之前写过TensorFlow Object Detection API的部署方法,如何用样本标定工具标定自己的样本数据,以及用tensorflow/kereas版本mask-rcnn进行训练。 本文记录如何用 TensorFlow Object Detection API 和 tensorflow的预训练模型训练自己的样本。
目录
准备工作:
准备工作可参考我之前的博客:
- Tensorflow Object Detection API 环境搭建
- 标定自己的训练数据集,参考自制图像标注软件
将标定样本生成为.record格式文件
本步骤参考了mahxn0的代码:
转换代码create_tf_record
创建create_tf_record_Label_Image.py文件,内容如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Monday February 25 09:34:09 2019
@author: QingShui-Cheng
"""
"""Convert labeled dataset with Label_Image tool to TFRecord for object_detection.
Please note that this tool only applies to Label_Image's annotations(json file).
Example usage:
python3 create_tf_record.py \
--images_dir=your absolute path to read images and annotaion json files.
--label_map_path=your path to label_map.pbtxt
--output_path=your path to write .record.
"""
import cv2
import glob
import hashlib
import io
import json
import numpy as np
import os
import PIL.Image
import tensorflow as tf
import logging
from object_detection.utils import label_map_util
flags = tf.app.flags
flags.DEFINE_string('images_dir', None, 'Absolute path to images and annotaion json files.')
flags.DEFINE_string('label_map_path', None, 'Path to label map proto.')
flags.DEFINE_string('output_path', None, 'Path to the output tfrecord.')
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
def int64_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value]))
def int64_list_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=value))
def bytes_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value]))
def bytes_list_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=value))
def float_list_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=value))
def create_tf_example(annotation_dict, label_map_dict=None):
"""Converts image and annotations to a tf.Example proto.
Args:
annotation_dict: A dictionary containing the following keys:
['height', 'width', 'filename', 'sha256_key', 'encoded_jpg',
'format', 'xmins', 'xmaxs', 'ymins', 'ymaxs', 'masks',
'class_names'].
label_map_dict: A dictionary maping class_names to indices.
Returns:
example: The converted tf.Example.
Raises:
ValueError: If label_map_dict is None or is not containing a class_name.
"""
if annotation_dict is None:
return None
if label_map_dict is None:
raise ValueError('`label_map_dict` is None')
height = annotation_dict.get('height', None)
width = annotation_dict.get('width', None)
filename = annotation_dict.get('filename', None)
sha256_key = annotation_dict.get('sha256_key', None)
encoded_jpg = annotation_dict.get('encoded_jpg', None)
image_format = annotation_dict.get('format', None)
xmins = annotation_dict.get('xmins', None)
xmaxs = annotation_dict.get('xmaxs', None)
ymins = annotation_dict.get('ymins', None)
ymaxs = annotation_dict.get('ymaxs', None)
masks = annotation_dict.get('masks', None)
class_names = annotation_dict.get('class_names', None)
print("class_names:",class_names)
labels = []
for class_name in class_names:
label = label_map_dict.get(class_name, 'None')
print("label:",label)
if label is None:
raise ValueError('`label_map_dict` is not containing {}.'.format(
class_name))
labels.append(label)
encoded_masks = []
for mask in masks:
pil_image = PIL.Image.fromarray(mask.astype(np.uint8))
output_io = io.BytesIO()
pil_image.save(output_io, format='PNG')
encoded_masks.append(output_io.getvalue())
feature_dict = {
'image/height': int64_feature(height),
'image/width': int64_feature(width),
'image/filename': bytes_feature(filename.encode('utf8')),
'image/source_id': bytes_feature(filename.encode('utf8')),
'image/key/sha256': bytes_feature(sha256_key.encode('utf8')),
'image/encoded': bytes_feature(encoded_jpg),
'image/format': bytes_feature(image_format.encode('utf8')),
'image/object/bbox/xmin': float_list_feature(xmins),
'image/object/bbox/xmax': float_list_feature(xmaxs),
'image/object/bbox/ymin': float_list_feature(ymins),
'image/object/bbox/ymax': float_list_feature(ymaxs),
'image/object/mask': bytes_list_feature(encoded_masks),
'image/object/class/label': int64_list_feature(labels)}
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(
feature=feature_dict))
return example
def _get_annotation_dict(images_path, json_path):
"""Get boundingboxes and masks.
Args:
images_path: Path to image.
json_path: Path to annotated json file corresponding to
the image. The json file annotated by labelme with keys:
"filename": "2018_6_27_18_3_45_523.jpg",
"size": "393954",
"file_attributes": "@Qingshui Cheng@Labixiaoxindian @ All Right Reserved!",
"regions": [
{
"region_attributes": {
"type": "stone"
},
"shape_attributes": {
"name": "polygon",
"all_points_x": [ ... ],
"all_points_y": [ ... ]
}
}
]
Returns:
annotation_dict: A dictionary containing the following keys:
['height', 'width', 'filename', 'sha256_key', 'encoded_jpg',
'format', 'xmins', 'xmaxs', 'ymins', 'ymaxs', 'masks',
'class_names'].
