in ARM
the spsr is a banked register.
after every change in mode, cpsr is copied into the spsr, and after the mode returns.
the spsr is copied back to cpsr.
the spsr is a banked cpsr for a different mode, just like the banked lr is the pc for a
different mode.
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/leesagacious/article/details/52711852
看下图的bit[8], 不止bit[7~6] 是 foreign_intr
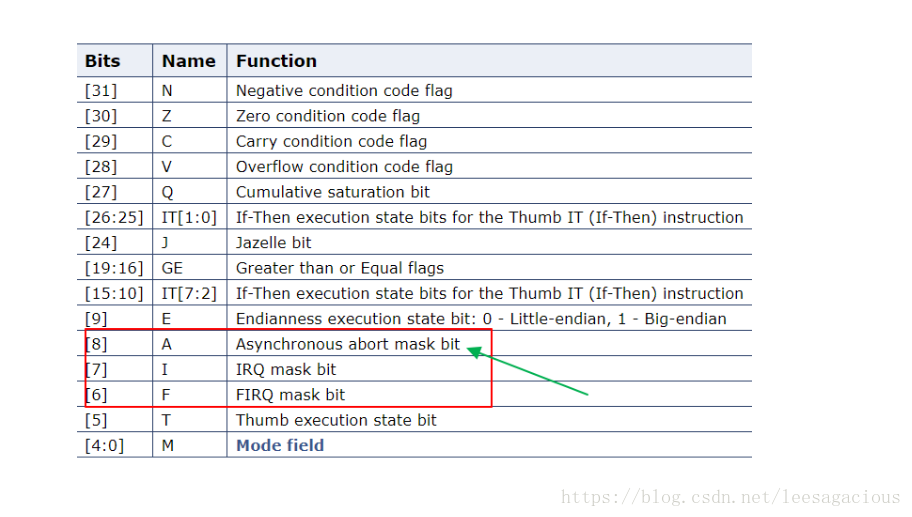
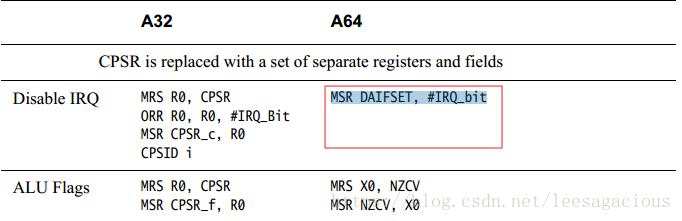
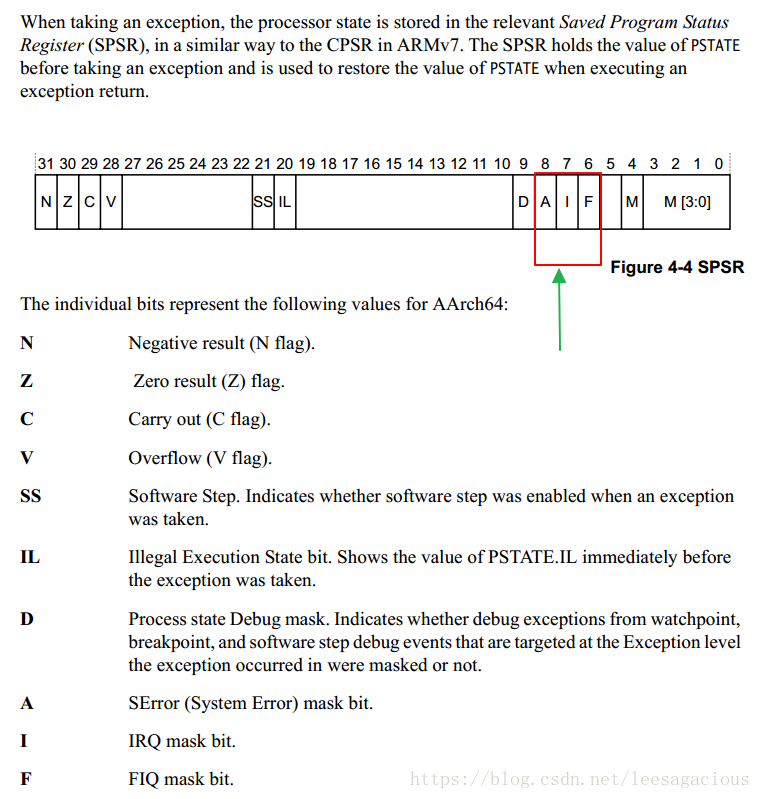
/**
func: 屏蔽中断
@exception 需要屏蔽的位
看清了,这里写 1 是mask, 不过x64 rflags bit[9] 却是写 0 是mask
只是屏蔽一个interrupt,就啰嗦了一大堆code来实现,NM吧!烦不烦!
