1_会话技术
概念–打开浏览器,访问服务器中资源,关闭浏览器;这个过程就是会话。
会话分类:
Cookie会话技术;浏览器会话技术
Session会话技术;服务器会话技术
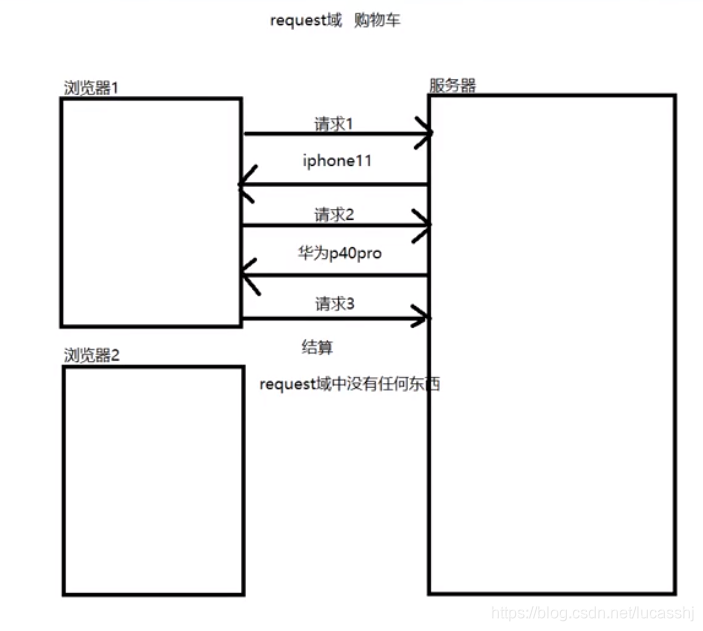
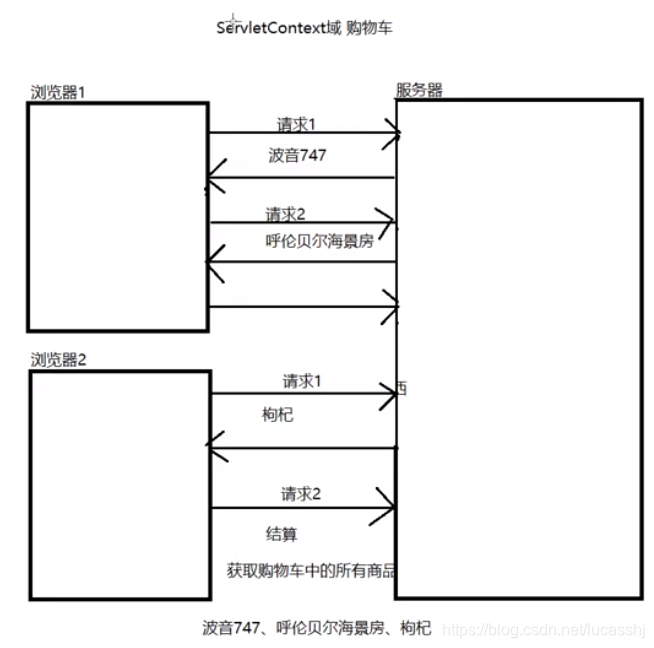
作用–解决ServletContext域对象、Request域对象存储数据所存在的问题
ServletContext域对象可以看到所有人的购物车
Request域对象,发起结算时购物车是空的
2_Cookie
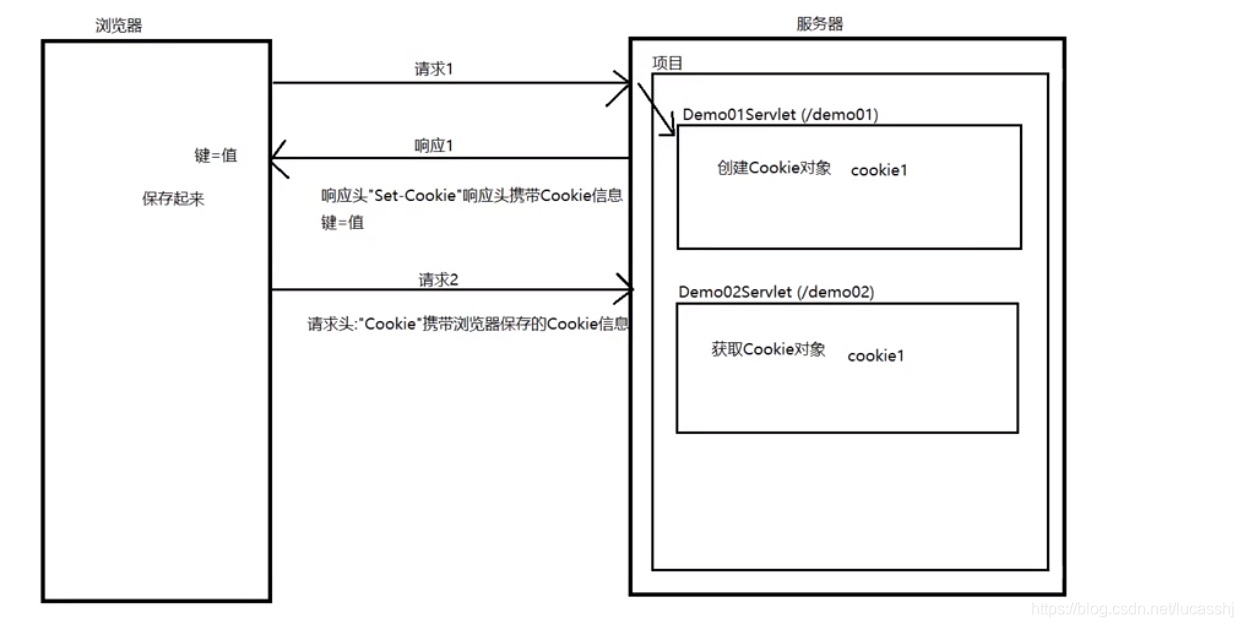
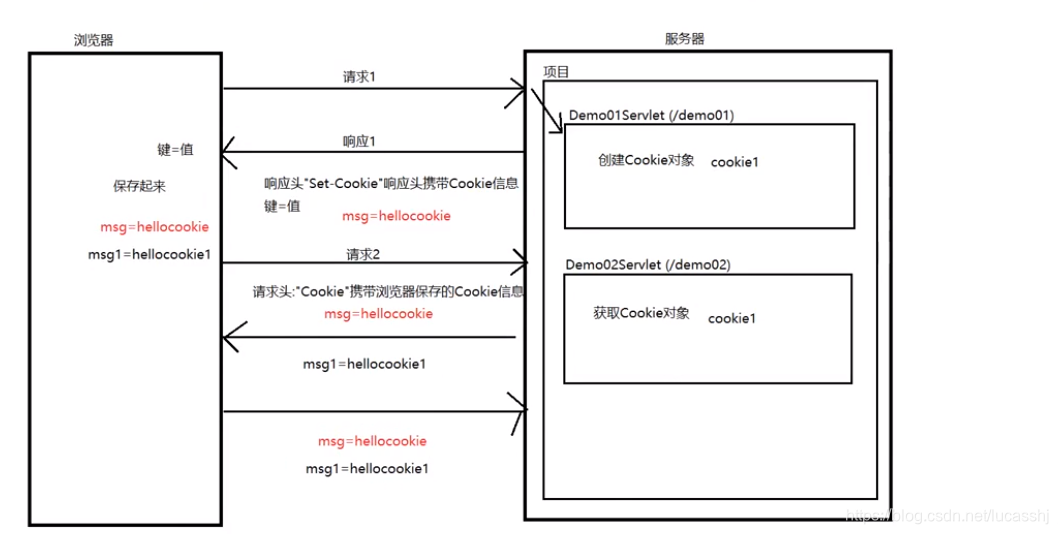
Cookie的流程–
浏览器请求服务器,请求Demo01Servlet,服务器会创建一个Cookie对象,名称为cookie1
可以通过响应头Set-Cookie,携带cookie给浏览器进行保存
浏览器再次请求服务器,请求Demo02Servlet,获取cookie1对象
3_Cookie的基本使用
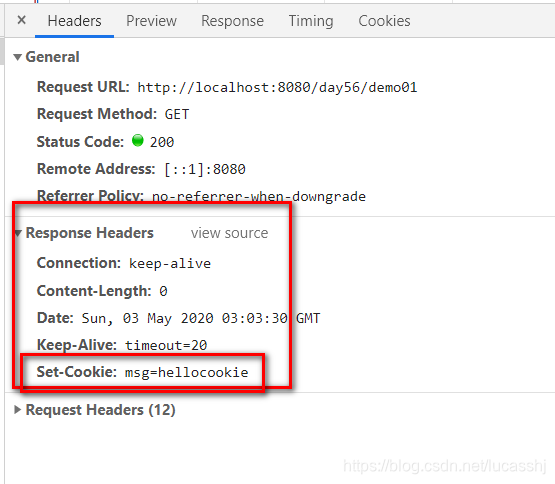
设置Cookie
推荐方法
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("msg","hellocookie");
response.addCookie(cookie);
获取Cookie
- 通过request对象获取所有的Cookie对象,存储到一个数组中
- 遍历该数组,匹配Cookie名称
- 如果匹配上,就知道了指定的Cookie对象
- 如果匹配不上,就没有指定的Cookie对象
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();
