1.常用类和基础API
API初识

为什么要学别人写好的程序?
不要重复造轮子
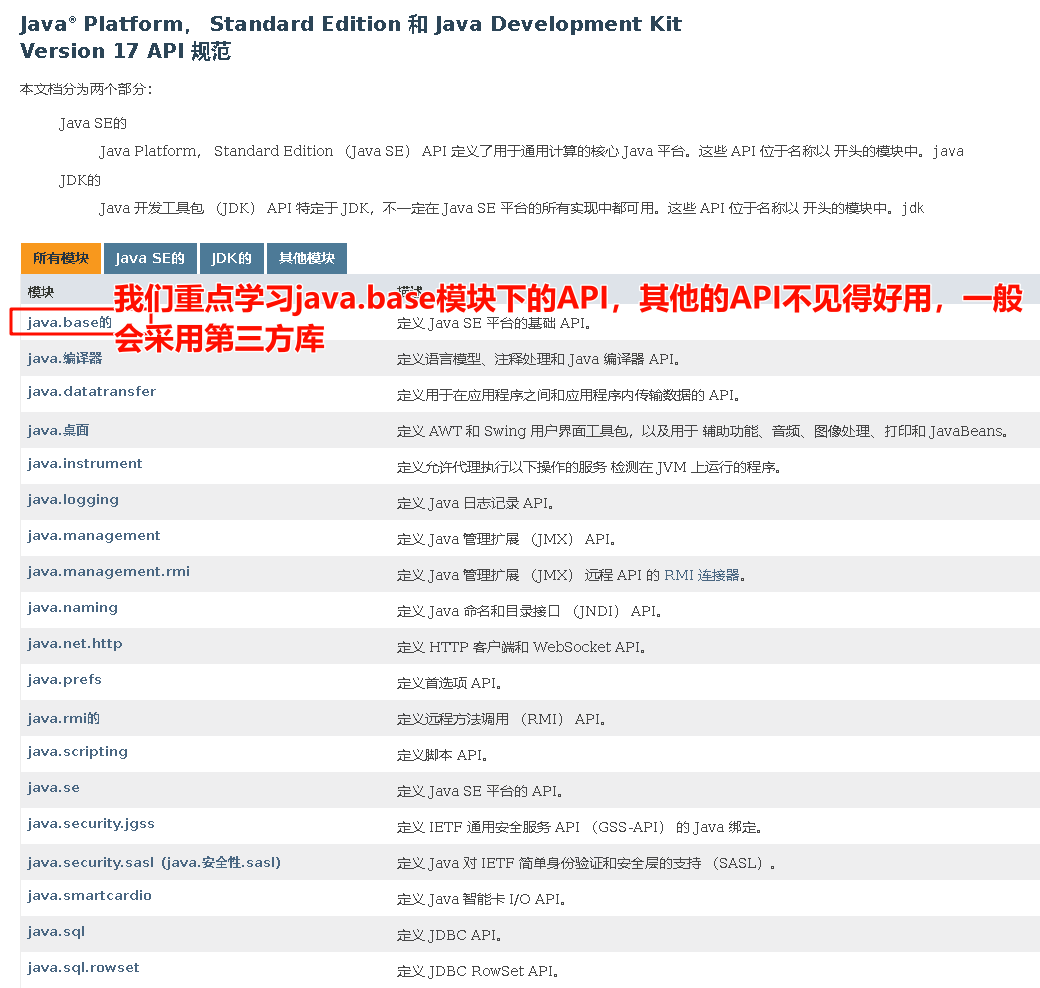
包
什么是包?

