v8字节码的编译过程
前面的文章中我们学习了调用V8 API的方法。本文我们讲解一下v8编译成字节码的主要过程。
我们来看一张编译的全局地图:
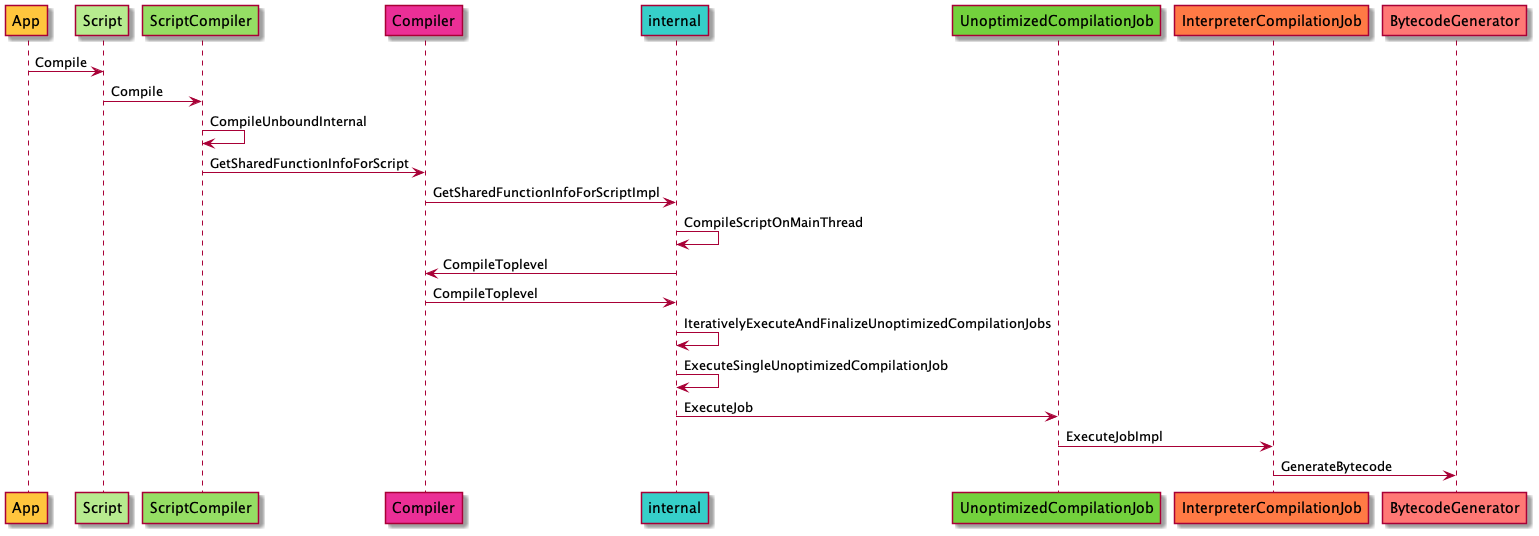
API调用部分
我们知道,v8中编译代码的方法是v8::Script::Compile:
v8::Local<v8::Script> script =
v8::Script::Compile(context, source).ToLocalChecked();
这将会调用api.cc中的Compile:
MaybeLocal<Script> Script::Compile(Local<Context> context, Local<String> source,
ScriptOrigin* origin) {
if (origin) {
ScriptCompiler::Source script_source(source, *origin);
return ScriptCompiler::Compile(context, &script_source);
}
ScriptCompiler::Source script_source(source);
return ScriptCompiler::Compile(context, &script_source);
}
Script::Compile会调用同属于api.cc中的ScriptCompiler::Compile:
MaybeLocal<Script> ScriptCompiler::Compile(Local<Context> context,
Source* source,
CompileOptions options,
NoCacheReason no_cache_reason) {
Utils::ApiCheck(
!source->GetResourceOptions().IsModule(), "v8::ScriptCompiler::Compile",
"v8::ScriptCompiler::CompileModule must be used to compile modules");
auto isolate = context->GetIsolate();
MaybeLocal<UnboundScript> maybe =
CompileUnboundInternal(isolate, source, options, no_cache_reason);
Local<UnboundScript> result;
if (!maybe.ToLocal(&result)) return MaybeLocal<Script>();
v8::Context::Scope scope(context);
return result->BindToCurrentContext();
}
然后会调用ScriptCompiler的CompileUnboundInternal函数,我们删节一下code cache部分:
MaybeLocal<UnboundScript> ScriptCompiler::CompileUnboundInternal(
Isolate* v8_isolate, Source* source, CompileOptions options,
NoCacheReason no_cache_reason) {
auto isolate = reinterpret_cast<i::Isolate*>(v8_isolate);
TRACE_EVENT_CALL_STATS_SCOPED(isolate, "v8", "V8.ScriptCompiler");
ENTER_V8_NO_SCRIPT(isolate, v8_isolate->GetCurrentContext(), ScriptCompiler,
CompileUnbound, MaybeLocal<UnboundScript>(),
InternalEscapableScope);
i::Handle<i::String> str = Utils::OpenHandle(*(source->source_string));