Cookie msgCookie = null;
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
if("msg".equals(cookie.getName())){
msgCookie=cookie;
}
}
if (msgCookie != null) {
System.out.println("name:"+msgCookie.getName()+",value:"+msgCookie.getValue());
}
4_Cookie的相关设置
持久化设置
cookie的生命周期:默认是随着浏览器的关闭而销毁
setMaxAge:设置cookie的存活时长,cookie就可以不随着会话的关闭而销毁!
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("msg","helloworld");
cookie.setMaxAge(7*24*60*60);
resp.addCookie(cookie);
路径设置
默认情况下,Cookie对象会随着任何一个请求携带到服务器
setPath–设置Cookie的访问路径

Cookie cookie = new Cookie("msg","helloworld");
cookie.setPath("/day56/demo04");
response.addCookie(cookie);
–cookie对象只有访问路径包含"/day56/demo04",才会跟随请求携带到服务器
5_Cookie案例之记录上一次访问时间
(如果是request域显然不能实现,第二次访问时,存得时间就没有了,ServletContext的话,自己上次的访问时间,其他人全部都可以看到)
需求:
第一次访问,就直接打印当前时间
不是第一次访问,就打印上一次的访问时间
开发步骤
- 获取对应的Cookie对象
- 判断是否是第一次访问
- 如果是第一次访问–打印当前时间,将当前时间存储到Cookie中
- 如果不是第一次访问–打印上一次访问时间,将当前时间存储到Cookie中
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();
Cookie cookie = null;
for (Cookie sonCookie : cookies) {
if("lastTime".equals(sonCookie.getName())){
cookie = sonCookie;
}
}
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyy年MM月dd日 hh:mm:ss");
if(cookie == null){
Date currentDate = new Date();
System.out.println("第一次访问,时间为"+format.format(currentDate));
cookie = new Cookie("lastTime",currentDate.getTime()+"");
}else {
long lastDateMills = Long.parseLong(cookie.getValue());
Date lastDate = new Date(lastDateMills);
String lastTimeStr = format.format(lastDate);
System.out.println("上一次访问时间为"+lastTimeStr);
Date currrentDate = new Date();
cookie = new Cookie("lastTime",currrentDate.getTime()+"");
}
resp.addCookie(cookie);
6_Cookie案例之商品浏览记录
需求:浏览商品,将商品的浏览的记录起来,并显示!