注意事项

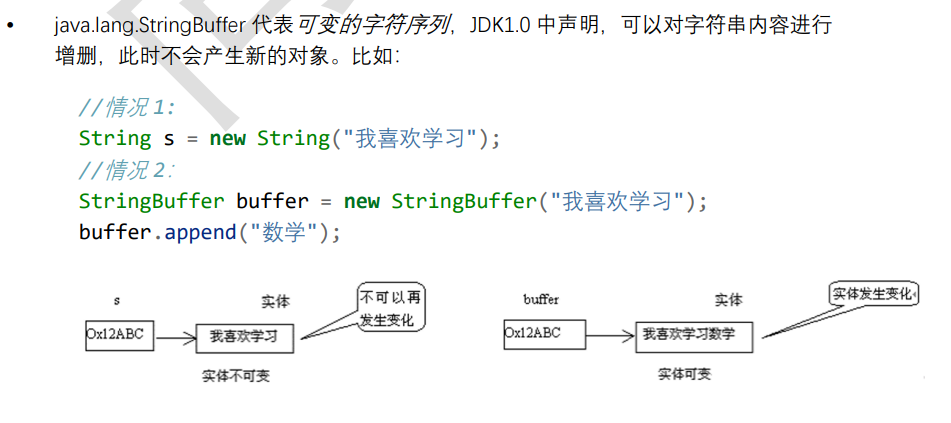
字符串相关类之不可变字符序列
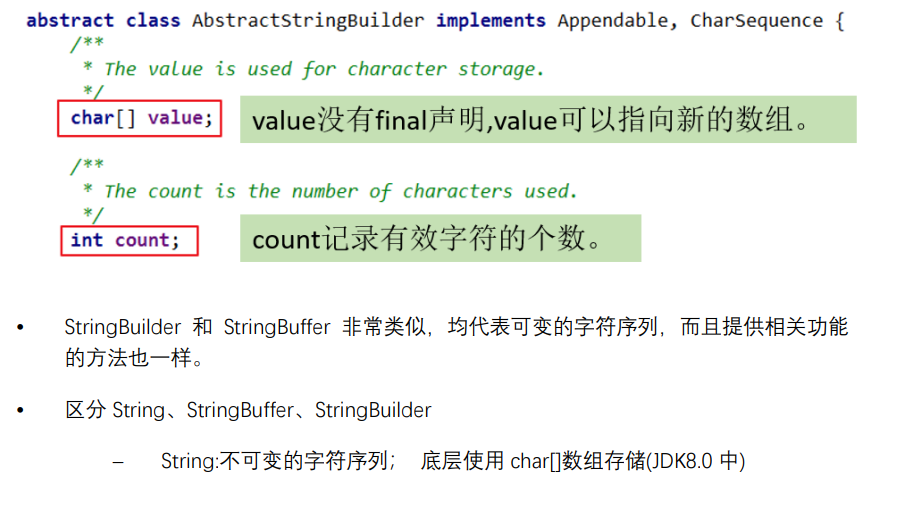
String类
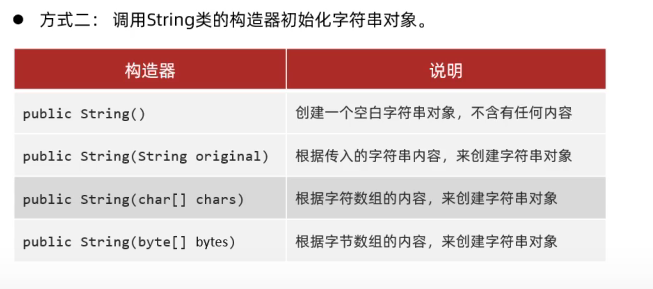
String创建对象方式(两种)
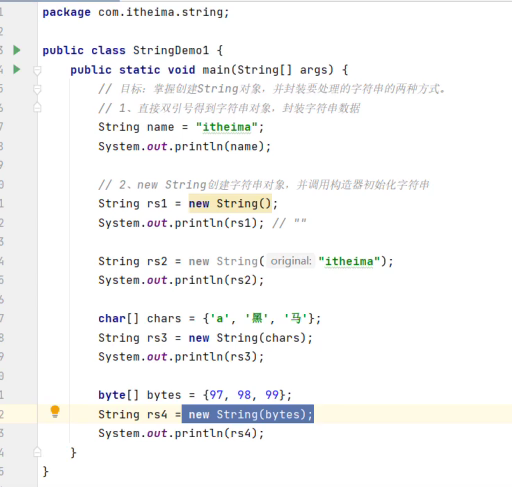
String创建对象封装字符串数据

