104. 二叉树的最大深度:
题目链接
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 :
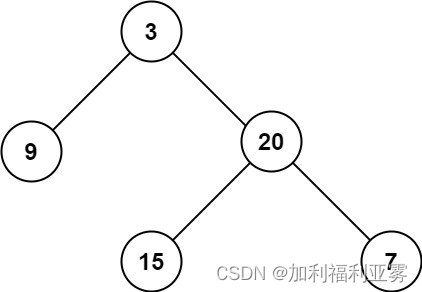
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3
解答:
class solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}
算法总结:
二叉树的最大深度遍历就是在遍历过程中通过递归的方式每次取到较大的深度,最后返回根结点
111. 二叉树的最小深度:
题目链接
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 :
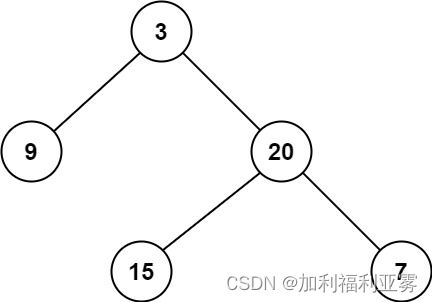
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
解答:
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = minDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = minDepth(root.right);
if (root.left == null) {
return rightDepth + 1;
}
if (root.right == null) {
return leftDepth + 1;
}
// 左右结点都不为null
return Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}
算法总结:
二叉树的最小深度遍历与最大深度不同是我们只有在左右结点都不为null的情况下才进行深度的添加,不然则遍历一边
101. 对称二叉树:
题目链接
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例 :
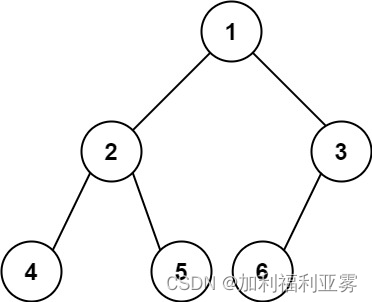
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6
解答:
class Solution {
int max = 0;
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
trackBacking(root);
return max;
}
public void trackBacking(TreeNode root){
if(root==null)return;
List<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.add(root);
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int size = que.size();
max++;
while(size>0){
TreeNode node = que.remove(0);
if(node.left!=null) que.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null) que.add(node.right);
size--;
}
}
}
}
算法总结:
完全二叉树的结点个数最简单的计算就是我们层序遍历一遍二叉树在遍历过程中添加结点个数,最后返回值




 文章介绍了如何计算二叉树的最大深度(通过递归遍历),最小深度(特殊条件下的递归),以及对称二叉树的节点个数(使用层序遍历)。
文章介绍了如何计算二叉树的最大深度(通过递归遍历),最小深度(特殊条件下的递归),以及对称二叉树的节点个数(使用层序遍历)。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








