#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define FALSE 1
void fun()
{
if (false)
{
cout << "hello1" << endl;
}
if (FALSE)
{
cout << "hello2" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
fun();
return 0;
}
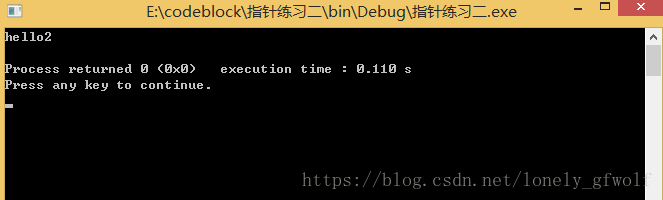
 本文通过一个简单的C++程序示例介绍了如何使用宏定义(FALSE)进行条件判断,并展示了不同条件下程序输出的变化。这对于理解C++中预处理指令的作用及如何在程序中合理运用条件语句具有一定的参考价值。
本文通过一个简单的C++程序示例介绍了如何使用宏定义(FALSE)进行条件判断,并展示了不同条件下程序输出的变化。这对于理解C++中预处理指令的作用及如何在程序中合理运用条件语句具有一定的参考价值。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define FALSE 1
void fun()
{
if (false)
{
cout << "hello1" << endl;
}
if (FALSE)
{
cout << "hello2" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
fun();
return 0;
}

 666
666

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?