具体代码

String的常用方法
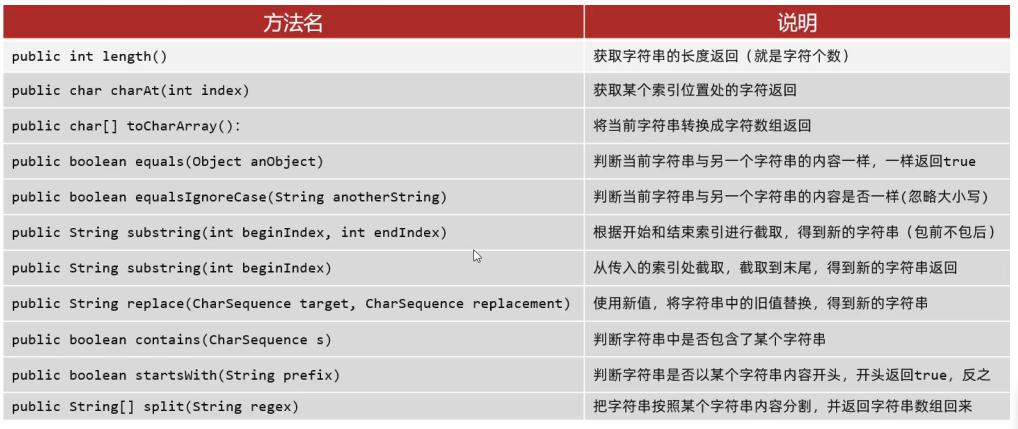

下面还有补充
String与其他结构间的转换


String的注意事项

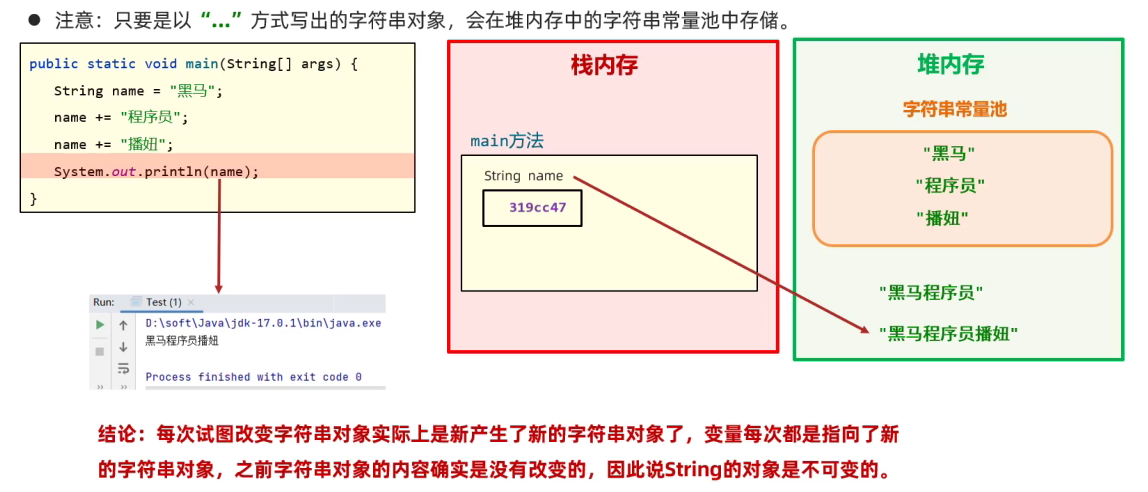
String是不可变的

虽然内容会改变,那也只是新创建了String对象,原对象的内容并不会变
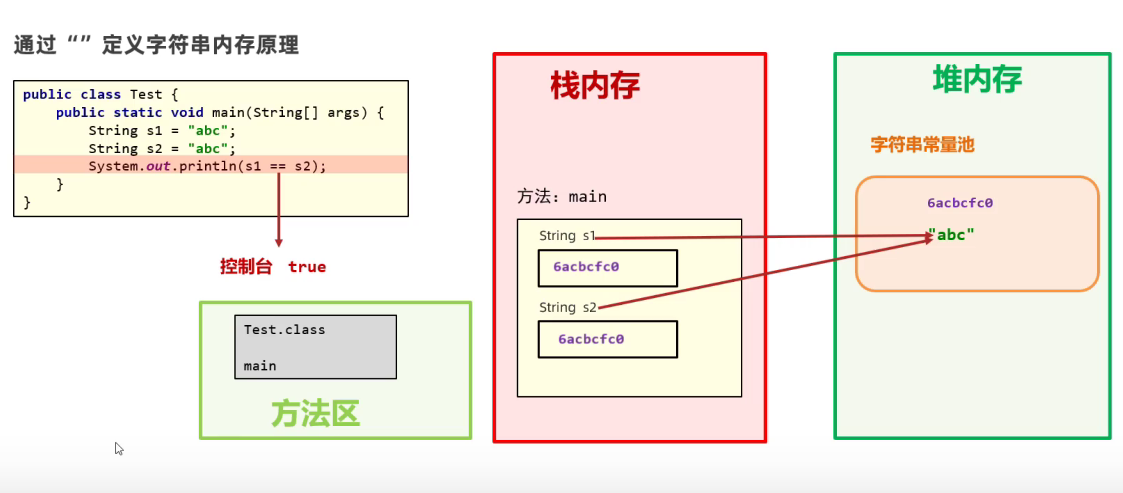
如下图:最初的String对象 name = "黑马",拼接了两次,也只不过是生成了两个新的字符串对象
这个图是有问题的,比如字符串常量池在方法区而非堆内存
以" "方式创建的字符串只存在一份