i::Handle<i::SharedFunctionInfo> result;
TRACE_EVENT0(TRACE_DISABLED_BY_DEFAULT("v8.compile"), "V8.CompileScript");
i::ScriptDetails script_details = GetScriptDetails(
isolate, source->resource_name, source->resource_line_offset,
source->resource_column_offset, source->source_map_url,
source->host_defined_options, source->resource_options);
i::MaybeHandle<i::SharedFunctionInfo> maybe_function_info;
if (options == kConsumeCodeCache) {
...
} else {
// Compile without any cache.
maybe_function_info = i::Compiler::GetSharedFunctionInfoForScript(
isolate, str, script_details, options, no_cache_reason,
i::NOT_NATIVES_CODE);
}
has_pending_exception = !maybe_function_info.ToHandle(&result);
RETURN_ON_FAILED_EXECUTION(UnboundScript);
RETURN_ESCAPED(ToApiHandle<UnboundScript>(result));
}
Compiler部分
此时调用internal::Compiler::GetSharedFunctionInfoForScript:
MaybeHandle<SharedFunctionInfo> Compiler::GetSharedFunctionInfoForScript(
Isolate* isolate, Handle<String> source,
const ScriptDetails& script_details,
ScriptCompiler::CompileOptions compile_options,
ScriptCompiler::NoCacheReason no_cache_reason, NativesFlag natives) {
return GetSharedFunctionInfoForScriptImpl(
isolate, source, script_details, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr,
compile_options, no_cache_reason, natives);
}
这是一层皮,最终调用到GetSharedFunctionInfoForScriptImpl:
MaybeHandle<SharedFunctionInfo> GetSharedFunctionInfoForScriptImpl(
Isolate* isolate, Handle<String> source,
const ScriptDetails& script_details, v8::Extension* extension,
AlignedCachedData* cached_data, BackgroundDeserializeTask* deserialize_task,
ScriptCompiler::CompileOptions compile_options,
ScriptCompiler::NoCacheReason no_cache_reason, NativesFlag natives) {
...
maybe_result =
CompileScriptOnMainThread(flags, source, script_details, natives,
extension, isolate, &is_compiled_scope);
}
...
