目录
设备服务是物理设备与EdgeX信息交换的桥梁,每个设备服务管理接口一致的同类多个设备。官方目前提供了支持mqtt,snmp,modbus等协议的设备服务,其他协议的设备服务需要另外开发。设备服务是物理设备与EdgeX通信的桥梁,每个设备服务管理接口一致的同类多个设备。
// ProtocolDriver is a low-level device-specific interface used by
// by other components of an EdgeX Device Service to interact with
// a specific class of devices.
type ProtocolDriver interface {
// Initialize performs protocol-specific initialization for the device
// service. The given *AsyncValues channel can be used to push asynchronous
// events and readings to Core Data.
Initialize(lc logger.LoggingClient, asyncCh chan<- *AsyncValues) error
// HandleReadCommands passes a slice of CommandRequest struct each representing
// a ResourceOperation for a specific device resource.
HandleReadCommands(deviceName string, protocols map[string]contract.ProtocolProperties, reqs []CommandRequest) ([]*CommandValue, error)
// HandleWriteCommands passes a slice of CommandRequest struct each representing
// a ResourceOperation for a specific device resource.
// Since the commands are actuation commands, params provide parameters for the individual
// command.
HandleWriteCommands(deviceName string, protocols map[string]contract.ProtocolProperties, reqs []CommandRequest, params []*CommandValue) error
// Stop instructs the protocol-specific DS code to shutdown gracefully, or
// if the force parameter is 'true', immediately. The driver is responsible
// for closing any in-use channels, including the channel used to send async
// readings (if supported).
Stop(force bool) error
}官方提供了device-sdk-go,开发者只需要实现ProtocolDriver接口便可开发一个针对特定协议的设备服务。本文以官方提供的device-mqtt-go分析设备服务的内部运行逻辑。
启动参数
Usage: %s [options]
Server Options:
-r, --registry Indicates service should use Registry
-p, --profile <name> Indicate configuration profile other than default
-c, --confDir Specify an alternate configuration directory- registry是一个bool量,True表示配置参数是从consul拉取,False表示从本地配置文件载入。
- profile本地配置文件名(默认configuration.toml), 即便registry=True, 该参数也必须要指明一个配置文件,因为连接consul服务所需的host,port等参数必须从本地的配置文件中获取。
- confDir是本地配置文件所在目录(默认./res),confDir/profile 组合可获得配置文件全名。
配置文件
[Writable]
LogLevel = 'INFO'
[Service]
Host = "localhost"
Port = 49990
ConnectRetries = 20
Labels = []
OpenMsg = "device simple started"
Timeout = 5000
EnableAsyncReadings = true
AsyncBufferSize = 16
[Registry]
Host = "localhost"
Port = 8500
Type = "consul"
CheckInterval = "10s"
FailLimit = 3
FailWaitTime = 10
[Clients]
[Clients.Data]
Name = "edgex-core-data"
Protocol = "http"
Host = "localhost"
Port = 48080
Timeout = 5000
[Clients.Metadata]
Name = "edgex-core-metadata"
Protocol = "http"
Host = "localhost"
Port = 48081
Timeout = 5000
[Clients.Logging]
Name = "edgex-support-logging"
Protocol = "http"
Host = "localhost"
Port = 48061
[Device]
DataTransform = true
InitCmd = ""
InitCmdArgs = ""
MaxCmdOps = 128
MaxCmdValueLen = 256
RemoveCmd = ""
RemoveCmdArgs = ""
ProfilesDir = "./res"
[Logging]
EnableRemote = false
File = "./device-simple.log"
# Pre-define Devices
[[DeviceList]]
Name = "Simple-Device01"
Profile = "Simple-Device"
Description = "Example of Simple Device"
Labels = [ "industrial" ]
[DeviceList.Protocols]
[DeviceList.Protocols.other]
Address = "simple01"
Port = "300"
[[DeviceList.AutoEvents]]
Frequency = "10s"
OnChange = false
Resource = "Switch"
[[DeviceList.AutoEvents]]
Frequency = "30s"
OnChange = false
Resource = "Image"
如上是device-sdk-go自带的配置文件,分为7个部分,设备服务启动后会将配置文件的信息导入如下结构中,若registry=True则根据Registry中的信息连接consul并拉取相应的配置信息覆盖之前从本地配置文件中读取到的信息。
// Config is a struct which contains all of a DS's configuration settings.
type Config struct {
// WritableInfo contains configuration settings that can be changed in the Registry .