Java为什么这么设计?节约内存
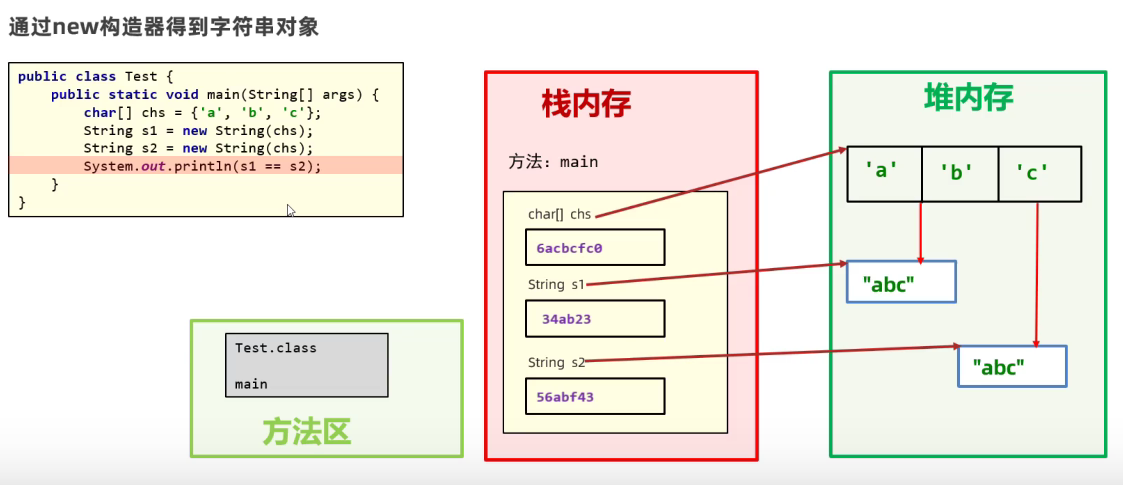
new或者运算出来的字符串对象不只存在一份

new出来的或者是拼接等运算出来的字符串对象会存在堆内存而不是字符串常量
字符串相关类之可变字符序列

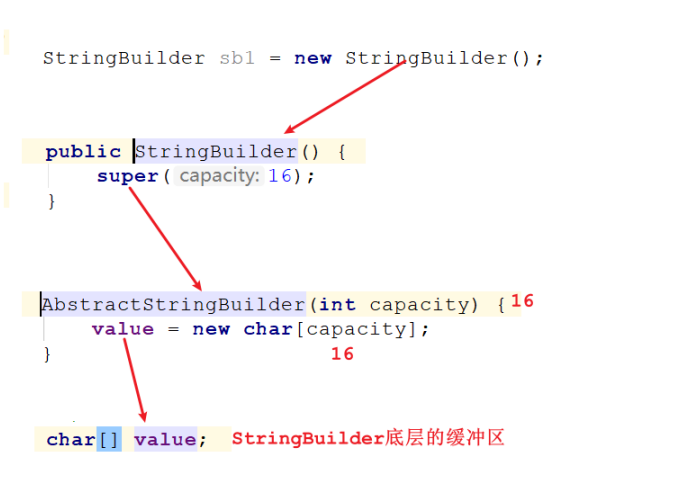
StringBuffer / StringBuilder类
底层
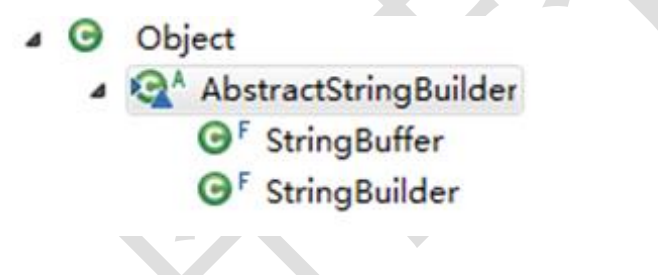
继承结构
String /StringBuffer /StringBuilder区别
常用方法



Stringjoinner类
很少有人用,效率比上面俩货好

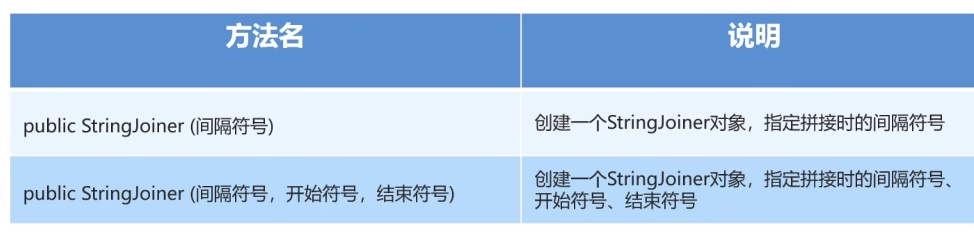
构造器
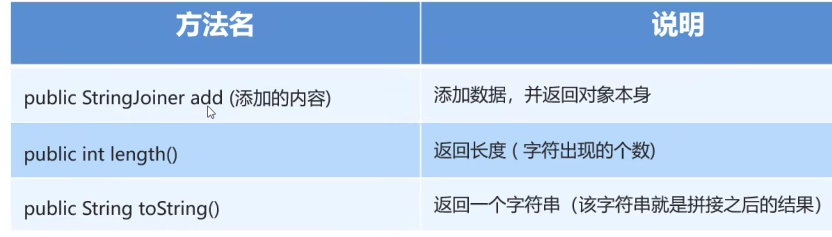
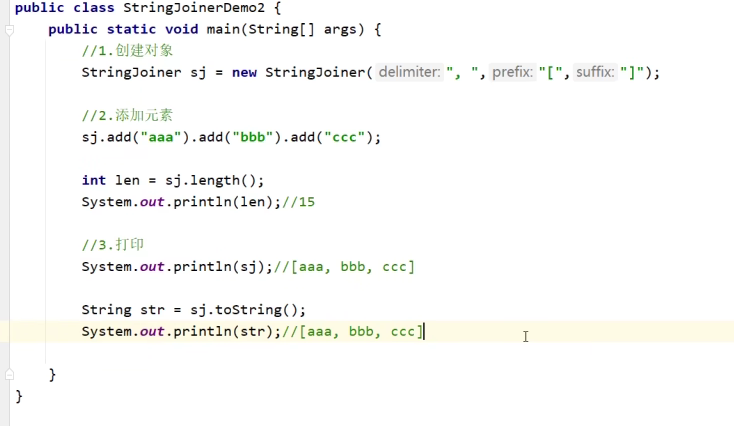
成员方法
JDK8之前:日期时间API
System.currentTimeMillis()
系统类java.lang.System类的方法