对于大多数情况,我们是在主线程中编译的,调用CompileScriptOnMainThread:
MaybeHandle<SharedFunctionInfo> CompileScriptOnMainThread(
const UnoptimizedCompileFlags flags, Handle<String> source,
const ScriptDetails& script_details, NativesFlag natives,
v8::Extension* extension, Isolate* isolate,
IsCompiledScope* is_compiled_scope) {
UnoptimizedCompileState compile_state(isolate);
ParseInfo parse_info(isolate, flags, &compile_state);
parse_info.set_extension(extension);
Handle<Script> script =
NewScript(isolate, &parse_info, source, script_details, natives);
DCHECK_IMPLIES(parse_info.flags().collect_type_profile(),
script->IsUserJavaScript());
DCHECK_EQ(parse_info.flags().is_repl_mode(), script->is_repl_mode());
return Compiler::CompileToplevel(&parse_info, script, isolate,
is_compiled_scope);
}
然后从全局函数回到Compiler类的CompileToplevel函数:
MaybeHandle<SharedFunctionInfo> Compiler::CompileToplevel(
ParseInfo* parse_info, Handle<Script> script, Isolate* isolate,
IsCompiledScope* is_compiled_scope) {
return v8::internal::CompileToplevel(parse_info, script, kNullMaybeHandle,
isolate, is_compiled_scope);
}
结果类中的又是个皮,实现的CompileToplevel会调用parsing::ParseProgram去解析代码为AST,然后调用IterativelyExecuteAndFinalizeUnoptimizedCompilationJobs去进行编译操作:
MaybeHandle<SharedFunctionInfo> CompileToplevel(
ParseInfo* parse_info, Handle<Script> script,
MaybeHandle<ScopeInfo> maybe_outer_scope_info, Isolate* isolate,
IsCompiledScope* is_compiled_scope) {
...
if (parse_info->literal() == nullptr &&
!parsing::ParseProgram(parse_info, script, maybe_outer_scope_info,
isolate, parsing::ReportStatisticsMode::kYes)) {
FailWithPendingException(isolate, script, parse_info,
Compiler::ClearExceptionFlag::KEEP_EXCEPTION);
return MaybeHandle<SharedFunctionInfo>();
}
...
if (!IterativelyExecuteAndFinalizeUnoptimizedCompilationJobs(
isolate, shared_info, script, parse_info, isolate->allocator(),
is_compiled_scope, &finalize_unoptimized_compilation_data_list,
nullptr)) {
FailWithPendingException(isolate, script, parse_info,
Compiler::ClearExceptionFlag::KEEP_EXCEPTION);
return MaybeHandle<SharedFunctionInfo>();
}
...
}
最终会落到 IterativelyExecuteAndFinalizeUnoptimizedCompilationJobs 中。
bool IterativelyExecuteAndFinalizeUnoptimizedCompilationJobs(
IsolateT* isolate, Handle<SharedFunctionInfo> outer_shared_info,
Handle<Script> script, ParseInfo* parse_info,
AccountingAllocator* allocator, IsCompiledScope* is_compiled_scope,
FinalizeUnoptimizedCompilationDataList*
finalize_unoptimized_compilation_data_list,
DeferredFinalizationJobDataList*
jobs_to_retry_finalization_on_main_thread) {
DeclarationScope::AllocateScopeInfos(parse_info, isolate);
std::vector<FunctionLiteral*> functions_to_compile;
functions_to_compile.push_back(parse_info->literal());
while (!functions_to_compile.empty()) {
FunctionLiteral* literal = functions_to_compile.back();
functions_to_compile.pop_back();
Handle<SharedFunctionInfo> shared_info =
Compiler::GetSharedFunctionInfo(literal, script, isolate);
if (shared_info->is_compiled()) continue;
std::unique_ptr<UnoptimizedCompilationJob> job =
ExecuteSingleUnoptimizedCompilationJob(parse_info, literal, allocator,
&functions_to_compile,
isolate->AsLocalIsolate());
if (!job) return false;
...
针对于每一个要编译的函数,将调用ExecuteSingleUnoptimizedCompilationJob去进行编译:
std::unique_ptr<UnoptimizedCompilationJob>
ExecuteSingleUnoptimizedCompilationJob(
ParseInfo* parse_info, FunctionLiteral* literal,
AccountingAllocator* allocator,
std::vector<FunctionLiteral*>* eager_inner_literals,
LocalIsolate* local_isolate) {
...
std::unique_ptr<UnoptimizedCompilationJob> job(
interpreter::Interpreter::NewCompilationJob(
parse_info, literal, allocator, eager_inner_literals, local_isolate));
if (job->ExecuteJob() != CompilationJob::SUCCEEDED) {
// Compilation failed, return null.
return std::unique_ptr<UnoptimizedCompilationJob>();
}
return job;
}
创建了Job之后,再调用Job的ExecuteJob 函数去具体执行。
CompilationJob::Status UnoptimizedCompilationJob::ExecuteJob() {
// Delegate to the underlying implementation.