Writable WritableInfo
// Service contains RegistryService-specific settings.
Service ServiceInfo
// Registry contains registry-specific settings.
Registry RegistryService
// Clients is a map of services used by a DS.
Clients map[string]ClientInfo
// Device contains device-specific configuration settings.
Device DeviceInfo
// Logging contains logging-specific configuration settings.
Logging LoggingInfo
// Watchers is a map provisionwatchers to be created on startup.
Watchers map[string]WatcherInfo
// DeviceList is the list of pre-define Devices
DeviceList []DeviceConfig `consul:"-"`
// Driver is a string map contains customized configuration for the protocol driver implemented based on Device SDK
Driver map[string]string
}-
Writable// WritableInfo is a struct which contains configuration settings that can be changed in the Registry . type WritableInfo struct { // Level is the logging level of writing log message LogLevel string }Writable结构中的参数可以在运行时被通过consul更新,LogLevel, 日志等级。 -
ServiceInfo
// ServiceInfo is a struct which contains service related configuration // settings. type ServiceInfo struct { // Host is the hostname or IP address of the service. Host string // Port is the HTTP port of the service. Port int // ConnectRetries is the number of times the DS will try to connect to all dependent services. // If exceeded for even one dependent service, the DS will exit. ConnectRetries int // Labels are... Labels []string // OpenMsg specifies a string logged on DS startup. OpenMsg string // Timeout (in milliseconds) specifies both // - timeout for processing REST calls and // - interval time the DS will wait between each retry call. Timeout int // EnableAsyncReadings to determine whether the Device Service would deal with the asynchronous readings EnableAsyncReadings bool // AsyncBufferSize defines the size of asynchronous channel AsyncBufferSize int }Host 提供设备服务绑定的IP,建议0.0.0.0 Port 提供设备服务的端口 ConnectRetries 设备服务启功尝试次数上限 Labels 标签,便于区分不同设备服务 OpenMsg 启动成功消息 Timeout 启动失败后下一次尝试之前的等待时间 EnableAsyncReadings 是否支持异步读取设备数据 AsyncBufferSize 异步读取数据缓冲长度
-
Registry
consul连接参数
type RegistryService struct {
// Host is the hostname or IP address of a RegistryService.
Host string
// Port is the HTTP port of a RegistryService.
Port int
// Type of Registry implementation to use, i.e. consul
Type string
// Timeout specifies a timeout (in milliseconds) for
// processing REST calls from other services.
Timeout int
// Health check interval
CheckInterval string
// Maximum number of retries
FailLimit int
// Time to wait until next retry
FailWaitTime int64
}-
Clients
设备服务运行时需要使用其他微服务提供的功能,Client便是连接其他微服务所必须的参数,这是一个map参数,key值便是其他微服务的类型,value便是接入其他服务所需的具体参数信息, 设备服务正常运行一般需要使用logging, core-data, core-metaddata三种微服务。
// ClientInfo provides the host and port of another service in the eco-system.
type ClientInfo struct {
// Name is the client service name
Name string
// Host is the hostname or IP address of a service.
Host string
// Port defines the port on which to access a given service
Port int
// Protocol indicates the protocol to use when accessing a given service
Protocol string
// Timeout specifies a timeout (in milliseconds) for
// processing REST calls from other services.
