java 的比较基础的功底就是对于java的集合类底层实现和原理的掌握!!!(不可轻视)
-----------------------------------------------hashmap存储原理-------------------------------------------
案例代码:
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();//line1
hashMap.put("one","hello1");//line2
hashMap.put("two","hello2");//line3
hashMap.put("three","hello3");//line4
hashMap.put("four","hello4");//line5
hashMap.put("five","hello5");//line6
hashMap.put("six","hello6");//line7
hashMap.put("seven","hello7");//line8put操作的伪代码可以表示如下:
public V put(K key, V value){
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//在table[i]的地方添加一个包含hash,key,value信息的Entry类。
}1、line1创建了一个HashMap,所以我们来看构造函数
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}hashmap初始化和存放,取数据源码:
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;
init();
}
void init() {
}存放数据的时候,如果未初始化,先进行初始化:
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);//如果是空的,加载
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);获取hash值
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);生成索引
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//遍历已存在的Entry,如果要存入的key和hash值都一样就覆盖。
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
//添加一个节点
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}1.7初始化大小为16
就是一个&操作,这样返回的值比较小适合我们的数组。
源码很简单,先判断table如果是空的,就初始化数组table,接着如果key是null就单独处理。否则的话就得到key的hash值再生成索引,这里用了indexFor()方法生成索引是因为:hash值一般都很大,是不适合我们的数组的。来看indexFor方法
/** * Returns index for hash code h. */ static int indexFor(int h, int length) { // assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2"; return h & (length-1); }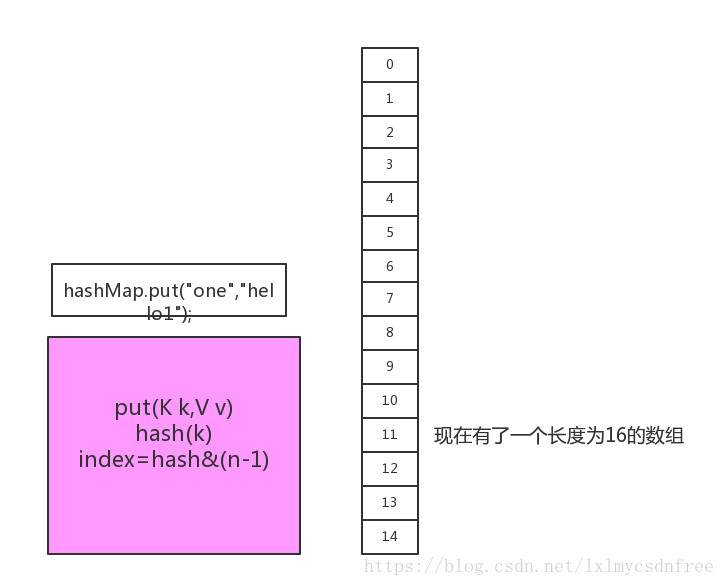
接着由于我们的key不为null,到了获取hash值和索引,这里假设int hash = hash(key)和int i = indexFor(hash, table.length)生成的索引i为hash=2306996,i = 4;那么就会在table索引为4的位置新建一个Entry,对应的代码是addEntry(hash, key, value, i);到此结果如下图: 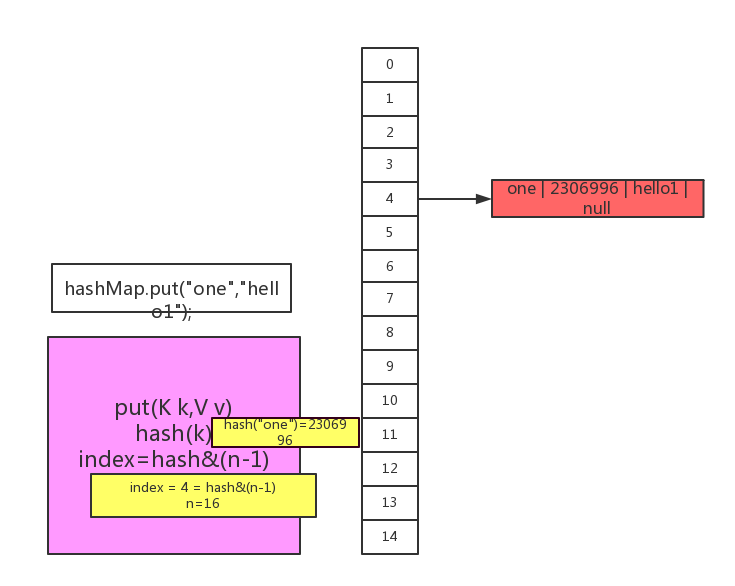
新建的Entry内部的变量分别是,hash,key,value,和指向下一节点的next Entry。
3、继续来看上面的源码line3,line3和line2一样,而且数组不为空直接hash(key)和index。所以直接看图了
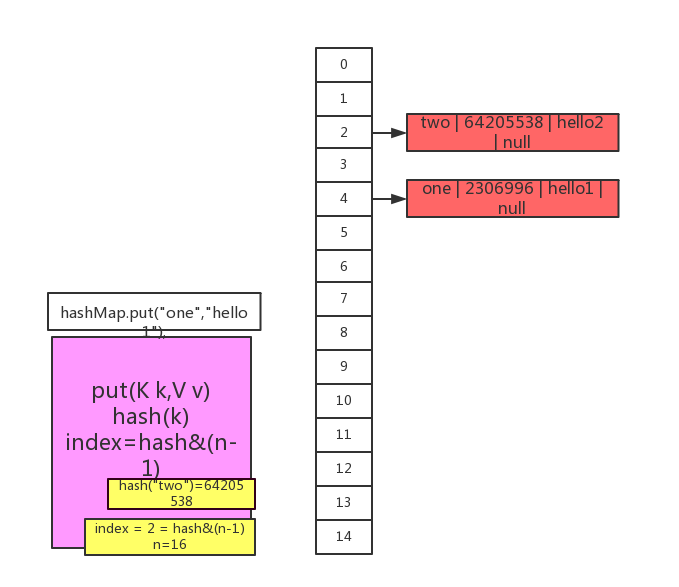
在这说明下:hashmap 中连表节点中保存的是key 和key对应的hashcode
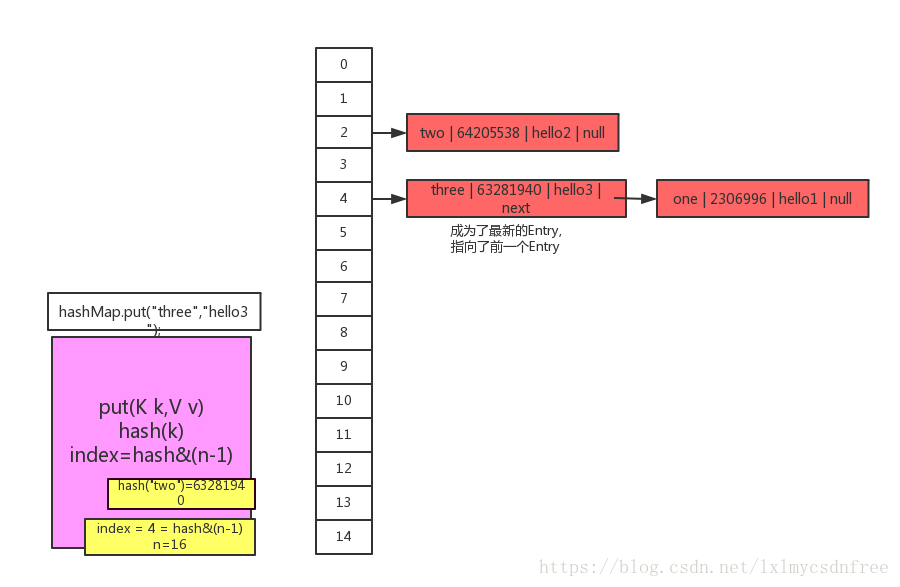
4、到了line4,这里line4情况有点特殊,我们假设line4里key生成的hashcode产生的index也为4,比如hash(“three”) 的值 63281940
hash&(15)产生的index为4。这种情况由于之前的位置已经有Entry了,所以遍历Entry如果key和hashcode都相同,就直接替换,否则新添加一个Entry,来看一下对应源码
public V put(K key, V value) {
...//一些代码
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
//for循环里判断如果hash和key都一样直接替换。
