vscode插件快餐教程(4) - 语言服务器协议lsp
语言服务器协议lsp是vscode为了解决语言扩展中的痛点来实现的一套协议。如下图所示:

总体说来,在有lsp之前,存在三个主要问题:
一是语言相关的扩展都是用该语言母语写的,不容易集成到插件中去。毕竟现在大量的语言都带有运行时。
二是语言扫描相关的工作都比较占用CPU资源,运行在vscode内部不如放在独立进程,甚至远程服务器上更好。
三是如上图左边所示,缺少一套协议的话,每种语言服务需要适配多个编辑器。同样,每种编辑器也需要各种语言服务。这造成了较大的资源浪费。
LSP协议概述
LSP是基于json rpc的协议。
我们先来看一个例子:
Content-Length: ...\r\n
\r\n
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "textDocument/didOpen",
"params": {
...
}
}
jsonrpc是json rpc协议的头,LSP主要是定义了method和params。
从服务端发给客户端的,是Request,客户端返回Response。客户端主动发起的是Notification.
下面我们用一张图来看看LSP目前都支持哪些功能:
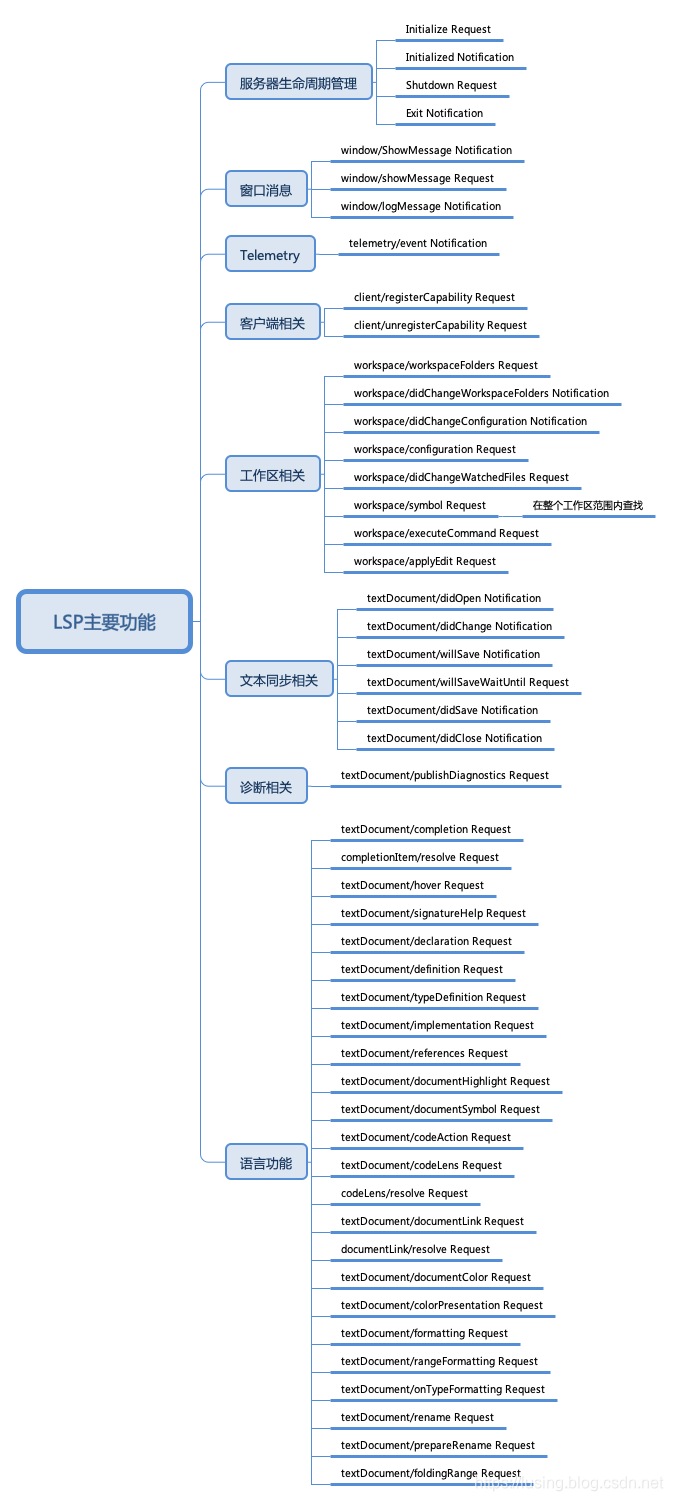
最大的一块是语言功能,这些也通可以通过本地的Provider等方法来实现。
生命周期管理
服务器的生命周期通过客户端发送initialize请求开始,负载为一个InitializeParameter对象:
interface InitializeParams {
/**
* The process Id of the parent process that started
* the server. Is null if the process has not been started by another process.
