UVM为什么会迅速成为业内标准(已经是IEEE的标准),在于UVM的TB的可复用性,用户友好性。想象一下下面的一个应用场景,我们在搭建TB时,某些case run起来需要配置某些参数,原有的思路是在TB中利用SV的系统函数比如$test $plusargs 或者 $value $plusargs来获取相应的参数,从而配置某些特定的应用场景。这样做在现在看来有两处不友好的地方,首先在run的时候需要命令行加入参数,参数的数量是如法控制的,其次如果在环境集成的时候,万一需要两个这样同样的子TB来构成上一层的环境,这个时候无法给两个TB配置不同的参数。资源配置机制(config_db机制)作为UVM重要的一个特性,很好的解决了上面的问题,下面介绍一下UVM是如何配置资源的以及获取资源的。
在我们使用UVM资源配置机制的时候,由于一些种种原因,不是使用uvm_config_db进行配置的,我们可能会看见uvm_resource_db来进行配置(一般不会使用,现在有uvm_config_db替代了),在这里我们有必要要先讲一下uvm_resource_db,以及这个配置的缺陷。看下面的例子
package UVM_cmd;
import uvm_pkg::*'
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
class unit_agent extends uvm_agent;
int A=10;
int i;
local int b;
uvm_resource#(int) re;
uvm_resource_types::rsrc_q_t rq;
uvm_resource_pool rp;
`uvm_component_utils(unit_agent)
function new(string name);
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
re=uvm_resource#(int)::get_type();
rp=uvm_resource_pool::get();
rq=rp.lookup_name("abcd","A",re);
`uvm_info("INT",$sformatf("before the config the a is %d",A),UVM_LOW)
if(!uvm_resource_db#(int)::read_by_name("abcd","A",A))
`uvm_error("error","the read is error")
else
`uvm_info("INT",$sformatf("after the config the a is %d",A),UVM_LOW)
`uvm_info("precedence",$sformatf("the precedence is %d",re.precednce),UVM_LOW)
`uvm_info("size",$sformatf("the size is %d",rq.size()),UVM_LOW)
while(rq.size()>0)begin
uvm_resource_base n;
uvm_resource#(int) n1;
n-rq.pop_front();
if(n!=null) begin
`void($cast(n1,n))
`uvm_info("precedence",$sformatf("the precedence is %d",n.precedence),UVM_LOW)
`uvm_info("precedence",$sformatf("the data is %d",n1.read()),UVM_LOW)
end
end
endfunction
function int ret();
return b;
endfunction
endclass
class unit_agent_child extends unit_agent;
`uvm_component_utils(unit_agent_child)
function new(string name,uvm_component parent);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
endfunction
endclass
class unit_env extends uvm_env;
unit_agent un;
unit_agent_child un_ch;
`uvm_component_utils(unit_env)
function new(string name,uvm_component parent);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
uvm_resource_db#(int)::set("abcd","A",20);
//un=unit_agent::type_id::create("un",this);
//un_ch=unit_agent_child::type_id::create("un_ch",this);
endfunction
endclass
class my_test extends uvm_test;
unit_env env;;
`uvm_component_utils(my_test)
