ChannelPipeline
首先需要知道添加到ChannelPipeline中的每个handler会生成一个ChannelHandlerContext,ChannelHandlerContext才是这条链上的节点,而不是handler,如下图

ChannelHandlerContext的主要作用就是和ChannelPipeline以及其他handler进行交互,并且可以动态地修改ChannelPipeline
类继承结构
下面看下ChannelHandlerContext的类继承结构

可以看到ChannelHandlerContext主要实现了三个接口,它们的作用如下:
- ChannelInboundInvoker
继承此接口,因此具有触发各种Channel生命周期事件的能力 - ChannelOutboundInvoker
继承此接口,因此具有向Channel进行写入的能力 - AttributeMap
存取属性
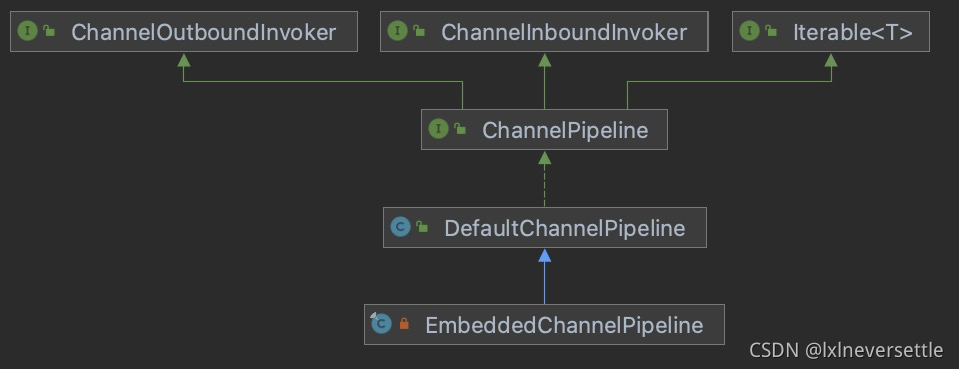
下面看下DefaultChannelPipeline的类继承结构
构造
下面从不同操作出发,看下handlerContext具体做了什么
AbstractChannelHandlerContext
重要属性
// 下一个节点
volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext next;
// 上一个节点
volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev;
// 当前context的handlerState的原子更新器
private static final AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<AbstractChannelHandlerContext> HANDLER_STATE_UPDATER =
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(AbstractChannelHandlerContext.class, "handlerState");
// 下面代表context当前的状态
/**
* {@link ChannelHandler#handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext)} is about to be called.
*/
// handlerAdded将要被调用
private static final int ADD_PENDING = 1;
/**
* {@link ChannelHandler#handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext)} was called.
*/
// handlerAdded被调用
private static final int ADD_COMPLETE = 2;
/**
* {@link ChannelHandler#handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext)} was called.
*/
// handlerRemoved被调用
private static final int REMOVE_COMPLETE = 3;
/**
* Neither {@link ChannelHandler#handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext)}
* nor {@link ChannelHandler#handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext)} was called.
*/
// handlerAdded和handlerRemoved都没被调用
private static final int INIT = 0;
// 是否作用于输入
private final boolean inbound;
// 是否作用于输出
private final boolean outbound;
// 关联的pipeline,从这里也可以看出,一个context只能关联到一个pipeline上
private final DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline;
// 名称
private final String name;
// 是否会按照顺序来执行提交的任务
private final boolean ordered;
// Will be set to null if no child executor should be used, otherwise it will be set to the
// child executor.
// 如果指定了,会将提交的任务提交到这个executor中执行,否则会提交到channel绑定的eventLoop中执行
final EventExecutor executor;
// 成功的对象
private ChannelFuture succeededFuture;
// Lazily instantiated tasks used to trigger events to a handler with different executor.
// There is no need to make this volatile as at worse it will just create a few more instances then needed.
// 执行不同事件的任务
private Runnable invokeChannelReadCompleteTask;
private Runnable invokeReadTask;
private Runnable invokeChannelWritableStateChangedTask;
private Runnable invokeFlushTask;
// 当前状态
private volatile int handlerState = INIT;
构造方法
AbstractChannelHandlerContext(DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline, EventExecutor executor, String name,
boolean inbound, boolean outbound) {
this.name = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(name, "name");
this.pipeline = pipeline;
this.executor = executor;
this.inbound = inbound;
this.outbound = outbound;
// Its ordered if its driven by the EventLoop or the given Executor is an instanceof OrderedEventExecutor.
ordered = executor == null || executor instanceof OrderedEventExecutor;
}
setXXX
首先看下setAddComplete,该方法会在当前context加入到pipeline后被调用,主要就是用来修改context的状态
final void setAddComplete() {
for (;;) {
int oldState = handlerState;
// Ensure we never update when the handlerState is REMOVE_COMPLETE already.
// oldState is usually ADD_PENDING but can also be REMOVE_COMPLETE when an EventExecutor is used that is not
// exposing ordering guarantees.
if (oldState == REMOVE_COMPLETE || HANDLER_STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, oldState, ADD_COMPLETE)) {
