一、定义
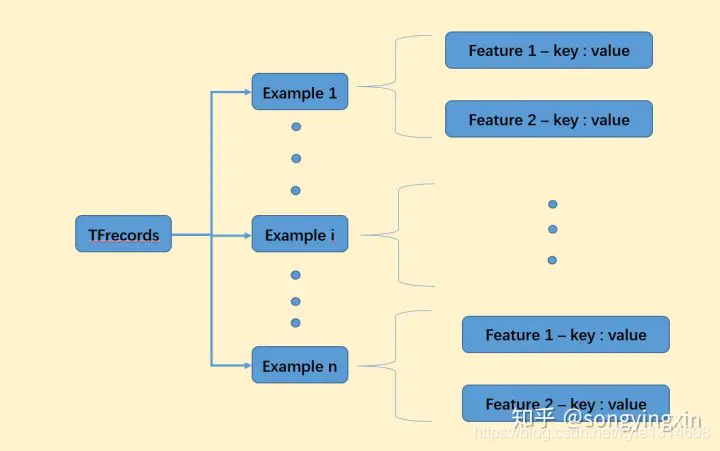
事先将数据编码为二进制的TFRecord文件,配合TF自带的多线程API,读取效率最高,且跨平台,适合规范化存储复杂的数据。上图为TFRecord的pb格式定义,可发现每个TFRecord由许多Example组成。
Example官方定义:An Example is a mostly-normalized data format for storing data for training and inference.
一个Example代表一个封装的数据输入,比如包含一张图片、图片的宽高、图片的label等信息。而每个信息用键值对的方式存储。因此一个Example包含了一个Features(Features 包含多个 feature)。
这种约定好的TFRecord格式,可以应用于所有数据集的制作。
二、Feature
官方定义:
// A Feature contains Lists which may hold zero or more values. These
// lists are the base values BytesList, FloatList, Int64List.
//
// Features are organized into categories by name. The Features message
// contains the mapping from name to Feature.、
eatures是Feature的字典合集,key为String,而value为tf.train.Feature(),value必须符合特定的三种格式之一:字符串(BytesList)、实数列表(FloatList)或者整数列表(Int64List)。
tf.train.Feature(**options)
options可以选择如下三种数据格式:
bytes_list = tf.train.BytesList(value = 输入)#输入的元素的数据类型为string
int64_list = tf.train.Int64List(value = 输入)#输入的元素的数据类型为int(int32,int64)
float_list = tf.trian.FloatList(value = 输入)#输入的元素的数据类型为float(float32,float64)
注:value必须是list(向量)
原始数据为矩阵或张量(比如图片格式)不管哪种方式存储都会使数据丢失形状信息,所以在向该样本中写入feature时应该额外加入shape信息作为额外feature。shape信息是int类型,建议采用原feature名字+’_shape’来指定shape信息的feature名。这样读取操作可获取到shape信息进行还原。
以下是两种存储矩阵的方式,都需要额外存储shape信息以便还原:(第二种更方便)
将矩阵或张量fatten成list(向量),再根据元素的数据类型选择使用哪个数据格式存储。
将矩阵或张量用.tostring()转换成string类型,再用tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[input.tostring()]))来存储。
# 定义函数转化变量类型。
def _int64_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value]))
def _bytes_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value]))
# 将每一个数据转化为tf.train.Example格式。
def _make_example(pixels, label, image):
image_raw = image.tostring() # np.array ---> String byte
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'pixels': _int64_feature(pixels),
'label': _int64_feature(np.argmax(label)),
'image_raw': _bytes_feature(image_raw)
}))
return example
三、完整的持久化mnist数据为TFRecord
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import numpy as np
# 定义函数转化变量类型。
def _int64_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value]))
def _bytes_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value]))
# 将数据转化为tf.train.Example格式。
def _make_example(pixels, label, image):
image_raw = image.tostring()
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'pixels': _int64_feature(pixels),
'label': _int64_feature(np.argmax(label)),
'image_raw': _bytes_feature(image_raw)
}))
return example
def save_tfrecords():
# 读取mnist训练数据。
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("../../datasets/MNIST_data",dtype=tf.uint8, one_hot=True)
images = mnist.train.images # (55000, 784) <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
labels = mnist.train.labels # (55000, 10) <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
pixels = images.shape[1] # 784 = 28 * 28
num_examples = mnist.train.num_examples
# 输出包含训练数据的TFRecord文件。
with tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter("output.tfrecords") as writer:
for index in range(num_examples):
# 生成一个Example并序列化后写入pb
example = _make_example(pixels, labels[index], images[index])
writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
print("TFRecord训练文件已保存。")
四、读取解析TFRecord
读取解析的步骤中,需要根据编码时候的定义,来指定解码时候的规则和还原的dtype,如image需要指定tf.string格式,之后再去解析成uint8。注意,这里的parse等op操作都是在graph中定义一些运算op,并没有运行。sess.run()的时候才会真正多线程开始读取解析。这种读取二进制了流文件的速度,多线程加持下远远超过读取硬盘中的原生图片。
def test_tfrecords():
# 读取文件。
print(len(tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.QUEUE_RUNNERS))) # 0
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(["output.tfrecords"]) # 队列默认自动添加进collection
print(len(tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.QUEUE_RUNNERS))) # 1
_, serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue)
# 解析读取的样例。
features = tf.parse_single_example(
serialized_example,
features={
'image_raw': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
'pixels': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'label': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64)
})
images = tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'], tf.uint8)
labels = tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int32)
pixels = tf.cast(features['pixels'], tf.int32)
sess = tf.Session()
# 启动多线程处理输入数据。
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
for i in range(5):
image, label, pixel = sess.run([images, labels, pixels])
print(label)




 本文详细介绍了TFRecord文件格式及其在TensorFlow中的应用。包括定义、特点、如何存储和读取复杂数据,以及通过实例演示如何持久化MNIST数据集并解析TFRecord文件。
本文详细介绍了TFRecord文件格式及其在TensorFlow中的应用。包括定义、特点、如何存储和读取复杂数据,以及通过实例演示如何持久化MNIST数据集并解析TFRecord文件。


















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








