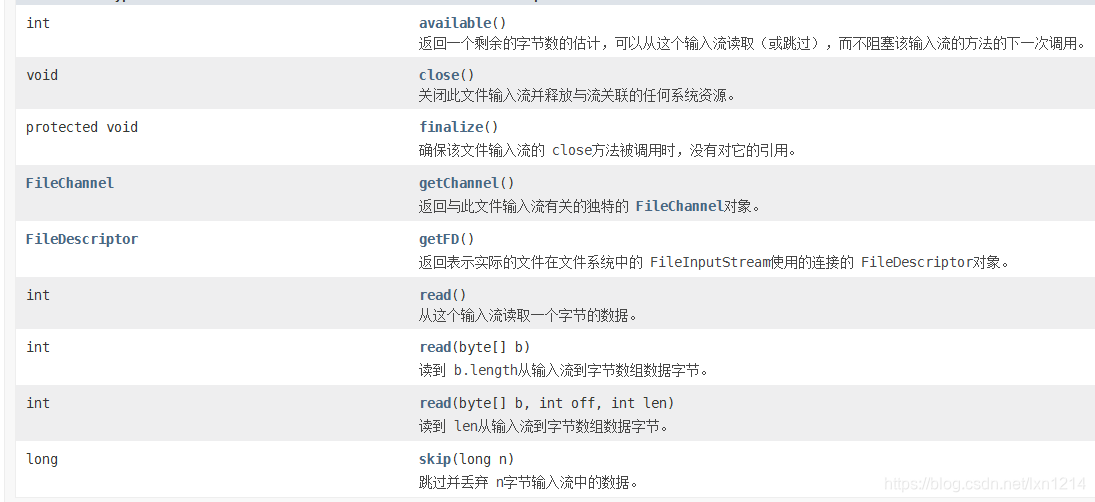
- 使用实例代码
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("资源路径");//如果找不到会抛出异常
//读取方式一:
//int n = is.read(); 一次读一个
//读取方式二:
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int n;
while((n = is.read(bytes))!=-1){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
System.out.print((char)bytes[i]);
}
}
is.close();
}
}
FileOutputStream输出字节节点流
- 是OutputStream子类
- 构造函数如下
FileOutputStream(File file)
创建一个文件输出流写入指定的 File对象表示的文件。
FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append)
创建一个文件输出流写入指定的 File对象表示的文件。
FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj)
创建一个文件输出流,写入指定的文件描述符,它表示在文件系统中的实际文件的现有连接。
FileOutputStream(String name)
创建一个文件输出流,用指定的名称写入文件。
FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append)
创建一个文件输出流,用指定的名称写入文件。
- 具体的方法
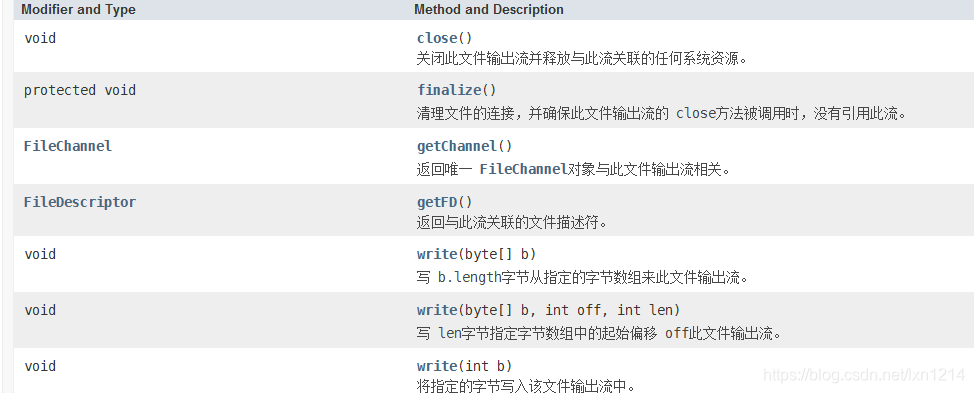
- 示例
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// 方式一
// String file = "./src/txt/target.txt";
// 方式二
File file = new File("./src/txt/target.txt");
OutputStream ios = new FileOutputStream(file);
// 每次写入
ios.write('3');
byte[] bytes = new byte[] {'1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9',65,66};
ios.write(bytes);
ios.close();
}
}
FileInputStream 与FileOutputStream综合案例
- 模仿上传文件也就是先读后写
public class TestFileIO {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 将指定图片,上传一份项目里来
// 文件是再存储设备中 -> 读到程序中来-->写入到存储设备中
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("1.png");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("./src/txt/1.png");
int n;
while((n = fis.read())!=-1) {
fos.write(n);
}
System.out.println("读取结束");
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
}
字节过滤流
- 提供了IO效率,减少访问磁盘的次数。数据存放在缓冲区中。flush()刷新缓冲区,提交数据
- 是一个增强节点流,需要节点流
BufferedInputStream
- 构造方法

- 自带和继承的方法
- 是InputStream孙子类
- 父类是FilterInputStream
int available()
返回一个可以从这个输入流读取(或跳过)的字节数的估计值,而不阻塞该输入流的下一个方法的调用。
void close()
关闭此输入流并释放与流关联的任何系统资源。
void mark(int readlimit)
看到的 InputStream的 mark方法一般合同。
boolean markSupported()
如果输入流的支持 mark和 reset方法。
int read()
看到的 InputStream的 read方法一般合同。
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)
从这个字节的输入流读取到指定的字节数组中的字节,从给定的偏移量开始。
void reset()
看到的 InputStream的 reset方法一般合同。
long skip(long n)
看到的 InputStream的 skip方法一般合同。
- 示例
public class TestBufferedInputStream{
public static void main(String[] args){
// 有参构造需要一个字节输出节点流
// 先创建字节输出节点流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("./src/txt/target.txt");
// 增强节点流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int n;
while((n = bis.read(bytes))!=-1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print((char)bytes[i]);
}
}
// -----------------------------------------
}
}
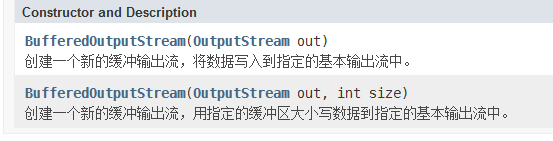
BufferedOutputStream
- 构造方法
`
- 方法
void flush()
刷新缓冲输出流。
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len)
写 len字节指定字节数组中的起始偏移 off这个缓冲输出流。
void write(int b)
public class TestBufferedOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.先构建节点流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("./src/txt/target.txt");
// 2.增强节点流,将节点流对象当参数传入
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//------------------写到缓冲区并提交
bos.write('a');
bos.write('c');
bos.write('a');
byte[] bytes = new byte[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
bos.write(bytes);
bos.flush();//将数据一次性从缓冲区刷入到文件
bos.close();// 关闭流并把缓冲区存在的数据一次性写入到文件里,级联执行flush()
}
}
- 综合案例
public class TestInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
String file = "./src/txt/target.txt";
bufferedInput(file);
bufferedOutput(file);
bufferedInput(file);
}
private static void bufferedInput(String file) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream);