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);//没有重复的话就addEntry
return null;
}上面代码先判断是否需要替换,不需要就调用了addEntry方法。来看addEntry
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}//判断数组容量是否足够,不足够扩容
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}里面又调用了createEntry
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
//获取当前节点,然后新建一个含有当前hash,key,value信息的一个节点,并且该节点的Entry指向了前一个Entry并赋值给table[index],成为了最新的节点Entry,同时将size加1。
}到这里相信大家很清楚了。来看看图:
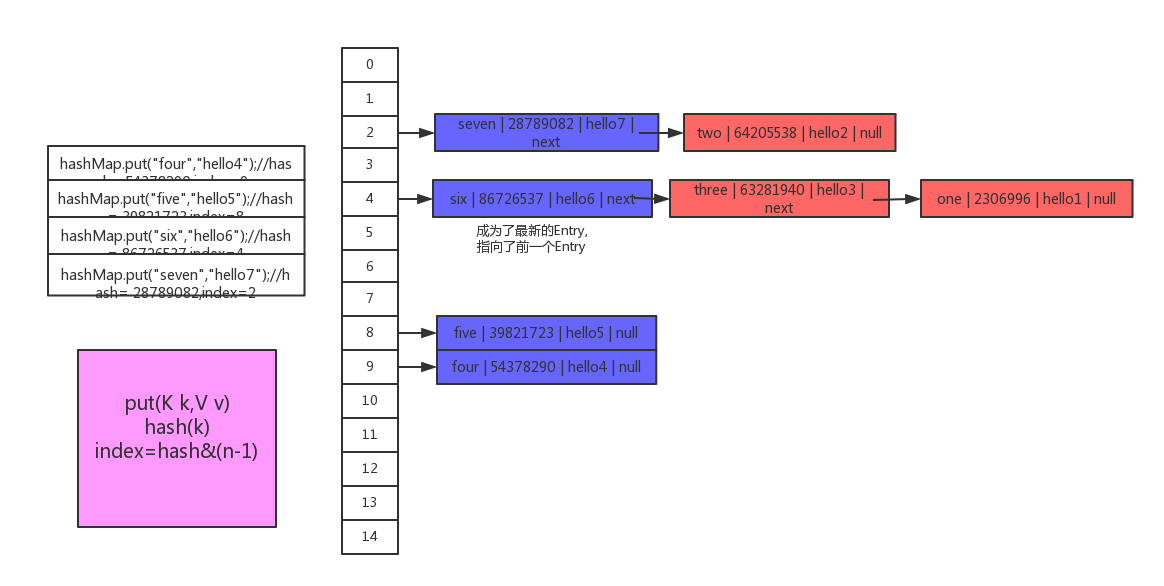
hashmap 取值过程:
我们通过hashMap.get(K key) 来获取存入的值,key的取值很简单了。我们通过数组的index直接找到Entry,然后再遍历Entry,当hashcode和key都一样就是我们当初存入的值啦。看源码:
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}调用getEntry(key)拿到entry ,然后返回entry的value,来看getEntry(key)方法
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}
思考几个问题:
问题1、HashMap是基于key的hashcode的存储的,如果两个不同的key产生的hashcode一样取值怎么办?
看了上面的分析,你肯定知道,再数组里面有链表结构的Entry来实现,通过遍历所有的Entry,比较key来确定到底是哪一个value;
问题2、HashMap是基于key的hashcode的存储的,如果两个key一样产生的hashcode一样怎么办?
在put操作的时候会遍历所有Entry,如果有key相等的则替换。所以get的时候只会有一个
问题3、如果我们使用我们定义的类作为hashMap的key,比如hashset 的实现,那么我们需要做什么
首先hashmap获取对象的hashcode和equal 判断是否相等。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
HashMap 和 HashSet 内部是如何工作的?散列函数(hashing function)是什么?