Timeout int
}-
Device
// DeviceInfo is a struct which contains device specific configuration settings. type DeviceInfo struct { // DataTransform specifies whether or not the DS perform transformations // specified by valuedescriptor on a actuation or query command. DataTransform bool // InitCmd specifies a device resource command which is automatically // generated whenever a new device is added to the DS. InitCmd string // InitCmdArgs specify arguments to be used when building the InitCmd. InitCmdArgs string // MaxCmdOps defines the maximum number of resource operations that // can be sent to a Driver in a single command. MaxCmdOps int // MaxCmdValueLen is the maximum string length of a command parameter or // result (including the valuedescriptor name) that can be returned // by a Driver. MaxCmdValueLen int // InitCmd specifies a device resource command which is automatically // generated whenever a new device is removed from the DS. RemoveCmd string // RemoveCmdArgs specify arguments to be used when building the RemoveCmd. RemoveCmdArgs string // ProfilesDir specifies a directory which contains deviceprofile // files which should be imported on startup. ProfilesDir string }DataTransform 是否对读取的设备数据进行转换,例如mask,shift,base,scale,offset. InitCmd 新设备加入时的初始化指令 InitCmdArgs 初始化指令参数 MaxCmdOps 单指令中所包含的最大可擦做资源数 MaxCmdValueLen 指令参数或相应结果的最大长度 RemoveCmd 设备移除时的指令 RemoveCmdArgs 设备移除指令参数 ProfilesDir 设备profile目录,目录下所有.yml或.yaml后缀的文件将被当作deviceprofile文件
-
Logging
EnableRemote True: log于support-logging微服务持久化(support-logging的连接参数由Clients字段提供), False:log于本地文件持久化
File log本地持久化时日志文件的路径
// LoggingInfo is a struct which contains logging specific configuration settings.
type LoggingInfo struct {
// EnableRemote defines whether to use Logging Service
EnableRemote bool
// File is the pathname of a local log file to be created.
File string
}
-
Watchers
// WatcherInfo is a struct which contains provisionwatcher configuration settings. type WatcherInfo struct { Profile string Key string MatchString string }
-
DeviceList
// DeviceConfig is the definition of Devices which will be auto created when the Device Service starts up
type DeviceConfig struct {
// Name is the Device name
Name string
// Profile is the profile name of the Device
Profile string
Description string
// Other labels applied to the device to help with searching
Labels []string
// Protocols for the device - stores protocol properties
Protocols map[string]dsModels.ProtocolProperties
// AutoEvent supports auto-generated events sourced from a device service
AutoEvents []dsModels.AutoEvent
}设备模型,设备服务启动时会读取该参数并写入cache。
-
Driver
协议驱动特定的配置参数,不同协议该字段可能有不同内容。
启动顺序
创建驱动协议驱动结构体(该结构体必须实现ProtocolDriver接口),并将设备服务名,版本与该结构体传入BootStrap启动设备服务,Bootstrap继续调用startService启动服务。
func main() {
sd := driver.NewProtocolDriver()
startup.Bootstrap(serviceName, device_mqtt.Version, sd)
}startService依次调用device.NewSerive创建设备服务实例,listenForInterrupt侦听中断,s.Start启动设备服务实例。若一切正常该函数永不退出,除非errChan通道收到出错信息才会继续运行s.Stop返回并停止服务。
func startService(serviceName string, serviceVersion string, driver dsModels.ProtocolDriver) error {
s, err := device.NewService(serviceName, serviceVersion, confProfile, confDir, useRegistry, driver)
if err != nil {
return err
}
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stdout, "Calling service.Start.\n")
errChan := make(chan error, 2)
listenForInterrupt(errChan)
go s.Start(errChan)
err = <-errChan
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stdout, "Terminating: %v.\n", err)
return s.Stop(false)
}
func listenForInterrupt(errChan chan error) {
go func() {
c := make(chan os.Signal)
signal.Notify(c, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM)
errChan <- fmt.Errorf("%s", <-c)
}()
}device.NewService依次记录当前启动时间,服务名,服务版本,以及载入profile配置文件并将读取的配置信息写入common.CurrentConfig,最后申请Service实例并赋值启动时间和服务配置并返回。其中LoadConfig根据useRegistry会选择从consul或本地文件装在配置参数结构体。