return;
}
}
}
接下来看下setAddPending,会在handler添加到pipeline之前进行调用,主要作用也是用来修改context的状态
final void setAddPending() {
boolean updated = HANDLER_STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, INIT, ADD_PENDING);
assert updated; // This should always be true as it MUST be called before setAddComplete() or setRemoved().
}
最后看下setRemoved,该方法会在handler从pipeline中移除的时候被调用,主要作用也是修改context的状态
final void setRemoved() {
handlerState = REMOVE_COMPLETE;
}
DefaultChannelHandlerContext
重要属性
// 当前context关联的handler
private final ChannelHandler handler;
构造方法
DefaultChannelHandlerContext(
DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline, EventExecutor executor, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
super(pipeline, executor, name, isInbound(handler), isOutbound(handler));
if (handler == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("handler");
}
this.handler = handler;
}
isXXXBound
private static boolean isInbound(ChannelHandler handler) {
return handler instanceof ChannelInboundHandler;
}
private static boolean isOutbound(ChannelHandler handler) {
return handler instanceof ChannelOutboundHandler;
}
HeadContext
重要属性
private final Unsafe unsafe;
构造方法
HeadContext(DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline) {
// 调用父类构造方法
super(pipeline, null, HEAD_NAME, false, true);
// 获取当前channel的unsafe,用来响应后续的事件
unsafe = pipeline.channel().unsafe();
// 设置状态
setAddComplete();
}
TailContext
构造方法
TailContext(DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline) {
super(pipeline, null, TAIL_NAME, true, false);
// 设置状态
setAddComplete();
// 这里不需要设置unsafe,因为tailContext后面没有hander了
}
添加Handler
这里以最常用的addLast为例
public final ChannelPipeline addLast(ChannelHandler... handlers) {
return addLast(null, handlers);
}
public final ChannelPipeline addLast(EventExecutorGroup executor, ChannelHandler... handlers) {
if (handlers == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("handlers");
}
for (ChannelHandler h: handlers) {
if (h == null) {
break;
}
addLast(executor, null, h);
}
return this;
}
public final ChannelPipeline addLast(EventExecutorGroup group, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx;
synchronized (this) {
// <1> 判断是否重复添加
checkMultiplicity(handler);
// <2> 创建context
newCtx = newContext(group, filterName(name, handler), handler);
// <3> 将context添加到context链中
addLast0(newCtx);
// If the registered is false it means that the channel was not registered on an eventloop yet.
// In this case we add the context to the pipeline and add a task that will call
// ChannelHandler.handlerAdded(...) once the channel is registered.
if (!registered) {
newCtx.setAddPending();
callHandlerCallbackLater(newCtx, true);
return this;
}
EventExecutor executor = newCtx.executor();
if (!executor.inEventLoop()) {
newCtx.setAddPending();
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
}
});
return this;
}
}
callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
return this;
}
处理输入
这里以fireChannelActive为例,首先看下DefaultPipeline的fireChannelActive
DefaultPipeline.fireChannelActive
可以看到,首先将时间传播给HeadContext进行处理
public final ChannelPipeline fireChannelActive() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelActive(head);
return this;
}
static void invokeChannelActive(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next) {
// 获取HeadContext绑定的executor
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
// 调用invokeChannelActive
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeChannelActive();
} else {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelActive();
}
});
}
}
private void invokeChannelActive() {
// 判断当前的handler的状态
// 如果就绪,那么会回调该handler的channelActive
if (invokeHandler()) {
try {
((ChannelInboundHandler) handler()).channelActive(this);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyHandlerException(t);