#
# Raises:
# ValueError: If images_path or json_path is not exist.
"""
if (not os.path.exists(images_path) or
not os.path.exists(json_path)):
return None
fo = open(json_path,encoding='utf-8')
text = fo.read()
fo.close()
if text.startswith(u'\ufeff'):
text = text.encode('utf8')[3:].decode('utf8')
annotations = json.loads(text)
regions = annotations.get('regions', None)
if regions is None:
return None
image_relative_path = images_path
print("imagePath",image_relative_path)
image_name = image_relative_path.split('/')[-1]
image_format = image_name.split('.')[-1].replace('jpg', 'jpeg')
with tf.gfile.GFile(images_path, 'rb') as fid:
encoded_jpg = fid.read()
image = cv2.imread(images_path)
height = image.shape[0]
width = image.shape[1]
key = hashlib.sha256(encoded_jpg).hexdigest()
xmins = []
xmaxs = []
ymins = []
ymaxs = []
masks = []
class_names = []
for mark in regions:
class_name = mark['region_attributes']['type']
class_names.append(class_name)
xarray = np.array(mark['shape_attributes']['all_points_x'])
yarray = np.array(mark['shape_attributes']['all_points_y'])
polygon = [xarray,yarray];
polygon = np.array(polygon).T
mask = np.zeros(image.shape[:2])
cv2.fillPoly(mask, [polygon], 1)
masks.append(mask)
# Boundingbox
x = polygon[:, 0]
y = polygon[:, 1]
xmin = np.min(x)
xmax = np.max(x)
ymin = np.min(y)
ymax = np.max(y)
xmins.append(float(xmin) / width)
xmaxs.append(float(xmax) / width)
ymins.append(float(ymin) / height)
ymaxs.append(float(ymax) / height)
annotation_dict = {'height': height,
'width': width,
'filename': image_name,
'sha256_key': key,
'encoded_jpg': encoded_jpg,
'format': image_format,
'xmins': xmins,
'xmaxs': xmaxs,
'ymins': ymins,
'ymaxs': ymaxs,
'masks': masks,
'class_names': class_names}
return annotation_dict
def create_tf_record(output_filename,
label_map_dict,
sample_dir,
samples_list):
"""Creates a TFRecord file from examples.
Args:
output_filename: File Path to where output file is saved.
label_map_dict: The label map dictionary.
sample_dir: Directory where image files are stored.
examples: Examples to parse and save to tf record.
"""
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(output_filename)
for idx, jpgname in enumerate(samples_list):
if idx % 100 == 0:
logging.info('On image %d of %d', idx, len(samples_list))
jsonname = jpgname[:-3]+"json"
try:
annotation_dict = _get_annotation_dict(jpgname,jsonname)
if annotation_dict is None:
continue
#print(annotation_dict)
tf_example = create_tf_example(annotation_dict, label_map_dict)
writer.write(tf_example.SerializeToString())
except ValueError:
logging.warning('Invalid example: %s, ignoring.', jpgname)
writer.close()
def main(_):
if not os.path.exists(FLAGS.images_dir):
raise ValueError('`images_dir` is not exist.')
if not os.path.exists(FLAGS.label_map_path):
raise ValueError('`label_map_path` is not exist.')
label_map_dict = label_map_util.get_label_map_dict(FLAGS.label_map_path)
#搜寻样本图片和标定文件
sublist = os.listdir(FLAGS.images_dir)
imagelist = [];
for i in range(0, len(sublist)):
path = os.path.join(FLAGS.images_dir, sublist[i])
if os.path.isfile(path) and path.lower().endswith(".jpg"):
jsonname = path[:-3]+"json";
if os.path.isfile(jsonname):
imagelist.append(path);
print("search {} sample images", len(imagelist))
#拆分训练和验证数据集
np.random.seed(25)
np.random.shuffle(imagelist)
num_images = len(imagelist)
num_train = int(0.7 * num_images)
train_images = imagelist[:num_train]
val_images = imagelist[num_train:]
logging.info('%d training and %d validation examples.',
len(train_images), len(val_images ))
train_output_path = os.path.join(FLAGS.output_path, 'sample_train.record')
val_output_path = os.path.join(FLAGS.output_path, 'sample_val.record')
create_tf_record(
train_output_path,
label_map_dict,
FLAGS.images_dir,
train_images)
create_tf_record(
val_output_path,
label_map_dict,
FLAGS.images_dir,
val_images)
print('Successfully created TFRecord to {}.'.format(FLAGS.output_path))
