继承与初始化
通过《Thinking in Java》Chapter Seven中的一个例子,我们浅谈一下Java中继承与初始化的一个过程。
1.代码
//: ChapterSeven/Beetle.java
// The full process of initialization.
package ChapterSeven;
import static net.mindview.util.Print.*;
class Insect {
private int i = 9;
protected int j;
Insect() {
print("i = " + i + ", j = " + j);
j = 39;
}
private static int x1 = printInit("static Insect.x1 initialized");
private static boolean b1 = printTrue();
private static String string = printString();
static String printString(){
System.out.println("This is printString");
return "The printString";
}
static boolean printTrue(){
System.out.println("This is static printTrue");
return true;
}
static int printInit(String s) {
print(s);
return 47;
}
}
public class Beetle extends Insect {
private int k = printInit("Beetle.k initialized");
public Beetle() {
print("k = " + k);
print("j = " + j);
}
private static int x2 = printInit("static Beetle.x2 initialized");
public static void main(String[] args) {
print("Beetle constructor");
Beetle b = new Beetle();
}
}
2. 执行过程:
- step 1.代码中有两个类,一个是Insect,一个是Beetle。后者为子类,前者为父类。我们研究一下初始化的过程。
- step 2.程序进入Beetle类中的static main()方法。发现Beetle类继承自Insect,将程序调转至Insect
- step 3.在Insect中,将static修饰的成员变量初始化,在本例中,即是x1,b1,string三个变量,相应的调用具体的方法实现这个初始化过程。
- step 4.如若Insect类继承自其它类,则按照Step2,3继续对成员进行初始化。
- step 5.所有的静态成员变量初始化之后。程序回到main()方法中,开始创建对象。在本例中,即是执行
print("Beetle constructor");
- 6.然后执行
Beetle b = new Beetle();
发现基类的构造器没有调用,先去调用基类构造器。在本例中是自动被调用,我们也可以用super来显式调用。
- 7.最后我们即按照程序书写部分进行输出即可。
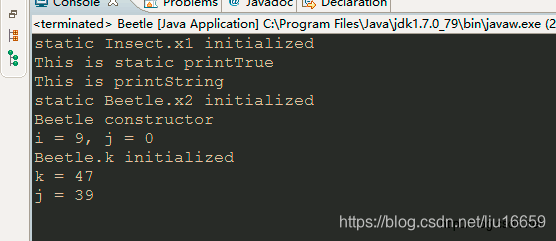
程序的最终执行结果如下:
二.简单泛型中的继承探讨
下面是一个元组,能够持有两个对象。
package net.mindview.util;
public class TwoTuple<A,B> {
public final A first;
public final B second;
public TwoTuple(A a, B b) { first = a; second = b; }
public String toString() {
return "(" + first + ", " + second + ")";
}
} ///:~
</pre><pre name="code" class="java">2.下面是一个是三元组,能够持有三个对象
package net.mindview.util;
public class ThreeTuple<A,B,C> extends TwoTuple<A,B> {
public final C third;
public ThreeTuple(A a, B b, C c) {
super(a, b);
third = c;
}
public String toString() {
return "(" + first + ", " + second + ", " + third +")";
}
public static void main(String [] args){
ThreeTuple tt = new ThreeTuple<String,Integer,Boolean>("My name is liushen and I'm ", 20, true);
System.out.println(tt);
}
}























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










