https://helloacm.com/model-view-controller-explained-in-c/
Model-View-Controller Explained in C++
Tags:C++ demo of MVC, model-view-controller, MVC
Model-View-Controller Explained in C++
January 24, 2017 4 Comments c / c++, MVC, programming languages,software design, software development, tutorial
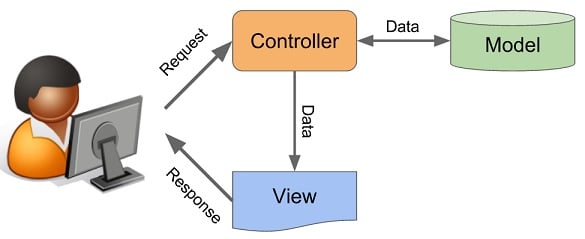
The Model-View-Controller (MVC) is not a technology, but a concept in software design/engineering. The MVC consists of three components, the Model, the View and the Controller, as illustrated in below figure.
model-view-controller-mvc-explained
THE MODEL
The Model is directly responsive for handling data. For example, the Model component accesses MySQL database. The Model should not rely on other components such as View or Controller. In other words, the Model does not care how its data can be displayed or when to be updated.
The data changes in the Model will generally be published through some event handlers. For example, the View model must register on the Model so that it understands the data changes. We can define a function callback when data changes:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | // common.h // https://helloacm.com/model-view-controller-explained-in-c/ #pragma once #include <string> using namespace std; typedef void (*DataChangeHandler)(string newData); |
DataChangeHandler is now a function pointer type that returns void and takes a parameter of a string (data type). The Model is responsible for data retrieval and optionally, it can register the data-change-event.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | // model.h // https://helloacm.com/model-view-controller-explained-in-c/ #pragma once #include <string> using namespace std; #include "common.h" // Model is responsible for data get and set class Model { public: Model(const string &data) { this->SetData(data); } Model() { } // default constructor string Data(){ return this->data; } void SetData(const string &data) { this->data = data; if (this->event != nullptr) { // data change callback event this->event(data); } } // register the event when data changes. void RegisterDataChangeHandler(DataChangeHandler handler) { this->event = handler; } private: string data = ""; DataChangeHandler event = nullptr; }; |
VIEW
The View component knows how to present the Data to the users. It needs to access the Model and normally needs to define its ‘Render()’ function.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | // view.h // https://helloacm.com/model-view-controller-explained-in-c/ #pragma once #include <iostream> #include "model.h" // View is responsible to present data to users class View { public: View(const Model &model) { this->model = model; } View() {} void SetModel(const Model &model) { this->model = model; } void Render() { std::cout << "Model Data = " << model.Data() << endl; } private: Model model; }; |
CONTROLLER
The Controller can ask the Model to update its data. Also, the Controller can ask the View to change its presentation, e.g. Showing a Dialog instead of Outputing to Console. Basically it is a component that takes input from the user and sends commands to the View or Model.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | // controller.h // https://helloacm.com/model-view-controller-explained-in-c/ #pragma once #include "model.h" #include "view.h" // Controller combines Model and View class Controller { public: Controller(const Model &model, const View &view) { this->SetModel(model); this->SetView(view); } void SetModel(const Model &model) { this->model = model; } void SetView(const View &view) { this->view = view; } // when application starts void OnLoad() { this->view.Render(); } private: Model model; View view; }; |
MVC DEMO
With the above three component classes, we can have the following code to demonstrate MVC.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | // mvc.cpp // https://helloacm.com/model-view-controller-explained-in-c/ #include <iostream> #include "view.h" #include "model.h" #include "controller.h" #include "common.h" using namespace std; void DataChange(string data) { cout << "Data Changes: " << data <<endl; } int main() { Model model("Model"); View view(model); // register the data-change event model.RegisterDataChangeHandler(&DataChange); // binds model and view. Controller controller(model, view); // when application starts or button is clicked or form is shown... controller.OnLoad(); model.SetData("Changes"); // this should trigger View to render return 0; } |
To avoid the circular dependency in C++ between class View and Model, we use a function pointer to represent the event of data-change instead of the pointer to a member of object. To compile the above code, use the following command:
1 | g++ --std=c++11 mvc.cpp |
Then run ./a.out should give you:
1 2 | Model Data = Model Data Changes: Changes |
The model.SetData(“Changes”); triggers the data-change event that is registered in the Model component.





 本文详细介绍了软件设计中的Model-View-Controller (MVC) 概念,通过C++实现了一个MVC模式的示例。MVC由三个组件组成:Model负责处理数据,View负责展示数据,Controller作为用户输入的接收者并指挥Model和View工作。
本文详细介绍了软件设计中的Model-View-Controller (MVC) 概念,通过C++实现了一个MVC模式的示例。MVC由三个组件组成:Model负责处理数据,View负责展示数据,Controller作为用户输入的接收者并指挥Model和View工作。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