x64这块做的比ARM要优秀的多.
这样不优化的ARM(32-bit),想在Server domain蚕食x64的市场, 则需要多努力
还好,ARM(64-bit) daif register 则优秀起来了
*/
uint32_t thread_mask_exceptions(uint32_t exceptions)
{
/*
就是读取CPSR寄存器,获取到bit[8~6]位的值
好,看下面的内嵌汇编 (ARM32位,ARM64位下面说)
uint32_t thread_get_exceptions(void)
{
uint32_t cpsr = read_cpsr();
{
uint32_t cpsr;
asm volatile ("mrs %[cpsr], cpsr"
: [cpsr] "=r" (cpsr)
);
return cpsr;
}
return (cpsr >> CPSR_F_SHIFT) & THREAD_EXCP_ALL;
}
*/
uint32_t state = thread_get_exceptions();
/*
整体读出 - 清空相应的位 - 写入
这里涉及到interrupt与spin_lock的一个问题 A-1.
问题是 ;
Foreign interrupts must not be unmasked while holding a spinlock
why ?
holding spinlock 的时,若interrupt 来了,神挡杀神,佛挡杀佛,
持有的锁一直没有被释放,死锁的概率就增加了.
Linux kernel 默认帮你扛21(s), 然后专门盯CPU的狗就给你rebooting了, 哈哈
那好,我maked这样的rebooting会这么样?
不好意思,你NONMASKABLE了这样的INTERRUPT. 即: NMI.
好吧,见图A-1
整个OS中,中断就是一个搅局者, foreign_intr 尤甚. 防不甚防!
*/
thread_set_exceptions(state | (exceptions & THREAD_EXCP_ALL));
/*
返回old value.
*/
return state;
}
好,下面看看spinlock 与 intr 在Linux kernel ,tee kernel中的实现
好,上面先放放,来看一个经典的 Classic bug : “page fault”.
struct thread_core_local *thread_get_core_local(void)
{
uint32_t cpu_id = get_core_pos();
assert(thread_get_exceptions() & THREAD_EXCP_FOREIGN_INTR);
assert(cpu_id < CFG_TEE_CORE_NB_CORE);
return &thread_core_local[cpu_id];
}先看TA
https://github.com/leesagacious/optee_os-Analysis/blob/master/tee_ta_init_session_f.c
/**
到全局链表tee_ctxes上根据UUID查找TA