开发步骤
- 获取history的Cookie对象
- 判断商品浏览记录是否为空
- 如果浏览记录没有
– 创建Cookie,并将当前的商品记录到Cookie中 - 如果浏览记录有 有当前的商品,不做任何处理 没有当前商品,就需要将当前的商品拼接到已有记录中

页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>商品页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>商品列表</h1>
<a href="/day56/history?id=0">西游记</a><br>
<a href="/day56/history?id=1">红楼梦</a><br>
<a href="/day56/history?id=2">水浒传</a><br>
<a href="/day56/history?id=3">三国志</a><br>
</body>
</html>
商品浏览记录
@WebServlet(name = "HistoryServlet",urlPatterns="/history")
public class HistoryServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String id = req.getParameter("id");
Cookie cookie = null;
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();
if (cookies!=null&&cookies.length!=0){
for (Cookie sonCookie : cookies) {
if("history".equals(sonCookie.getName())){
cookie = sonCookie;
}
}
}
if (null == cookie) {
//之前没有任何浏览记录 ,创建Cookie对象 ,并存储浏览记录(id)
cookie = new Cookie("history",id);
} else {
//之前有一些浏览记录
String historyStr = cookie.getValue();
if (!historyStr.contains(id)) {
//有一些记录,但是不包含当前浏览的商品;
//将浏览商品拼接到已有浏览记录中
//120
//1-2-0
historyStr += "-"+id;
cookie.setValue(historyStr);
} else {
//有一些记录,包含当前浏览的商品 ,不做任何处理
}
}
resp.addCookie(cookie);
resp.sendRedirect(req.getContextPath()+ File.separator+"showHistory");
//上述代码,已经完成了商品浏览记录功能,剩下就是要显示商品浏览记录
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
显示商品浏览记录
获取history对应的Cookie对象
获取对应的商品浏览记录
判断是否有浏览记录
如果没有,就显示“没有浏览记录”
如果有,就显示–处理浏览记录字符串
Cookie cookie = null;
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();
if (cookies!=null && cookies.length!=0){
for (Cookie sonCookie : cookies) {
if("history".equals(sonCookie.getName())){
cookie = sonCookie;
}
}
}
StringBuffer responseContent = new StringBuffer();
if(cookie == null){
responseContent.append("<font color='red'>没有浏览记录</font>,");
responseContent.append("<a href='books.html'>浏览商品</a>");
}else{
String[] bookNames = {"西游记","红楼梦","水浒传","三国志"};
String historyStr = cookie.getValue();
String[] historys = historyStr.split("-");
responseContent.append("您的浏览记录如下:<br>");
for (String history : historys) {
String bookName = bookNames[Integer.parseInt(history)];
responseContent.append(bookName+"<br>");
}
}
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
resp.getWriter().write(responseContent.toString());
7_CookieUtils工具类
获取指定名称的Cookie对象
public static Cookie getCookie(Cookie[] cookies ,String cookieName){
if (null != cookies && 0 != cookies.length) {
for (Cookie sonCookie : cookies) {
if (cookieName.equals(sonCookie.getName())) {
return sonCookie;
}
}
}
return null;
}
8_Session基本使用
Session之所以叫做服务器会话,原因是Session的数据存储到服务器!
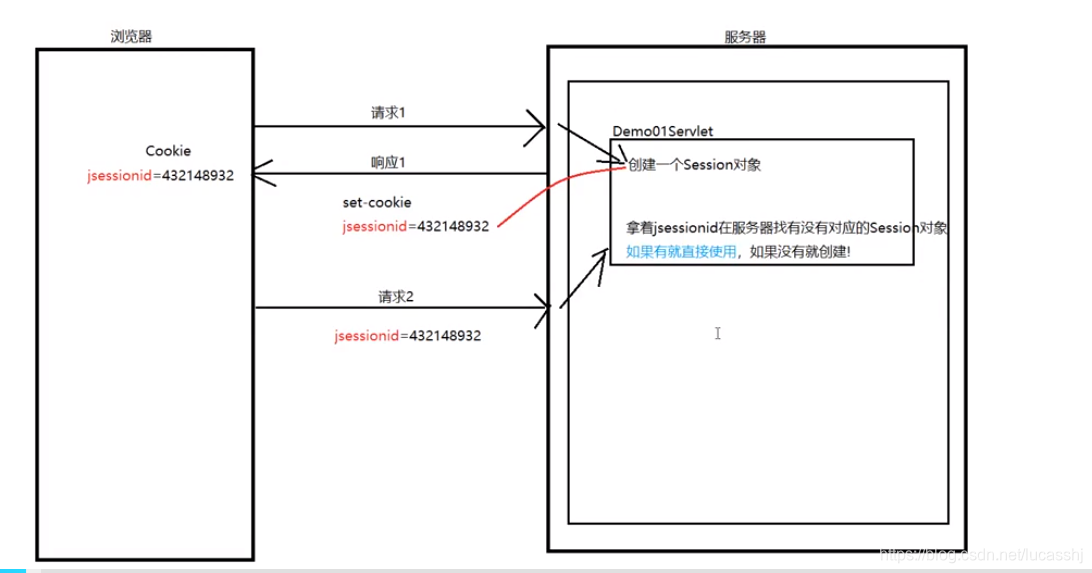
执行流程:
第一次请求Demo01Servlet时,根据request.getSession方法, 新建一个session对象;
当第一次响应时,会将该session对象的id作为cookie头响应给浏览器保存
第二次请求Demo01Servlet时,根据request.getSession方法,请求中会有cookie头
会根据该JSESSIONID去服务器中找有没有对应的session对象,如果有就直接用,没有就新建!!!