Date类
构造器与常用方法

@Test
public void test1(){
Date d = new Date();
System.out.println(d);
}
@Test
public void test2(){
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(time);//1559806982971
//当前系统时间距离 1970-1-1 0:0:0 0 毫秒的时间差,毫秒为单位
}
@Test
public void test3(){
Date d = new Date();
long time = d.getTime();
System.out.println(time);//1559807047979
}
@Test
public void test4(){
long time = 1559807047979L;
Date d = new Date(time);
System.out.println(d);
}
@Test
public void test5(){
long time = Long.MAX_VALUE;
Date d = new Date(time);
System.out.println(d);
}
SimpleDateFormat类
java.text.SimpleDateFormat 类是一个不与语言环境有关的方式来格式化和解析日期的具体 类。
可以进行格式化:日期 --> 文本
可以进行解析:文本 --> 日期
构造器

格式化

解析

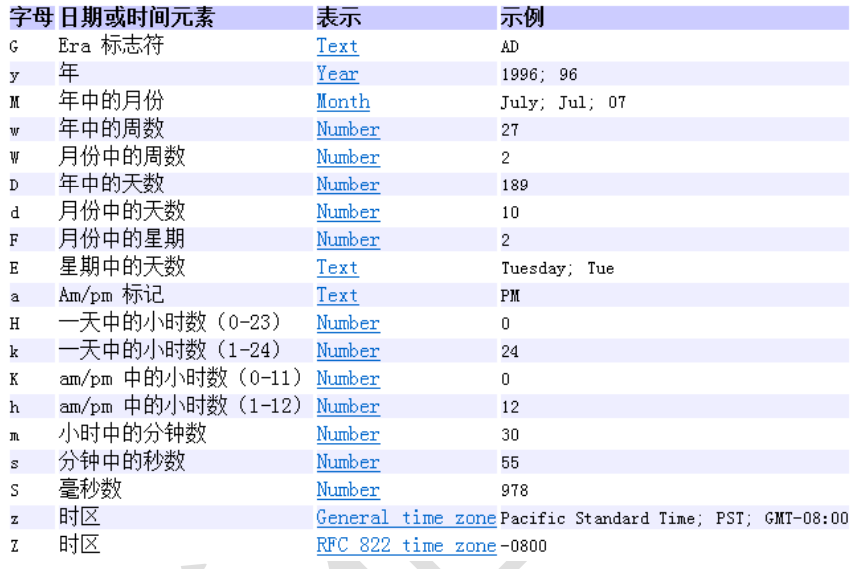
//格式化
@Test
public void test1(){
Date d = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy 年 MM 月 dd 日 HH 时
mm 分 ss 秒 SSS 毫秒 E Z");
//把 Date 日期转成字符串,按照指定的格式转
String str = sf.format(d);
System.out.println(str);
}
//解析
@Test
public void test2() throws ParseException{
String str = "2022 年 06 月 06 日 16 时 03 分 14 秒 545 毫秒 星期四 +080
0";
SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy 年 MM 月 dd 日 HH 时
mm 分 ss 秒 SSS 毫秒 E Z");
Date d = sf.parse(str);
System.out.println(d);
}
Calendar类(日历)
Date 类的 API 大部分被废弃了,替换为 Calendar
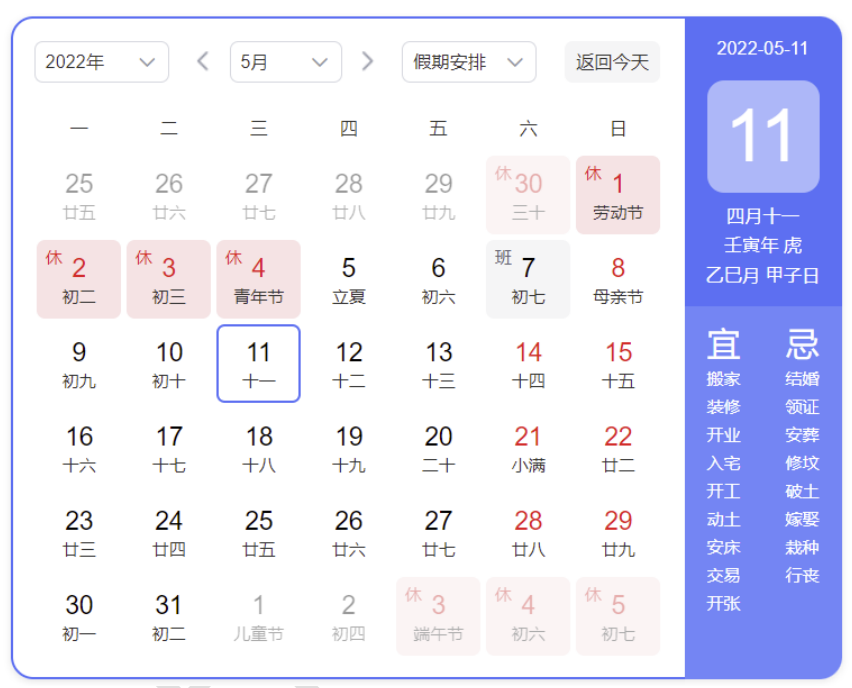
获取实例(两种)
Calendar 类是一个抽象类,主用用于完成日期字段之间相互操作的功能。
- 获取 Calendar 实例的方法 – 使用 Calendar.getInstance()方法
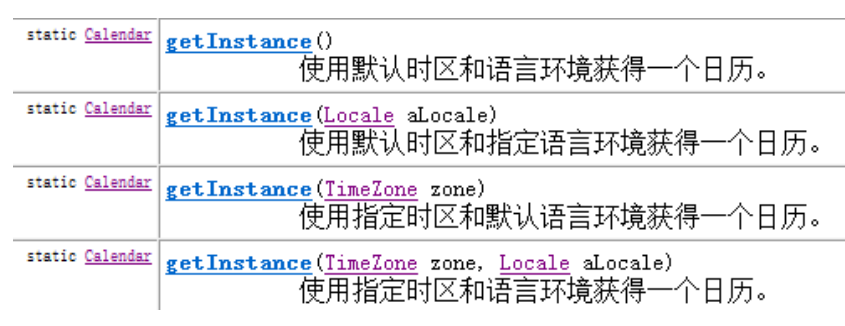
也可以调用子类的构造器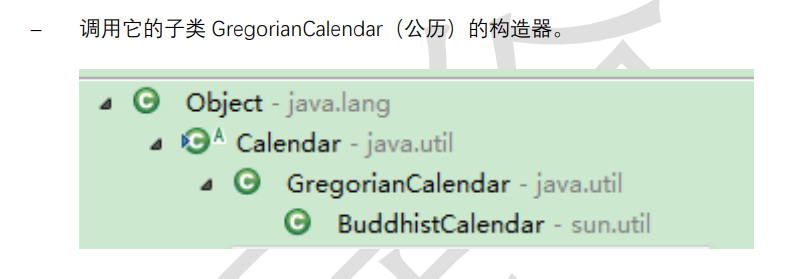
常用方法
常用字段
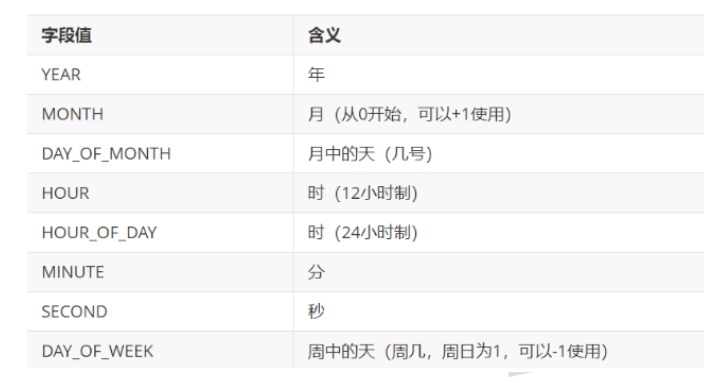
注意点