}
} else {
// 如果没有就绪,会寻找下一个inbound handler来处理
fireChannelActive();
}
}
public ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelActive() {
invokeChannelActive(findContextInbound());
return this;
}
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextInbound() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
do {
ctx = ctx.next;
} while (!ctx.inbound);
return ctx;
}
HeadContext.channelActive
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 找到下一个inbound handler,执行channelActive回调
ctx.fireChannelActive();
readIfIsAutoRead();
}
TailContext.channelActive
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
onUnhandledInboundChannelActive();
}
protected void onUnhandledInboundChannelActive() {
}
处理输出
这里以bind为例
DefaultChannelPipeline.bind
可以看到首先将事件传播个TailContext
public final ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress) {
return tail.bind(localAddress);
}
TailContext.bind
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress) {
return bind(localAddress, newPromise());
}
public ChannelFuture bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (localAddress == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("localAddress");
}
if (isNotValidPromise(promise, false)) {
// cancelled
return promise;
}
// 找到下一个outbound context
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = findContextOutbound();
// 回调其handler的invokeBind
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);
} else {
safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);
}
}, promise, null);
}
return promise;
}
HeadContext
public void bind(
ChannelHandlerContext ctx, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise)
throws Exception {
unsafe.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
public final void bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
assertEventLoop();
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
// See: https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/576
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(config().getOption(ChannelOption.SO_BROADCAST)) &&
localAddress instanceof InetSocketAddress &&
!((InetSocketAddress) localAddress).getAddress().isAnyLocalAddress() &&
!PlatformDependent.isWindows() && !PlatformDependent.maybeSuperUser()) {
// Warn a user about the fact that a non-root user can't receive a
// broadcast packet on *nix if the socket is bound on non-wildcard address.
logger.warn(
"A non-root user can't receive a broadcast packet if the socket " +
"is not bound to a wildcard address; binding to a non-wildcard " +
"address (" + localAddress + ") anyway as requested.");
}
boolean wasActive = isActive();
try {
// 主要逻辑,具体的子类实现完成绑定操作
doBind(localAddress);
} catch (Throwable t) {
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
closeIfClosed();
return;
}
if (!wasActive && isActive()) {
invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
});
}
safeSetSuccess(promise);
}





 本文深入探讨了Netty中的ChannelHandlerContext及其在ChannelPipeline中的作用,包括它如何作为handler之间的交互桥梁,以及如何动态修改ChannelPipeline。ChannelHandlerContext实现了ChannelInboundInvoker、ChannelOutboundInvoker和AttributeMap接口,分别用于触发Channel生命周期事件、写入Channel以及存储属性。在DefaultChannelPipeline中,每个handler由AbstractChannelHandlerContext表示,通过状态管理确保handler的正确添加和移除。此外,文章还详细解析了handler的添加过程、输入和输出事件的处理,如fireChannelActive和bind操作。
本文深入探讨了Netty中的ChannelHandlerContext及其在ChannelPipeline中的作用,包括它如何作为handler之间的交互桥梁,以及如何动态修改ChannelPipeline。ChannelHandlerContext实现了ChannelInboundInvoker、ChannelOutboundInvoker和AttributeMap接口,分别用于触发Channel生命周期事件、写入Channel以及存储属性。在DefaultChannelPipeline中,每个handler由AbstractChannelHandlerContext表示,通过状态管理确保handler的正确添加和移除。此外,文章还详细解析了handler的添加过程、输入和输出事件的处理,如fireChannelActive和bind操作。
















 279
279

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