* If the parent process is not alive then the server should exit (see exit notification) its process.
*/
processId: number | null;
/**
* The rootPath of the workspace. Is null
* if no folder is open.
*
* @deprecated in favour of rootUri.
*/
rootPath?: string | null;
/**
* The rootUri of the workspace. Is null if no
* folder is open. If both `rootPath` and `rootUri` are set
* `rootUri` wins.
*/
rootUri: DocumentUri | null;
/**
* User provided initialization options.
*/
initializationOptions?: any;
/**
* The capabilities provided by the client (editor or tool)
*/
capabilities: ClientCapabilities;
/**
* The initial trace setting. If omitted trace is disabled ('off').
*/
trace?: 'off' | 'messages' | 'verbose';
/**
* The workspace folders configured in the client when the server starts.
* This property is only available if the client supports workspace folders.
* It can be `null` if the client supports workspace folders but none are
* configured.
*
* Since 3.6.0
*/
workspaceFolders?: WorkspaceFolder[] | null;
}
而服务端返回的,是服务器的能力:
interface InitializeResult {
/**
* The capabilities the language server provides.
*/
capabilities: ServerCapabilities;
}
ServerCapabilities的定义如下。主要对应了Workspace和TextDocument两大类型的API:
interface ClientCapabilities {
/**
* Workspace specific client capabilities.
*/
workspace?: WorkspaceClientCapabilities;
/**
* Text document specific client capabilities.
*/
textDocument?: TextDocumentClientCapabilities;
/**
* Experimental client capabilities.
*/
experimental?: any;
}
客户端收到initialize result之后,按照三次握手的原则,将返回一个initialized消息做确认。至此,一个服务端与客户端通信的生命周期就算是成功建立。
LSP协议的实现
除了整个协议的详细描述之外,微软还为我们准备了LSP的SDK,源码在:https://github.com/microsoft/vscode-languageserver-node
我们首先从server侧来讲解LSP sdk的用法。
createConnection
服务端首先要获取一个Connection对象,通过vscode-languageserver提供的createConnection函数来创建Connection.
let connection = createConnection(ProposedFeatures.all);
Connection中对于LSP的消息进行了封装,比如:
onInitialize: (handler) => initializeHandler = handler,
onInitialized: (handler) => connection.onNotification(InitializedNotification.type, handler),
onShutdown: (handler) => shutdownHandler = handler,
onExit: (handler) => exitHandler = handler,
...
onDidChangeConfiguration: (handler) => connection.onNotification(DidChangeConfigurationNotification.type, handler),
onDidChangeWatchedFiles: (handler) => connection.onNotification(DidChangeWatchedFilesNotification.type, handler),
...
onDidOpenTextDocument: (handler) => connection.onNotification(DidOpenTextDocumentNotification.type, handler),
onDidChangeTextDocument: (handler) => connection.onNotification(DidChangeTextDocumentNotification.type, handler),
onDidCloseTextDocument: (handler) => connection.onNotification(DidCloseTextDocumentNotification.type, handler),
onWillSaveTextDocument: (handler) => connection.onNotification(WillSaveTextDocumentNotification.type, handler),
onWillSaveTextDocumentWaitUntil: (handler) => connection.onRequest(WillSaveTextDocumentWaitUntilRequest.type, handler),
onDidSaveTextDocument: (handler) => connection.onNotification(DidSaveTextDocumentNotification.type, handler),
sendDiagnostics: (params) => connection.sendNotification(PublishDiagnosticsNotification.type, params),
...