1 : 什么时机将TA添加到该链表上的
2 : 什么时机从链表上删除的, 删除后资源都释放掉了吗
3 :既然是全局性资源 为什么这里没有防竞态的手段
会不会出现 Linux kernel list “惊群效应”
4 :该global list 存在的意义是什么? 还有什么更好的方法吗
好,下面逐一来回答
*/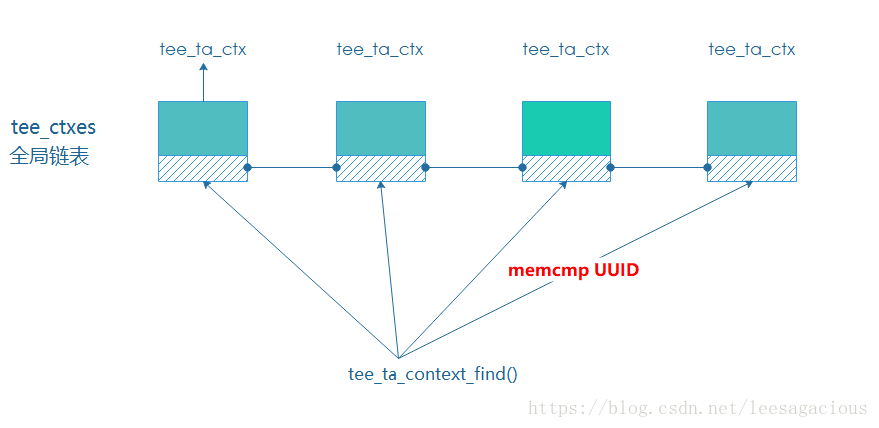
1:什么时候add,foreach,remove的
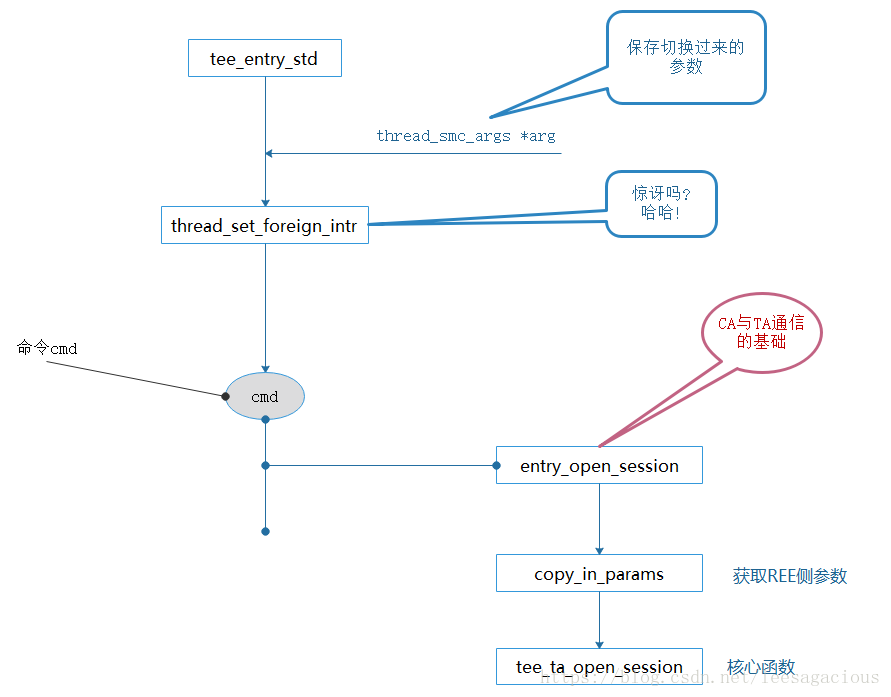
2:fast smc
1 : enable shm cache
/*
tee driver probe函数
在该函数的最后会触发一次fast smc
*/
static struct optee *optee_probe(void)
{
....
....
/*
触发fast smc
会切换到secure world,将thread_prealloc_rpc_cache设置为true
*/
optee_enable_shm_cache(optee);
}
/*
该函数主要是触发该fast smc
fast smc,std smc 都是通过 driver来触发的,
*/
void optee_enable_shm_cache(struct optee *optee)
{
struct optee_call_waiter w;
/*
做了两件事情:
1 : 初始化一个完成量
2 : 将该waiter加入到optee维护的call_queue链表上
*/
optee_cq_wait_init(&optee->call_queue, &w);
/*
linaro那帮人说 We need to retry until secure world isn't busy.
好吧,这让我想到了 iic controller要将数据放到iic bus上会尝试400次来
判断iic bus是否一直处于忙的状态
*/
while (true) {
/*
作为out参数使用
*/
struct arm_smccc_res res;
/*
看传给secure world的参数, 尼玛,几乎都是0 !
res 是out参数 通过r0寄存器来传递
*/
optee->invoke_fn(OPTEE_SMC_ENABLE_SHM_CACHE, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, &res);
/*
通过判断r0的值来判断此次请求是否成功
*/
if (res.a0 == OPTEE_SMC_RETURN_OK)
break;
optee_cq_wait_for_completion(&optee->call_queue, &w);
}
optee_cq_wait_final(&optee->call_queue, &w);
}
/*
处理 fast smc, 类似的是 tee_entry_std 用来处理 std smc
args : 空空如也,只包含一个cmd, 用来区分是那个请求
*/
void tee_entry_fast(struct thread_smc_args *args)
{
.....