9_Session相关配置
生命周期–session默认是有30分钟的存活时间,参考tomcat中的web.xml
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config>
session和cookie是相关联的,cookie中存储了jsessionid,request.getSession方法会根据jsessionid去选择,到底是新建session对象,还是引用原来的session对象;如果,将浏览器关闭了,就意味着cookie中存储的jsessionid就会销毁,对应request.getSession就会新建一个session对象,但是原来的session对象还存在!
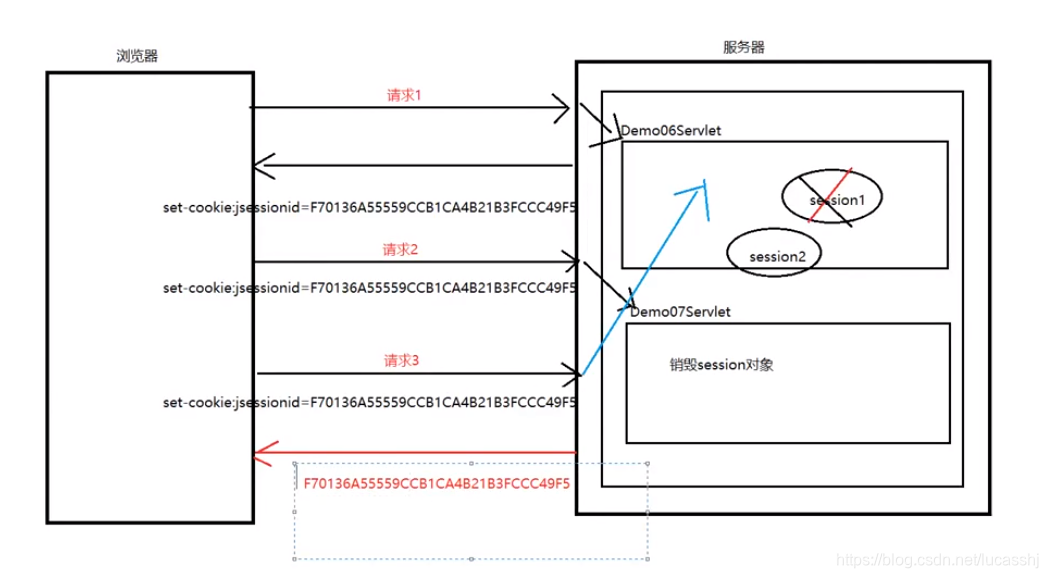
注意事项
- 关闭浏览器,session会怎么样? jsessionid会销毁,但是session不会
- 销毁session,下一次的getSession怎么样?会再次创建一个新的session
总结
session只有两种情况会销毁
- 调用了invalidate方法
- 过了30分钟





 本文深入探讨了会话技术的基础概念,包括Cookie和Session的工作原理、使用方法及案例应用,如记录访问时间和商品浏览记录,同时解析了它们在解决数据存储问题上的作用。
本文深入探讨了会话技术的基础概念,包括Cookie和Session的工作原理、使用方法及案例应用,如记录访问时间和商品浏览记录,同时解析了它们在解决数据存储问题上的作用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