DCHECK_EQ(state(), State::kReadyToExecute);
ScopedTimer t(&time_taken_to_execute_);
return UpdateState(ExecuteJobImpl(), State::kReadyToFinalize);
}
解释器部分
ExecuteJobImpl是一个虚函数。目前的实现有两种,一种是asm.js的实现,另一种是解释器的实现。
正常我们用的都是解释器的实现方法:
InterpreterCompilationJob::Status InterpreterCompilationJob::ExecuteJobImpl() {
RCS_SCOPE(parse_info()->runtime_call_stats(),
RuntimeCallCounterId::kCompileIgnition,
RuntimeCallStats::kThreadSpecific);
...
base::Optional<ParkedScope> parked_scope;
if (local_isolate_) parked_scope.emplace(local_isolate_);
generator()->GenerateBytecode(stack_limit());
if (generator()->HasStackOverflow()) {
return FAILED;
}
return SUCCEEDED;
}
最终将调用BytecodeGenerator的GenerateBytecode方法去生成字节码。
void BytecodeGenerator::GenerateBytecode(uintptr_t stack_limit) {
...
if (NeedsContextInitialization(closure_scope())) {
// Push a new inner context scope for the function.
BuildNewLocalActivationContext();
ContextScope local_function_context(this, closure_scope());
BuildLocalActivationContextInitialization();
GenerateBytecodeBody();
} else {
GenerateBytecodeBody();
}
// Check that we are not falling off the end.
DCHECK(builder()->RemainderOfBlockIsDead());
}
字节码生成的核心部分在GenerateBytecodeBody中,其主要的工作是遍历AST,所以主要的操作全在Visit*:
void BytecodeGenerator::GenerateBytecodeBody() {
// Build the arguments object if it is used.
VisitArgumentsObject(closure_scope()->arguments());
// Build rest arguments array if it is used.
Variable* rest_parameter = closure_scope()->rest_parameter();
VisitRestArgumentsArray(rest_parameter);
// Build assignment to the function name or {.this_function}
// variables if used.
VisitThisFunctionVariable(closure_scope()->function_var());
VisitThisFunctionVariable(closure_scope()->this_function_var());
// Build assignment to {new.target} variable if it is used.
VisitNewTargetVariable(closure_scope()->new_target_var());
...
// Visit declarations within the function scope.
if (closure_scope()->is_script_scope()) {
VisitGlobalDeclarations(closure_scope()->declarations());
} else if (closure_scope()->is_module_scope()) {
VisitModuleDeclarations(closure_scope()->declarations());
} else {
VisitDeclarations(closure_scope()->declarations());
}
// Emit initializing assignments for module namespace imports (if any).
VisitModuleNamespaceImports();
...
// Visit statements in the function body.
VisitStatements(literal->body());
...