// 缓冲流
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int n;
while ((n = bis.read(bytes))!=-1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print((char)bytes[i]);
}
}
bis.close();
fileInputStream.close();
}
private static void bufferedOutput(String file) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fileInputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
BufferedOutputStream bis = new BufferedOutputStream(fileInputStream);
// 缓冲流
byte[] bytes = new byte[] {'a','c','d','1','2','3','4'};
int n;
bis.write(bytes);
bis.close();
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
序列化和反序列化
序列化需要实现几个必备条件:
- 必须实现接口Serializable
- 必须保证所有属性均支持序列化
- Transient修饰的为临时属性,不参与序列化
- 读取到文件末尾时:java.IO.EOFException
class Student implements Serializable{
String name;
transient Integer age;
String sex;
Double score;
// 数组:基本数据类型可以序列化
// 引用数据类型的数组,数组类型要支持序列化
// static 会影响序列化
public Student(String name, Integer age, String sex, Double score) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", sex=" + sex + ", score=" + score + " ]";
}
//public native int add();
}
对象流
- 增强读写8中基本数据类型和字符串功能
- 读写对象,可以实现对象的持久化存储
- 虽然可以跟以上BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream一样用同样的功能而且增强了读写8种基本数据类型和字符串功能但常用的还是读写对象,对对象实现持久化存储
- 父类是InputStream
ObjectInputStream
- 构造方法
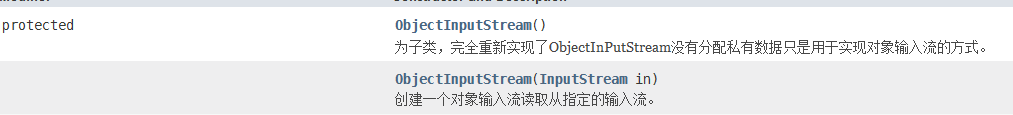
- 普通方法
int available()
返回可以不阻塞读取的字节数。
void close()
关闭输入流。
void defaultReadObject()
从该流中读取当前类的非静态和非瞬态字段。
protected boolean enableResolveObject(boolean enable)
使流能够允许从流中读取的对象被替换。
int read()
读取一个字节的数据。
int read(byte[] buf, int off, int len)
读入一个字节数组。
boolean readBoolean()
在布尔值中读取。
byte readByte()
读取一个8位字节。
char readChar()
读取一个16位字符。
protected ObjectStreamClass readClassDescriptor()
从序列化流中读取类描述符。
double readDouble()
读一个64位的双。
ObjectInputStream.GetField readFields()
从流中读取持久字段,并使它们可用名称命名。
float readFloat()
读取一个32位浮点。
void readFully(byte[] buf)
读取字节,阻塞,直到所有的字节都读。
void readFully(byte[] buf, int off, int len)
读取字节,阻塞,直到所有的字节都读。
int readInt()
读取一个32位int。
String readLine()
过时的。
此方法没有正确地将字节转换为字符。详见和替代输入流。
long readLong()
读一个64位长的。
Object readObject()
从对象输入流对象。
protected Object readObjectOverride()
这种方法被称为对象,通过构建保护对象使用无参数构造函数受信任的子类。
short readShort()
读一个16位的短。
protected void readStreamHeader()
的readstreamheader方法是提供让子类来读取和验证自己的流头。
Object readUnshared()
读取对象输入流“独享”的对象。
int readUnsignedByte()
读取一个无符号的8位字节。
int readUnsignedShort()
读取一个无符号的16位短。
String readUTF()
读 modified UTF-8格式字符串。
void registerValidation(ObjectInputValidation obj, int prio)
在返回图形之前注册一个要验证的对象。
protected 类<?> resolveClass(ObjectStreamClass desc)
加载指定的流类描述的本地类等价。
protected Object resolveObject(Object obj)
这种方法将允许受信任的子类对象输入流用另一个来代替在反序列化期间。
protected 类<?> resolveProxyClass(String[] interfaces)
返回实现代理类描述符中命名的接口的代理类;子类可以实现此方法从流中读取自定义数据以及动态代理类的描述符,从而允许它们使用接口和代理类的替代加载机制。
int skipBytes(int len)
跳过的字节。
- 这个对象流的方法就有很多了尤其是其对八种基本类型和字符串增强的方法
ObjectOutputStream
-
构造方法
-
普通方法
ObjectOutputStream和ObjectInputStream使用示例
- 示例一:
public class TestObjectStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("./src/txt/target.txt");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
//oos.writeInt(30);
//oos.writeDouble(3.5);
//oos.writeBoolean(true);
//oos.flush();
//______________________________--
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("./src/txt/target.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
//int result = ois.readInt();
//System.out.println(result);
Student stu = new Student("李敢敢",23,"男",150D);
Student stu1 = new Student("赵岩岩",22,"女",150D);
Student stu2 = new Student("李某人",10,"未知",150D);
oos.writeObject(stu);
oos.writeObject(stu1);
