There are N dominoes in a line, and we place each domino vertically upright.
In the beginning, we simultaneously push some of the dominoes either to the left or to the right.
After each second, each domino that is falling to the left pushes the adjacent domino on the left.
Similarly, the dominoes falling to the right push their adjacent dominoes standing on the right.
When a vertical domino has dominoes falling on it from both sides, it stays still due to the balance of the forces.
For the purposes of this question, we will consider that a falling domino expends no additional force to a falling or already fallen domino.
Given a string "S" representing the initial state. S[i] = 'L', if the i-th domino has been pushed to the left; S[i] = 'R', if the i-th domino has been pushed to the right; S[i] = '.', if the i-th domino has not been pushed.
Return a string representing the final state.
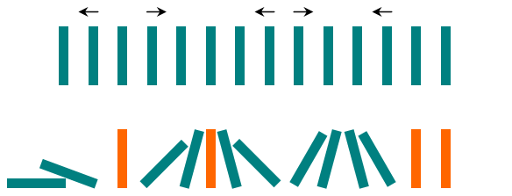
Example 1:
Input: ".L.R...LR..L.."
Output: "LL.RR.LLRRLL.."
Example 2:
Input: "RR.L"
Output: "RR.L"
Explanation: The first domino expends no additional force on the second domino.
Note:
0 <= N <= 10^5
String dominoes contains only 'L', 'R' and '.'
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/push-dominoes
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
暴力破解法:
class Solution {
public String pushDominoes(String dominoes) {
if (dominoes.length() <= 1) {
return dominoes;
}
boolean has;
char[] ans = dominoes.toCharArray();
while (true) {
char[] tmp = ans.clone();
has = false;
for (int i = 0; i < ans.length; i++) {
if (ans[i] == '.') {
if (i == 0) {
if (ans[i + 1] == 'L') {
tmp[i] = 'L';
has = true;
}
} else if (i == ans.length - 1) {
if (ans[i - 1] == 'R') {
tmp[i] = 'R';
has = true;
}
} else {
if (ans[i - 1] == 'R' && ans[i + 1] != 'L') {
tmp[i] = 'R';
has = true;
} else if (ans[i + 1] == 'L' && ans[i - 1] != 'R') {
tmp[i] = 'L';
has = true;
}
}
}
}
ans = tmp.clone();
if (!has) {
break;
}
}
return String.valueOf(ans);
}
}
分类计算:
1. 如果是两个相同字母之间的.,如L。。。L,或者R。。。R,那么最后都会变成一样的。
2. 如果是方向相反的,如L。。。R,那么不变。
3. 如果是R。。。L,那么就计算中间点的数量,如果是偶数个,那么就对半分,如果是奇数个,那么就中间留一个不变。
class Solution {
public String pushDominoes(String dominoes) {
if (dominoes.length() <= 1) {
return dominoes;
}
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
// 两边先加一个L,R
dominoes = "L" + dominoes + 'R';
int index = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < dominoes.length(); i++) {
if (dominoes.charAt(i) == '.') {
continue;
}
if (index > 0) {
ans.append(dominoes.charAt(index));
}
if (dominoes.charAt(i) == dominoes.charAt(index)) {
for (int j = index; j < i - 1; j++) {
ans.append(dominoes.charAt(i));
}
} else if (dominoes.charAt(index) == 'L' && dominoes.charAt(i) == 'R') {
for (int j = index; j < i - 1; j++) {
ans.append('.');
}
} else if (dominoes.charAt(index) == 'R' && dominoes.charAt(i) == 'L') {
int num = i - index - 1;
int dot = num % 2;
for (int j = 0; j < num / 2; j++) {
ans.append('R');
}
for (int j = 0; j < dot; j++) {
ans.append('.');
}
for (int j = 0; j < num / 2; j++) {
ans.append('L');
}
}
index = i;
}
return ans.toString();
}
}





 探讨当多米诺骨牌被推向左右两侧时的状态变化,通过实例展示最终形成的稳定状态,并提供两种算法实现。
探讨当多米诺骨牌被推向左右两侧时的状态变化,通过实例展示最终形成的稳定状态,并提供两种算法实现。
















 2180
2180

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