/*
enable shm cache.
*/
case OPTEE_SMC_ENABLE_SHM_CACHE:
tee_entry_enable_shm_cache(args);
break;
}
static void tee_entry_enable_shm_cache(struct thread_smc_args *args)
{
/*
调用真正处理该次cmd的函数
无论enable是否成功,都通过a0 register来传递状态返回给normal world
*/
if (thread_enable_prealloc_rpc_cache())
args->a0 = OPTEE_SMC_RETURN_OK;
else
args->a0 = OPTEE_SMC_RETURN_EBUSY;
}
bool thread_enable_prealloc_rpc_cache(void)
{
bool rv;
size_t n;
/*
整个运行处于关闭中断环境中运行
运行完毕后又开启中断.
*/
uint32_t exceptions = thread_mask_exceptions(THREAD_EXCP_FOREIGN_INTR);
lock_global();
/*
查找一个状态为THREAD_STATE_FREE的thread
如果所有的thread都die的了,那么就表示本次enable就success了
在系统初始化时 会将第一个thread 设置为 THREAD_STATE_ACTIVE
thread_init_boot_thread()
{
.....
threads[0].state = THREAD_STATE_ACTIVE;
}
*/
for (n = 0; n < CFG_NUM_THREADS; n++) {
if (threads[n].state != THREAD_STATE_FREE) {
rv = false;
goto out;
}
}
rv = true;
/*
真正的目的
*/
thread_prealloc_rpc_cache = true;
out:
unlock_global();
/*
这里又enable foreign_intr mask
*/
thread_unmask_exceptions(exceptions);
return rv;
}FUNC thread_rpc , :
/* Read daif and create an SPSR */
mrs x1, daif
orr x1, x1, #(SPSR_64_MODE_EL1 << SPSR_64_MODE_EL_SHIFT)
/* Mask all maskable exceptions before switching to temporary stack */
msr daifset, #DAIFBIT_ALL
push x0, xzr
push x1, x30
bl thread_get_ctx_regs
ldr x30, [sp, #8]
store_xregs x0, THREAD_CTX_REGS_X19, 19, 30
mov x19, x0
bl thread_get_tmp_sp
pop x1, xzr /* Match "push x1, x30" above */
mov x2, sp
str x2, [x19, #THREAD_CTX_REGS_SP]
ldr x20, [sp] /* Get pointer to rv[] */
mov sp, x0 /* Switch to tmp stack */
adr x2, .thread_rpc_return
mov w0, #THREAD_FLAGS_COPY_ARGS_ON_RETURN
bl thread_state_suspend
mov x4, x0 /* Supply thread index */
ldr w0, =TEESMC_OPTEED_RETURN_CALL_DONE
load_wregs x20, 0, 1, 3 /* Load rv[] into w0-w2 */
smc #0
b . /* SMC should not return */
.thread_rpc_return:
/*
* At this point has the stack pointer been restored to the value
* stored in THREAD_CTX above.
*
* Jumps here from thread_resume above when RPC has returned. The
* IRQ and FIQ bits are restored to what they where when this
* function was originally entered.
*/
pop x16, xzr /* Get pointer to rv[] */
store_wregs x16, 0, 0, 5 /* Store w0-w5 into rv[] */
ret
END_FUNC thread_rpc






 本文深入探讨了ARM架构中的中断管理机制,特别是CPSR和SPSR寄存器的作用及如何通过它们进行中断屏蔽和恢复。同时,文章还讨论了在特定场景下,如持有自旋锁时中断的影响,并分析了Linux内核中与中断相关的实现。
本文深入探讨了ARM架构中的中断管理机制,特别是CPSR和SPSR寄存器的作用及如何通过它们进行中断屏蔽和恢复。同时,文章还讨论了在特定场景下,如持有自旋锁时中断的影响,并分析了Linux内核中与中断相关的实现。
















 546
546

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








