-
前言
安卓框架其实做的挺好,它已经把跟linux交互的过程都装起来,我们开发的时候基本不用再去关注这个实现。只要把对应的硬件设备对接好,比如触摸驱动替换等,基本不影响用户使用平台。这对平台移植,替换模块来说非常方便,对开发工程师来说也非常省事,只要关注应用开发就可以了。但是,搞清楚它的逻辑还是很必要的。
这篇文章主要是记录个人对按键处理流程的一些理解。其实已经有很多小伙伴都有写过很多文章介绍过相关内容,但自己去看一遍源码更加能加深印象,也会有更多不一样的收获。
-
整个交互流程

-
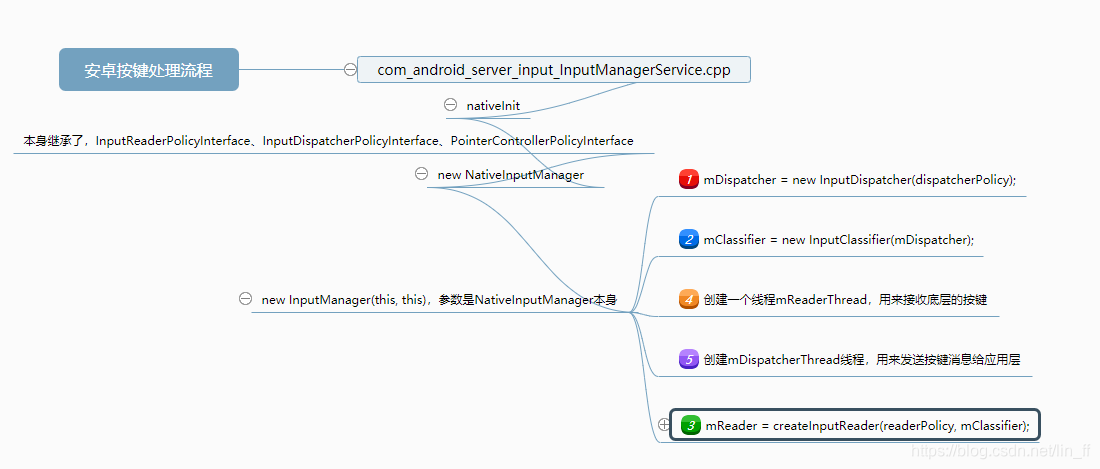
InputManagerService
安卓的按键处理一定离不开InputManagerService,这是系统运行起来就开始的一个服务,没有它我们就不能操作APP。在SystemServer.java的startOtherServices中完成初始化:
traceBeginAndSlog("StartInputManagerService");
inputManager = new InputManagerService(context);
traceEnd();SystemServer怎么工作,不在本文介绍范围内,这个涉及framework的启动,如果需要在framework中添加一个新的service,初始化的地方可以参考InputManagerService的启动添加。
public InputManagerService(Context context) {
this.mContext = context;
this.mHandler = new InputManagerHandler(DisplayThread.get().getLooper());
mUseDevInputEventForAudioJack =
context.getResources().getBoolean(R.bool.config_useDevInputEventForAudioJack);
Slog.i(TAG, "Initializing input manager, mUseDevInputEventForAudioJack="
+ mUseDevInputEventForAudioJack);
mPtr = nativeInit(this, mContext, mHandler.getLooper().getQueue());
String doubleTouchGestureEnablePath = context.getResources().getString(
R.string.config_doubleTouchGestureEnableFile);
mDoubleTouchGestureEnableFile = TextUtils.isEmpty(doubleTouchGestureEnablePath) ? null :
new File(doubleTouchGestureEnablePath);
LocalServices.addService(InputManagerInternal.class, new LocalService());
}nativeInit是在com_android_server_input_InputManager





 本文深入剖析了Android系统的按键处理流程,从InputManagerService到NativeInputManager,再到InputDispatcher的工作原理,详细介绍了按键事件如何被捕捉、处理并传递给应用程序。
本文深入剖析了Android系统的按键处理流程,从InputManagerService到NativeInputManager,再到InputDispatcher的工作原理,详细介绍了按键事件如何被捕捉、处理并传递给应用程序。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