import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.TimeZone;
public class TestCalendar {
@Test
public void test1(){
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(c);
int year = c.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int month = c.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1;
int day = c.get(Calendar.DATE);
int hour = c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
int minute = c.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
System.out.println(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " " + hour
+ ":" + minute);
}
@Test
public void test2(){
TimeZone t = TimeZone.getTimeZone("America/Los_Angeles");
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance(t);
int year = c.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int month = c.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1;
int day = c.get(Calendar.DATE);
int hour = c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
int minute = c.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
System.out.println(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " " + hour
+ ":" + minute);
}
@Test
public void test3(){
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
// 从一个 Calendar 对象中获取 Date 对象
Date date = calendar.getTime();
// 使用给定的 Date 设置此 Calendar 的时间
date = new Date(234234235235L);
calendar.setTime(date);
calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 8);
System.out.println("当前时间日设置为 8 后,时间是:" + calendar.get
Time());
calendar.add(Calendar.HOUR, 2);
System.out.println("当前时间加 2 小时后,时间是:" + calendar.getT
ime());
calendar.add(Calendar.MONTH, -2);
System.out.println("当前日期减 2 个月后,时间是:" + calendar.getT
ime());
}
}
JDK8:新的日期时间API
废物的Date和Calendar



本地日期时间
- LocalDate
- LocalTime
- LocalDateTime


public class TestLocalDateTime {
@Test
public void test01(){
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println(now);
}
@Test
public void test02(){
LocalTime now = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println(now);
}
@Test
public void test03(){
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(now);
}
@Test
public void test04(){
LocalDate lai = LocalDate.of(2019, 5, 13);
System.out.println(lai);
}
@Test
public void test05(){
LocalDate lai = LocalDate.of(2019, 5, 13);
System.out.println(lai.getDayOfYear());
}
@Test
public void test06(){
LocalDate lai = LocalDate.of(2019, 5, 13);
LocalDate go = lai.plusDays(160);
System.out.println(go);//2019-10-20
}
@Test
public void test7(){
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate before = now.minusDays(100);
System.out.println(before);//2019-02-26
}
}
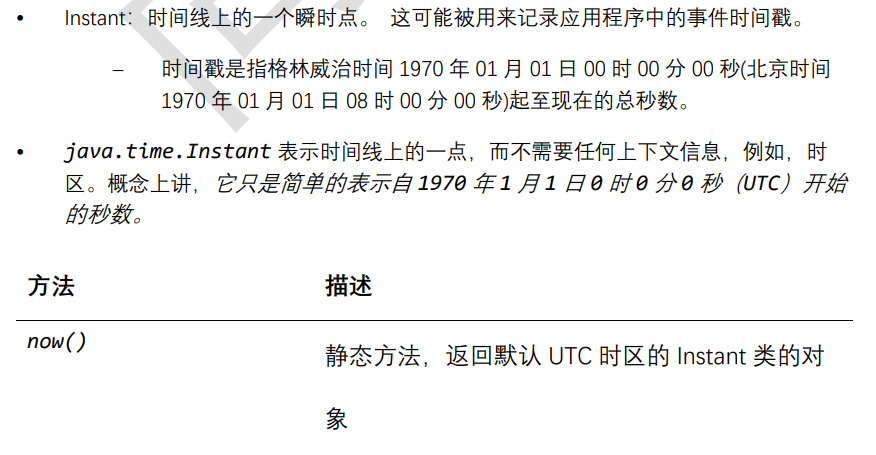
瞬时:Instant