HashMap 不仅是一个常用的数据结构,在面试中也是热门话题。
Q1. HashMap 如何存储数据?
A1. 以键/值对(key/value)形式存储。你可以使用键(key)来存、取值。
Q2. HashMap 查询时间的复杂度是怎样的?
A2. 是O(n) = O(k * n)。如果 hashCode() 方法能向下面讨论的那样把数据分散到桶(bucket)中,那么平均是O(1)。
Q3. HashMap 内部是如何存储数据的?
A3. HashMap 使用后台数组(backing array)作为桶,并使用链表(linked list)存储键/值对。
桶的后台数组:如下所示
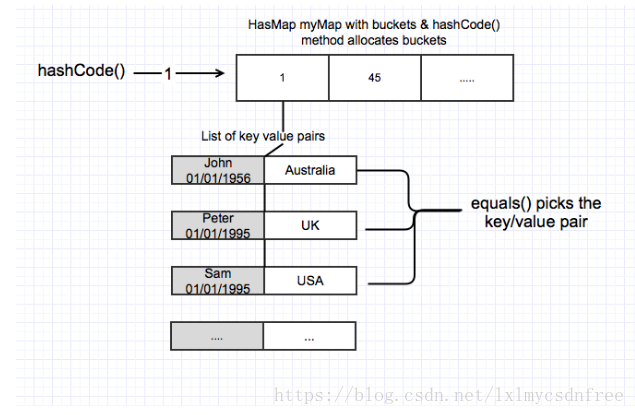
1)使用键(key)和值(value)将一个对象放入 map 中时,会隐式调用 hashCode() 方法,返回哈希值(hash code value),比如 123。两个不同的键能够返回一样的哈希值。良好的哈希算法(hashing algorithm)能够将数值分散开。在上面的例子中,我们假设 (“John”,01/01/1956) 的键和 (“Peter”, 01/01/1995) 的键返回相同的哈希值,都是 123。
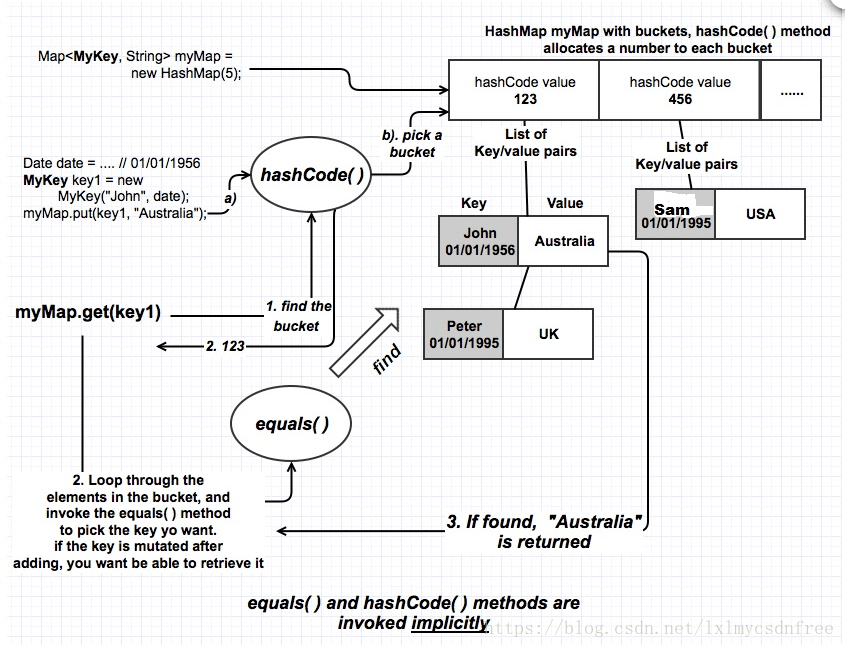
2)当返回一个 hashCode,例如是 123,初始的 HashMap 容量为 10,它如何知道存储到后台数组(backing array)的哪个索引(index)呢?HashMap 内部会调用 hash(int ) 和 indexFor(int h, int length) 方法。这被称为哈希函数(hashing function)。
简要解释下这个函数:
1 2 3 4 | hashCode() % capacity123 % 10 = 3456 % 10 = 6 |
这表示,“hashCode = 123”存储在备份数组的索引3上。
容量为 10 的情况下,你可能得到的数字在 0 到 9 之间。
一旦 HashMap 达到容量的 75%,也就是哈希因子(hash factor)默认值 0.75,后台数组(backing array)的容量就会加倍,发生重散列(rehashing)为新的 20 的容量重新分配桶。
1 2 3 4 | hashCode() % capacity123 % 20 = 3456 % 20 = 16 |
上面重散列的取模方法有一个缺陷。如果 hashCode 是负数会怎样?负索引可不是你想要的。因此,一个改进的哈希公式会移出符号位,然后再用取模(即 %)运算符计算剩余部分。
1 2 | (123 & 0x7FFFFFFF) % 20 = 3(456 & 0x7FFFFFFF) % 20 = 16 |
这确保你得到的索引值为正数。如果你查看 Java 8 的 HashMap 源码,它的实现使用以下方法:
a). 通过只抽取重要的低位,来防止不良离散值(poorer hashes)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | static int hash(int h) { // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by // constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded // number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor). h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12); return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);} |