function new(string name,uvm_component parent);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
uvm_resource_db#(int)::set("abcd","A",30);
uvm_resource_db#(int)::set("abcd","A",40);
env=unit_env::type_id::create("env",this);
endfunction
endclass
endpackage
我们在uvm_test中以及uvm_env中分别对uvm_agent中的变量A进行了配置,那么最终A的值是多少呢,30,40还是20?
答案是30。
下面我们来分析一下为什么是30,而不是40或者20,分析完之后将会对uvm_resource_db如何工作机制非常熟悉的。
在这个机制工作的过程中主要有3个class在相互交互,这里先列出来
uvm_resource#(T):资源
uvm_resource_pool:存放资源的地方
uvm_resource_db:配置以及获取资源
首先调用uvm_resource_db::set方法
在上面我们给的这个例子中会创建类型是int,scope是“abcd”,name是A的资源,这里由于uvm_test的build_phase先执行,因此会先后创建3个资源,按照资源val的不同,分别是30,40,20。如下图,其中T1是int
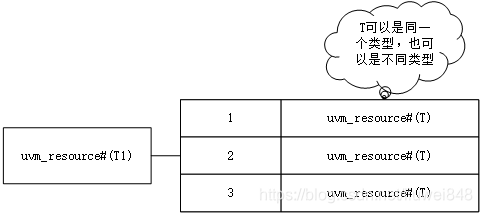
那么这些资源放哪了,在UVM中有一个uvm_resource_pool这个类(全局唯一),专门用来存放各种配置的资源。
在uvm_resource_pool这个类中有两个非常重要的变量来存放资源
uvm_queue#(uvm_resource_base) rtab [string]
uvm_queue#(uvm_resource_base) ttab [uvm_resource_base];
set方法就是向着两个联合数组中存放资源,一个是按照name区分,一个是按照类型区分。
最终uvm_resorce_pool中有3个资源,val分别是30,40,20(按照这个顺序存放的在队列中。
分别对应rtab[“A”]以及ttab[uvm_resource#(int)],下面给出rtab[“A”]的元素分布,name1的值是A
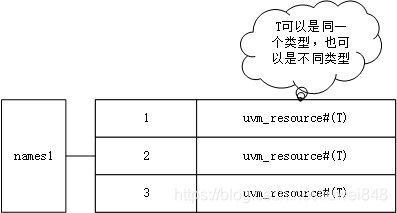
以上完成了资源的set,下面讲一下资源的get,在uvm_resource_db中可以使用read_by_name来获取资源。
在agent中通过调用uvm_resource_db#(int)::read_by_name方法来从uvm_resource_pool中获取资源,那么是如何获取资源的呢?下面来讲解一下,
在上面我们以及指导rtab[“A”]存放3个资源,3个资源的scope以及type均一样,区别在于资源值val的不同,
read_by_name方法首先根据name A确定要从rtab[“A”]这个队列中找,
接着遍历这个队列下的所有资源,找到scope以及type匹配的资源放入一个队列中并且返回,这里我们返回3个资源,
下面将会遍历这3个资源,找到优先级最大的资源(这里我们没有对资源的优先级进行设置,所有3个资源的优先级完全一样,默认是1000)。
由于资源的优先级一样,这个时候会将队列的第一个元素返回,当做最终有效的资源,这个资源的val是30.所以agent中返回的值是30.
以上就是uvm_resource_db的工作机制。
因此在我们正常使用uvm_resource_db的时候,由于同类型,同scope,同name,不同val的资源是以push_back的方式放入uvm_resource_pool::rtab[name]这个队列中的,如果这些资源的优先级一样,name最先放入的资源是有效资源,这样就无法实现同一组件配置同一个资源,导致后配置的资源无法覆盖之前配置资源。当然这里可以使用uvm_resource_db::set_overrirde的方式进行配置,或者改变资源的优先级,但是这样子就显的不是那么友好,那么有没有别的方式可以直接通过set方式实现以上的弊端呢,方法是有的,就是uvm_config_db





 本文探讨了UVM中资源配置的重要性,特别是config_db机制如何解决命令行参数配置的不足。通过一个示例解释了uvm_resource_db的工作原理,展示了在uvm_test和uvm_env中配置uvm_agent变量时可能出现的问题。资源的set和get过程被详细阐述,揭示了由于资源按push_back方式存储可能导致的覆盖问题,并提出了uvm_config_db作为更优的解决方案。
本文探讨了UVM中资源配置的重要性,特别是config_db机制如何解决命令行参数配置的不足。通过一个示例解释了uvm_resource_db的工作原理,展示了在uvm_test和uvm_env中配置uvm_agent变量时可能出现的问题。资源的set和get过程被详细阐述,揭示了由于资源按push_back方式存储可能导致的覆盖问题,并提出了uvm_config_db作为更优的解决方案。
















 4701
4701

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