DateTimeFormatter (日期时间格式化)


import org.junit.Test;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.time.format.FormatStyle;
public class TestDatetimeFormatter {
@Test
public void test1(){
// 方式一:预定义的标准格式。如:ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;ISO_LOCAL_D
ATE;ISO_LOCAL_TIME
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DAT
E_TIME;
// 格式化:日期-->字符串
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
String str1 = formatter.format(localDateTime);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
System.out.println(str1);//2022-12-04T21:02:14.808
// 解析:字符串 -->日期
TemporalAccessor parse = formatter.parse("2022-12-04T21:02:1
4.808");
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.from(parse);
System.out.println(dateTime);
}
@Test
public void test2(){
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
// 方式二:
// 本地化相关的格式。如:ofLocalizedDateTime()
// FormatStyle.LONG / FormatStyle.MEDIUM / FormatStyle.SHORT
:适用于 LocalDateTime
DateTimeFormatter formatter1 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedD
ateTime(FormatStyle.LONG);
// 格式化
String str2 = formatter1.format(localDateTime);
System.out.println(str2);// 2022 年 12 月 4 日 下午 09 时 03 分 55 秒
// 本地化相关的格式。如:ofLocalizedDate()
// FormatStyle.FULL / FormatStyle.LONG / FormatStyle.MEDIUM /
FormatStyle.SHORT : 适用于 LocalDate
DateTimeFormatter formatter2 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedD
ate(FormatStyle.FULL);
// 格式化
String str3 = formatter2.format(LocalDate.now());
System.out.println(str3);// 2022 年 12 月 4 日 星期日
}
@Test
public void test3(){
//方式三:自定义的方式(关注、重点)
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPat
tern("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss");
//格式化
String strDateTime = dateTimeFormatter.format(LocalDateTime.n
ow());
System.out.println(strDateTime); //2022/12/04 21:05:42
//解析
TemporalAccessor accessor = dateTimeFormatter.parse("2022/12/
04 21:05:42");
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.from(accessor);
System.out.println(localDateTime); //2022-12-04T21:05:42
}
}
系统相关类
System类