b). 根据哈希码(hashCode)和容量(capacity),来决定索引(index)。
1 2 3 | static int indexFor(int h, int length) { return h & (length-1);} |
实际的名称值对(name value pairs)作为一个键/值对存储在 LinkedList 中。
如上图所示,键/值对以链表形式存储。两个不同的键可以产生一样的 hashCode,例如123,并存储在同一个 bucket 中,理解这点至关重要。例如,上面例子中的 “John, 01/01/1956” 和 “Peter, 01/01/1995“ 。你如何只检索 “John, 01/01/1956” 呢?此时你的 key 所属类的 equals() 方法会被调用。它遍历 bucket 为 “123” 的 LinkedList 中的每个条目,使用 equals() 方法找到并检索出键为 “John, 01/01/1956” 的条目。这就是在你的类中实现 hashCode() 和 equals() 方法重要性的原因。如果你使用一个现有的包装类,如 Integer 或 String 作为键,它们已经实现了这两个方法。如果你使用自己写的类作为键,如 “John, 01/01/1956” 这样含有名字和出生日期属性的“MyKey”,你有责任正确地实现这些方法。
Q5. 为什么恰当地设置 HashMap 的初始容量(initial capacity)是最佳实践?
A5. 这样可以减少重散列的发生。
Q6. HashSet 内部如何存储数据?
A6. HashSet 内部使用 HashMap 。它将元素存储为键和值。(译者注:HashSet 把存储的值作为 key)
对于我们如果将一个自定义的类作为key存储,我们应该做哪些事情? 一个例子:
private class IntInt {
int v,w;
@Override
public boolean equals(Object object) {
if (this == object) return true;
if (!(object instanceof IntInt)) return false;
IntInt o = (IntInt) object;
if (v == o.v && w == o.w) return true;
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return v * 31 + w;
}
IntInt (int a, int b) {
this.v = a;
this.w = b;
}
} Q7. 为 Object 实现了一个糟糕的 hashcode() 会有什么影响?
A7. 不同的对象调用 hashCode() 方法应该返回不同的值。如果不同的对象返回相同的值,会导致更多的键/值对存储在同一个 bucket 中。这会降低 HashMap 和 HashSet 的性能。
参考:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/yissan/article/details/50888070
http://www.importnew.com/21841.html





 本文深入解析Java中HashMap的工作原理,包括存储与检索机制、散列函数应用及内部数据结构。探讨了HashMap如何处理哈希冲突,以及如何通过合理设置初始容量来优化性能。
本文深入解析Java中HashMap的工作原理,包括存储与检索机制、散列函数应用及内部数据结构。探讨了HashMap如何处理哈希冲突,以及如何通过合理设置初始容量来优化性能。
















 9413
9413

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