oos.writeObject(stu2);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
// 返回个异常
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println((Student)ois.readObject());
} catch (Exception e) {
// 到达文件末尾
break;
}
}
ois.close();
}
}
class Student implements Serializable{
String name;
transient Integer age;
String sex;
Double score;
// 数组:基本数据类型可以序列化
// 引用数据类型的数组,数组类型要支持序列化
// static 会影响序列化
public Student(String name, Integer age, String sex, Double score) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", sex=" + sex + ", score=" + score + " ]";
}
//public native int add();
}
综合示例:
public class TestInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
String file = "./src/txt/target.txt";
// 输入接口
//____FileInputStream方式读
//fileInputRead(file);
//____FileOutputStream方式取
//fileOutputWrite(file);
//fileInputRead(file);
//____bufferedInput(file)
//bufferedInput(file);
//bufferedOutput(file);
//bufferedInput(file);
//_________________
objecttOutputStream(file);
objecttInputStream(file);
}
private static void fileInputRead(String file) throws IOException {
InputStream ios = new FileInputStream(file);
// 输出接口
//OutputStream outStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
// 每次读一个字节
//inputStream.read();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int n;
while ((n = ios.read(bytes))!= -1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print((char)bytes[i]);
}
}
ios.close();
}
private static void fileOutputWrite(String file) throws IOException {
OutputStream ios = new FileOutputStream(file);
// 每次写入
byte[] bytes = new byte[] {'1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9',65,66};
ios.write(bytes);
ios.close();
}
private static void bufferedInput(String file) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream);
// 缓冲流
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int n;
while ((n = bis.read(bytes))!=-1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print((char)bytes[i]);
}
}
bis.close();
fileInputStream.close();
}
private static void bufferedOutput(String file) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fileInputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
BufferedOutputStream bis = new BufferedOutputStream(fileInputStream);
// 缓冲流
byte[] bytes = new byte[] {'a','c','d','1','2','3','4'};
int n;
bis.write(bytes);
bis.close();
fileInputStream.close();
}
private static void objecttOutputStream(String file) throws IOException{
FileOutputStream fileInputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream objectout = new ObjectOutputStream(fileInputStream);
objectout.writeObject(new Student("李大大","33"));
objectout.writeObject(new Student("赵岩岩","43"));
objectout.writeObject(new Student("李敢敢","63"));
objectout.close();
fileInputStream.close();
}
private static void objecttInputStream(String file) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
ObjectInputStream objectout = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println((Student)objectout.readObject());
} catch (Exception e) {
// 到达文件末尾
break;
}
}
objectout.close();
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
class Student implements Serializable{
private final static long serialVersionUID = 71282334L;
private String name;
private String age;
public Student(String name, String age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
- 欢迎交流探讨




 本文深入解析字节流的概念,包括输入与输出字节流的分类,节点流与过滤流的功能,以及如何利用缓冲流提高IO效率。同时,详细介绍了序列化与反序列化的过程,演示了对象流在实现对象持久化存储中的应用。
本文深入解析字节流的概念,包括输入与输出字节流的分类,节点流与过滤流的功能,以及如何利用缓冲流提高IO效率。同时,详细介绍了序列化与反序列化的过程,演示了对象流在实现对象持久化存储中的应用。
















 1377
1377

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