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()编辑*.pbtxt类别定义
我们命名为为sample_class.pbtxt文件,文件内容格式如下
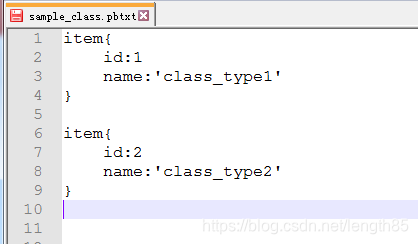
可参考上述内容,修改item数目及内容,定义自己的样本类别。
生成.record数据
执行命令
python create_tf_record_mine.py --images_dir /home/kc/code/tensorflow/MyData_Samples/ --label_map_path /home/kc/code/tensorflow/sample_class.pbtxt --output_path /home/kc/code/tensorflow/sample
- --images_dir:样本图片及标注.json文件所在目录
- --label_map_path:类别定义文件sample_class.pbtxt 全路径文件名
- --output_path:转换后sample_train.record和sample_val.record存放路径。
训练样本数据
1、下载预训练模型
在Tensorflow提供的Tensorflow detection model zoo 下载COCO-trained models mask_rcnn_inception_v2_coco
下载后解压:
tar -zxvf mask_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28.tar.gz
2、编辑pipeline_config文件
将 <git clone dir>/models/research/object_detection/samples/configs/下的 mask_rcnn_inception_v2_coco.config拷贝一份
cp /home/kc/code/tensorflow/models/research/object_detection/samples/configs/mask_rcnn_inception_v2_coco.config /home/kc/code/tensorflow/sample/
修改其中内容:
1、num_classes 修改为自己样本类别数
model {
faster_rcnn {
num_classes: 2
image_resizer {
keep_aspect_ratio_resizer {
min_dimension: 800
max_dimension: 1365
}
}2、修改与训练模型路径:
- fine_tune_checkpoint 项修改为:mask_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28.tar.gz解压后目录/model.ckpt
gradient_clipping_by_norm: 10.0
fine_tune_checkpoint: "/home/kc/code/tensorflow/mask_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28/model.ckpt"
from_detection_checkpoint: true
# Note: The below line limits the training process to 200K steps, which we
# empirically found to be sufficient enough to train the pets dataset. This
# effectively bypasses the learning rate schedule (the learning rate will
# never decay). Remove the below line to train indefinitely.3、修改train_input_reader:
- input_path: 前面生成的 sample_train.record 全路径
- label_map_path:前面编辑的自己样本类别定义文件sample_class.pbtxt 全路径
train_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "/home/kc/code/tensorflow/sample/sample_train.record"
}
label_map_path: "/home/kc/code/tensorflow/sample/sample_class.pbtxt"
load_instance_masks: true
mask_type: PNG_MASKS
}4、修改eval_input_reader:
- input_path: 前面生成的 sample_val.record 全路径
- label_map_path:前面编辑的自己样本类别定义文件sample_class.pbtxt 全路径
eval_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "/home/kc/code/tensorflow/sample/sample_val.record"
}
label_map_path: "/home/kc/code/tensorflow/sample/sample_class.pbtxt"
load_instance_masks: true
mask_type: PNG_MASKS
shuffle: false
num_readers: 1
}进行训练:
进入搭建好的环境或conda虚拟环境
source ./anaconda/bin/activate py35tf
进入 <git clone path>/models/research/ 目录,执行
export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:`pwd`:`pwd`/slim
进入 <git clone path>/models/research/object_detection/legacy/目录 开始训练 执行:
python train.py --logtostderr --train_dir=/home/kc/code/tensorflow/log --pipeline_config_path /home/kc/code/tensorflow/sample/mask_rcnn_inception_v2_coal.config
- --train_dir: 训练模型保存目录
- --pipeline_config_path: 前面修改的pipeline_config文件全路径
如果没有意外,会出现训练信息:
tensorboad:
输入命令:
tensorboard --logdir=/home/kc/code/tensorflow/log
在浏览器中输入http://0.0.0.0:6006,就能看到训练曲线了
导出模型:
进入 <git clone path>/models/models/research/object_detection/
python3 export_inference_graph.py \
--input_type image_tensor \
--pipeline_config_path /home/kc/code/tensorflow/sample/mask_rcnn_inception_v2_coco.config \
--trained_checkpoint_prefix /home/kc/code/tensorflow/log/model.ckpt-200000\
--output_directory /home/kc/code/tensorflow/output
- --pipeline_config_path: 前面修改的pipeline_config文件全路径
- --trained_checkpoint_prefix: 训练模型目录训练最后保存的model.ckpt-????
- --output_directory: 导出模型目录





 本文详细介绍使用TensorFlow Object Detection API及预训练模型训练自定义数据集的全过程,涵盖数据准备、模型选择、配置修改、训练执行及模型导出等关键步骤。
本文详细介绍使用TensorFlow Object Detection API及预训练模型训练自定义数据集的全过程,涵盖数据准备、模型选择、配置修改、训练执行及模型导出等关键步骤。

















 1388
1388

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










