Wall
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 37484 | Accepted: 12769 |
Description
Once upon a time there was a greedy King who ordered his chief Architect to build a wall around the King's castle. The King was so greedy, that he would not listen to his Architect's proposals to build a beautiful brick wall with a perfect shape and nice tall towers. Instead, he ordered to build the wall around the whole castle using the least amount of stone and labor, but demanded that the wall should not come closer to the castle than a certain distance. If the King finds that the Architect has used more resources to build the wall than it was absolutely necessary to satisfy those requirements, then the Architect will loose his head. Moreover, he demanded Architect to introduce at once a plan of the wall listing the exact amount of resources that are needed to build the wall.
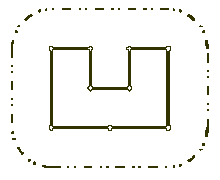
Your task is to help poor Architect to save his head, by writing a program that will find the minimum possible length of the wall that he could build around the castle to satisfy King's requirements.
The task is somewhat simplified by the fact, that the King's castle has a polygonal shape and is situated on a flat ground. The Architect has already established a Cartesian coordinate system and has precisely measured the coordinates of all castle's vertices in feet.

Your task is to help poor Architect to save his head, by writing a program that will find the minimum possible length of the wall that he could build around the castle to satisfy King's requirements.
The task is somewhat simplified by the fact, that the King's castle has a polygonal shape and is situated on a flat ground. The Architect has already established a Cartesian coordinate system and has precisely measured the coordinates of all castle's vertices in feet.
Input
The first line of the input file contains two integer numbers N and L separated by a space. N (3 <= N <= 1000) is the number of vertices in the King's castle, and L (1 <= L <= 1000) is the minimal number of feet that King allows for the wall to come close to the castle.
Next N lines describe coordinates of castle's vertices in a clockwise order. Each line contains two integer numbers Xi and Yi separated by a space (-10000 <= Xi, Yi <= 10000) that represent the coordinates of ith vertex. All vertices are different and the sides of the castle do not intersect anywhere except for vertices.
Next N lines describe coordinates of castle's vertices in a clockwise order. Each line contains two integer numbers Xi and Yi separated by a space (-10000 <= Xi, Yi <= 10000) that represent the coordinates of ith vertex. All vertices are different and the sides of the castle do not intersect anywhere except for vertices.
Output
Write to the output file the single number that represents the minimal possible length of the wall in feet that could be built around the castle to satisfy King's requirements. You must present the integer number of feet to the King, because the floating numbers are not invented yet. However, you must round the result in such a way, that it is accurate to 8 inches (1 foot is equal to 12 inches), since the King will not tolerate larger error in the estimates.
Sample Input
9 100 200 400 300 400 300 300 400 300 400 400 500 400 500 200 350 200 200 200
Sample Output
1628
Hint
结果四舍五入就可以了
凸包题目,题目不难理解,就是求走一周的路程。
结果等于,凸包周长+一个完整的圆周长。
因为走一圈,经过拐点时,所形成的扇形的内角和是360度,故一个完整的圆。
注意精度,四舍五入!=(int)类型强制转换。。。
//poj1113
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
#define esp 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1)
int Sign(double x){//判断x大于0,小于0,还是等于0
return fabs(x)<esp?0:x>0?1:-1;
}
struct Point{ //存点
double x,y;
Point(){
}
Point(double xx,double yy):x(xx),y(yy) { }
Point operator-(const Point & p) const {
return Point(x-p.x,y-p.y);
}
bool operator <(const Point & p) const {
if( y < p.y)
return true;
else if( y > p.y)
return false;
else
return x < p.x;
}
};
typedef Point Vector;
double Cross(const Vector & v1, const Vector & v2){//叉积
return v1.x * v2.y - v2.x * v1.y;
}
double Distance(const Point & p1,const Point & p2){//求距离
return sqrt( (p1.x - p2.x)*(p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y));
}
struct Comp { //用来定义极角排序规则的函数对象
Point p0; //以p0为原点进行极角排序,极角相同的,离p0近算小
Comp(const Point & p):p0(p.x,p.y) { }
bool operator ()(const Point & p1,const Point & p2) const {
int s = Sign( Cross(p1-p0,p2-p0));
if( s > 0)
return true;
else if( s < 0)
return false;
else {
if( Distance(p0,p1)<Distance(p0,p2))
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
};
int Graham(vector<Point> & points,vector<Point> & stack) {//求凸包
//points是点集合
if( points.size() < 3)
return 0; //返回凸包顶点数
stack.clear();
//先按坐标排序,最左下的放到points[0]
sort(points.begin(),points.end());
//以points[0] 为原点进行极角排序
sort(points.begin()+1,points.end(),Comp(points[0]));
stack.push_back(points[0]);
stack.push_back(points[1]);
stack.push_back(points[2]);
for(int i = 3; i< points.size(); ++i) {
while(true) {
Point p2 = * (stack.end()-1);
Point p1 = * (stack.end()-2);
if( Sign(Cross(p2-p1,points[i]-p2) <= 0))
//p2->points[i]没有向左转,就让p2出栈
stack.pop_back();
else
break;
}
stack.push_back(points[i]);
}
return stack.size();
}
int main(){
double N,L,n,l;
Point p;
vector<Point> points;
vector<Point> stack;
double res=0;
while(scanf("%lf%lf",&N,&L)!=EOF){
points.clear();
stack.clear();
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
scanf("%lf %lf",&n,&l);
p.x=n,p.y=l;
points.push_back(p);
}
int size = Graham(points,stack);
for(int i=0;i<size-1;i++)//求凸包周长
res+=Distance(stack[i],stack[i+1]);
res+=Distance(stack[0],stack[size-1]);
res+=2*PI*L;
printf("%d\n",(int)(res+0.5));
}
return 0;
} 



 本文介绍了一个关于计算围绕国王城堡的最小周长墙的问题。通过使用几何和算法的知识,文章提供了一种解决方案来确定满足特定条件的墙的最小长度。
本文介绍了一个关于计算围绕国王城堡的最小周长墙的问题。通过使用几何和算法的知识,文章提供了一种解决方案来确定满足特定条件的墙的最小长度。

















 526
526

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