onHover: (handler) => connection.onRequest(HoverRequest.type, handler),
onCompletion: (handler) => connection.onRequest(CompletionRequest.type, handler),
onCompletionResolve: (handler) => connection.onRequest(CompletionResolveRequest.type, handler),
onSignatureHelp: (handler) => connection.onRequest(SignatureHelpRequest.type, handler),
onDeclaration: (handler) => connection.onRequest(DeclarationRequest.type, handler),
onDefinition: (handler) => connection.onRequest(DefinitionRequest.type, handler),
onTypeDefinition: (handler) => connection.onRequest(TypeDefinitionRequest.type, handler),
onImplementation: (handler) => connection.onRequest(ImplementationRequest.type, handler),
onReferences: (handler) => connection.onRequest(ReferencesRequest.type, handler),
onDocumentHighlight: (handler) => connection.onRequest(DocumentHighlightRequest.type, handler),
onDocumentSymbol: (handler) => connection.onRequest(DocumentSymbolRequest.type, handler),
onWorkspaceSymbol: (handler) => connection.onRequest(WorkspaceSymbolRequest.type, handler),
onCodeAction: (handler) => connection.onRequest(CodeActionRequest.type, handler),
onCodeLens: (handler) => connection.onRequest(CodeLensRequest.type, handler),
onCodeLensResolve: (handler) => connection.onRequest(CodeLensResolveRequest.type, handler),
onDocumentFormatting: (handler) => connection.onRequest(DocumentFormattingRequest.type, handler),
onDocumentRangeFormatting: (handler) => connection.onRequest(DocumentRangeFormattingRequest.type, handler),
onDocumentOnTypeFormatting: (handler) => connection.onRequest(DocumentOnTypeFormattingRequest.type, handler),
onRenameRequest: (handler) => connection.onRequest(RenameRequest.type, handler),
onPrepareRename: (handler) => connection.onRequest(PrepareRenameRequest.type, handler),
onDocumentLinks: (handler) => connection.onRequest(DocumentLinkRequest.type, handler),
onDocumentLinkResolve: (handler) => connection.onRequest(DocumentLinkResolveRequest.type, handler),
onDocumentColor: (handler) => connection.onRequest(DocumentColorRequest.type, handler),
onColorPresentation: (handler) => connection.onRequest(ColorPresentationRequest.type, handler),
onFoldingRanges: (handler) => connection.onRequest(FoldingRangeRequest.type, handler),
onExecuteCommand: (handler) => connection.onRequest(ExecuteCommandRequest.type, handler),
协议中的所有的消息都有封装。
onInitialize
通过createConnection创建了Connection对象之后,我们就可以调用connection.listen()来实现对client的监听了。
在监听之前,我们需要把处理监听事件的回调函数设好。
首先是处理initialize消息的onInitialize,之前我们讲协议时介绍了,主要工作是告知client这个服务端的能力:
connection.onInitialize((params: InitializeParams) => {
let capabilities = params.capabilities;
return {
capabilities: {
textDocumentSync: documents.syncKind,
// Tell the client that the server supports code completion
completionProvider: {
resolveProvider: true
}
}
};
});
根据三次握手的原则,客户端还会返回initialized notification进行通知,服务端可以借用处理这个notification的返回值进行一些初始化的工作。例:
connection.onInitialized(() => {
if (hasWorkspaceFolderCapability) {
connection.workspace.onDidChangeWorkspaceFolders(_event => {
connection.console.log('Workspace folder change event received.');
});
}
});
 VSCode插件:语言服务器协议LSP教程
VSCode插件:语言服务器协议LSP教程





 本文是VSCode插件快餐教程,介绍语言服务器协议LSP。LSP是VSCode为解决语言扩展痛点而实现的协议,能解决语言扩展集成难、扫描占CPU、适配资源浪费等问题。还阐述了LSP协议概述、生命周期管理及实现,包括createConnection和onInitialize等内容。
本文是VSCode插件快餐教程,介绍语言服务器协议LSP。LSP是VSCode为解决语言扩展痛点而实现的协议,能解决语言扩展集成难、扫描占CPU、适配资源浪费等问题。还阐述了LSP协议概述、生命周期管理及实现,包括createConnection和onInitialize等内容。

















 991
991