}
字节码生成器
在Visit*函数中,除了遍历AST,然后就是调用字节码生成器去生成字节码。
我们来看个简单的例子,void运算符的实现:
void BytecodeGenerator::VisitVoid(UnaryOperation* expr) {
VisitForEffect(expr->expression());
builder()->LoadUndefined();
}
这个builder()获取到的是BytecodeArrayBuilder类的对象:
BytecodeArrayBuilder& BytecodeArrayBuilder::LoadUndefined() {
OutputLdaUndefined();
return *this;
}
不过当我们试图寻找OutputLdaUndefined函数的时候,会发现在代码中搜不到。
这是因为,这些Output函数的名字,是用宏拼出来的:
#define DEFINE_BYTECODE_OUTPUT(name, ...) \
template <typename... Operands> \
BytecodeNode BytecodeArrayBuilder::Create##name##Node( \
Operands... operands) { \
return BytecodeNodeBuilder<Bytecode::k##name, __VA_ARGS__>::Make( \
this, operands...); \
} \
\
template <typename... Operands> \
void BytecodeArrayBuilder::Output##name(Operands... operands) { \
BytecodeNode node(Create##name##Node(operands...)); \
Write(&node); \
} \
\
template <typename... Operands> \
void BytecodeArrayBuilder::Output##name(BytecodeLabel* label, \
Operands... operands) { \
DCHECK(Bytecodes::IsForwardJump(Bytecode::k##name)); \
BytecodeNode node(Create##name##Node(operands...)); \
WriteJump(&node, label); \
}
BYTECODE_LIST(DEFINE_BYTECODE_OUTPUT)
#undef DEFINE_BYTECODE_OUTPUT
通过这个宏,会帮我们生成BytecodeArrayBuilder::OutputLdaUndefined 方法,然后它会调用到BytecodeArrayBuilder的Write方法。
void BytecodeArrayBuilder::OutputLdaUndefined(Operands... operands) {
BytecodeNode node(CreateLdaUndefinedNode(operands...));
Write(&node);
}
然后BytecodeArrayBuilder的Write方法再调用BytecodeArrayWriter的Write方法。
void BytecodeArrayBuilder::Write(BytecodeNode* node) {
AttachOrEmitDeferredSourceInfo(node);
bytecode_array_writer_.Write(node);
}
最后通过BytecodeArrayWriter的EmitBytecode函数去最终生成字节码。
void BytecodeArrayWriter::Write(BytecodeNode* node) {
DCHECK(!Bytecodes::IsJump(node->bytecode()));
if (exit_seen_in_block_) return; // Don't emit dead code.
UpdateExitSeenInBlock(node->bytecode());
MaybeElideLastBytecode(node->bytecode(), node->source_info().is_valid());
UpdateSourcePositionTable(node);
EmitBytecode(node);
}
EmitBytecode的作用,除了将字节码节点所对应的字节码压到生成的字节码栈中之外,还需要根据字节码的特性,将其操作数也压栈:
void BytecodeArrayWriter::EmitBytecode(const BytecodeNode* const node) {
DCHECK_NE(node->bytecode(), Bytecode::kIllegal);
Bytecode bytecode = node->bytecode();
OperandScale operand_scale = node->operand_scale();
if (operand_scale != OperandScale::kSingle) {
Bytecode prefix = Bytecodes::OperandScaleToPrefixBytecode(operand_scale);
bytecodes()->push_back(Bytecodes::ToByte(prefix));
}
bytecodes()->push_back(Bytecodes::ToByte(bytecode));
const uint32_t* const operands = node->operands();
const int operand_count = node->operand_count();
const OperandSize* operand_sizes =
Bytecodes::GetOperandSizes(bytecode, operand_scale);
for (int i = 0; i < operand_count; ++i) {
switch (operand_sizes[i]) {
case OperandSize::kNone:
UNREACHABLE();
case OperandSize::kByte:
bytecodes()->push_back(static_cast<uint8_t>(operands[i]));
break;
case OperandSize::kShort: {
uint16_t operand = static_cast<uint16_t>(operands[i]);
const uint8_t* raw_operand = reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(&operand);
bytecodes()->push_back(raw_operand[0]);
bytecodes()->push_back(raw_operand[1]);
break;
}
case OperandSize::kQuad: {
const uint8_t* raw_operand =
reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(&operands[i]);
bytecodes()->push_back(raw_operand[0]);
bytecodes()->push_back(raw_operand[1]);
bytecodes()->push_back(raw_operand[2]);
bytecodes()->push_back(raw_operand[3]);
break;
}
}
}
}
小结
我们初步带大家一起浏览了下v8解释器生成字节代码的过程。
细节比较多,我们后面慢慢展开。






















 1660
1660

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