成员变量

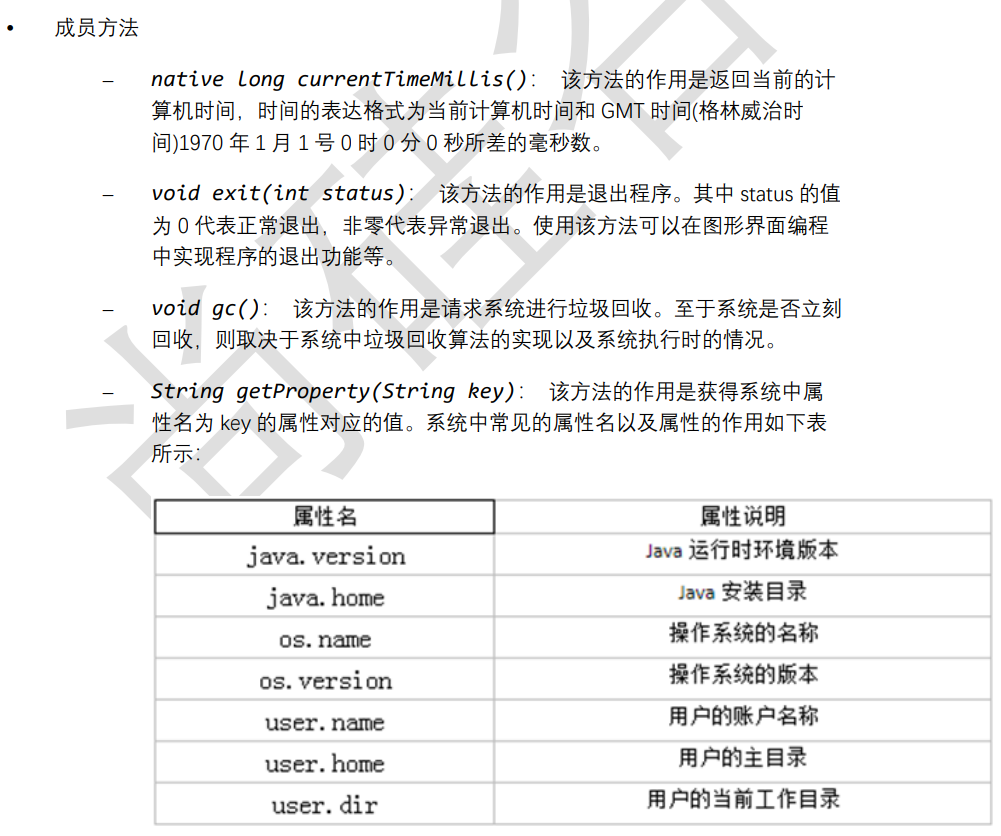
成员方法
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestSystem {
@Test
public void test01(){
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("现在的系统时间距离 1970 年 1 月 1 日凌晨:" + t
ime + "毫秒");
System.exit(0);
System.out.println("over");//不会执行
}
@Test
public void test02(){
String javaVersion = System.getProperty("java.version");
System.out.println("java 的 version:" + javaVersion);
String javaHome = System.getProperty("java.home");
System.out.println("java 的 home:" + javaHome);
String osName = System.getProperty("os.name");
System.out.println("os 的 name:" + osName);
String osVersion = System.getProperty("os.version");
System.out.println("os 的 version:" + osVersion);
String userName = System.getProperty("user.name");
System.out.println("user 的 name:" + userName);
String userHome = System.getProperty("user.home");
System.out.println("user 的 home:" + userHome);
String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
System.out.println("user 的 dir:" + userDir);
}
@Test
public void test03() throws InterruptedException {
for (int i=1; i <=10; i++){
MyDemo my = new MyDemo(i);
//每一次循环 my 就会指向新的对象,那么上次的对象就没有变量引用它
了,就成垃圾对象
}
//为了看到垃圾回收器工作,我要加下面的代码,让 main 方法不那么快结
束,因为 main 结束就会导致 JVM 退出,GC 也会跟着结束。
System.gc();//如果不调用这句代码,GC 可能不工作,因为当前内存很充
足,GC 就觉得不着急回收垃圾对象。
//调用这句代码,会让 GC 尽快来工作。
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
class MyDemo{
private int value;
public MyDemo(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDemo{" + "value=" + value + '}';
}
//重写 finalize 方法,让大家看一下它的调用效果
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
// 正常重写,这里是编写清理系统内存的代码
// 这里写输出语句是为了看到 finalize()方法被调用的效果
System.out.println(this+ "轻轻的我走了,不带走一段代码....");
}
}
• static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int
destPos, int length):
从指定源数组中复制一个数组,复制从指定的位置开始,到目标数组的指定位置结
束。常用于数组的插入和删除
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestSystemArrayCopy {
@Test
public void test01(){
int[] arr1 = {1,2,3,4,5};
int[] arr2 = new int[10];
System.arraycopy(arr1,0,arr2,3,arr1.length);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
}
@Test
public void test02(){
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
System.arraycopy(arr,0,arr,1,arr.length-1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
@Test
public void test03(){
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
System.arraycopy(arr,1,arr,0,arr.length-1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
Runtime类

package com.atguigu.system;
public class TestRuntime {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
long initialMemory = runtime.totalMemory(); //获取虚拟机初始化
时堆内存总量
long maxMemory = runtime.maxMemory(); //获取虚拟机最大堆内存总
量
String str = "";
//模拟占用内存
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
str += i;
}
long freeMemory = runtime.freeMemory(); //获取空闲堆内存总量
System.out.println("总内存:" + initialMemory / 1024 / 1024 *
64 + "MB");
System.out.println("总内存:" + maxMemory / 1024 / 1024 * 4 +
"MB");
System.out.println("空闲内存:" + freeMemory / 1024 / 1024 +
"MB") ;
System.out.println("已用内存:" + (initialMemory-freeMemory) /
1024 / 1024 + "MB");
}
}
数学相关类
java.lang.Math


java.math包
BigInteger类

构造器
![]()
方法
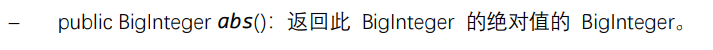

@Test
public void test01(){
//long bigNum = 123456789123456789123456789L;
BigInteger b1 = new BigInteger("12345678912345678912345678");
BigInteger b2 = new BigInteger("78923456789123456789123456789");
//System.out.println("和:" + (b1+b2));//错误的,无法直接使用+进行
求和
System.out.println("和:" + b1.add(b2));
System.out.println("减:" + b1.subtract(b2));
System.out.println("乘:" + b1.multiply(b2));
System.out.println("除:" + b2.divide(b1));
System.out.println("余:" + b2.remainder(b1));
}
BigDecimal类

构造器

常用方法

@Test
public void test03(){
BigInteger bi = new BigInteger("12433241123");
BigDecimal bd = new BigDecimal("12435.351");
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("11");
System.out.println(bi);
// System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2));
System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));
System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2, 15, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));
}
Random类

@Test
public void test04(){
Random r = new Random();
System.out.println("随机整数:" + r.nextInt());
System.out.println("随机小数:" + r.nextDouble());
System.out.println("随机布尔值:" + r.nextBoolean());
}






















 493
493

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