func NewService(serviceName string, serviceVersion string, confProfile string, confDir string, useRegistry string, proto dsModels.ProtocolDriver) (*Service, error) {
startTime := time.Now()
if svc != nil {
err := fmt.Errorf("NewService: service already exists!\n")
return nil, err
}
if len(serviceName) == 0 {
err := fmt.Errorf("NewService: empty name specified\n")
return nil, err
}
common.ServiceName = serviceName
config, err := configLoader.LoadConfig(useRegistry, confProfile, confDir)
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "error loading config file: %v\n", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
common.CurrentConfig = config
if len(serviceVersion) == 0 {
err := fmt.Errorf("NewService: empty version number specified\n")
return nil, err
}
common.ServiceVersion = serviceVersion
if proto == nil {
err := fmt.Errorf("NewService: no Driver specified\n")
return nil, err
}
svc = &Service{}
svc.startTime = startTime
svc.svcInfo = &config.Service
common.Driver = proto
return svc, nil
}errChan通道的写入源有两个,一个来自系统中断信号signal.Notify(c, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM),另一个来自s.Start启动失败信号。
func (s *Service) Start(errChan chan error) (err error) {
err = clients.InitDependencyClients()
if err != nil {
return err
}
// If useRegistry selected then configLoader.RegistryClient will not be nil
if configLoader.RegistryClient != nil {
// Logging has now been initialized so can start listening for configuration changes.
go configLoader.ListenForConfigChanges()
}
err = selfRegister()
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("Couldn't register to metadata service")
}
// initialize devices, objects & profiles
cache.InitCache()
err = provision.LoadProfiles(common.CurrentConfig.Device.ProfilesDir)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("Failed to create the pre-defined Device Profiles")
}
err = provision.LoadDevices(common.CurrentConfig.DeviceList)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("Failed to create the pre-defined Devices")
}
s.cw = newWatchers()
// initialize driver
if common.CurrentConfig.Service.EnableAsyncReadings {
s.asyncCh = make(chan *dsModels.AsyncValues, common.CurrentConfig.Service.AsyncBufferSize)
go processAsyncResults()
}
err = common.Driver.Initialize(common.LoggingClient, s.asyncCh)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("Driver.Initialize failure: %v", err)
}
// Setup REST API
r := controller.InitRestRoutes()
autoevent.GetManager().StartAutoEvents()
http.TimeoutHandler(nil, time.Millisecond*time.Duration(s.svcInfo.Timeout), "Request timed out")
// TODO: call ListenAndServe in a goroutine
common.LoggingClient.Info(fmt.Sprintf("*Service Start() called, name=%s, version=%s", common.ServiceName, common.ServiceVersion))
go func() {
errChan <- http.ListenAndServe(common.Colon+strconv.Itoa(s.svcInfo.Port), r)
}()
common.LoggingClient.Info("Listening on port: " + strconv.Itoa(common.CurrentConfig.Service.Port))
common.LoggingClient.Info("Service started in: " + time.Since(s.startTime).String())
common.LoggingClient.Debug("*Service Start() exit")
return err
}s.Start启动服务过程:
1,调用clients.InitDependencyClients初始化设备服务正常运行所必须的客户端,其内部初始化逻辑是:检查配置参数中连接core-data与core-metadata的IP和PORT的完整性;初始化loggingClient;检查core-data与core-metadata服务是否正常运行;初始化连接core-data与core-metadata的客户端。
2,如果useRegistry,开启configLoader.ListenForConfigChanges协程监测并更新配置结构中Writable。
3,selfRegister注册自己,如果consul中已经存在相同服务名的实例则直接拉区相应服务实例参数,若果不存在则创建新的服务实例并写入consul。最后设置svc.initialized = true表明初始化成功。
4,初始化cache,cache首先从consul拉取数据初始化,然后调用provision.LoadProfiles和provision.LoadDevices从配置参数中更新cache。
5,s.cw = newWatchers()
6,若使能异步读取设备数据则启动processAsyncResults协程,他直接接受来自svc.asyncCh的设备测量数据并处理打包最终发送给core-data。
7,调用common.Driver.Initialize初始化协议驱动,该函数即是设备服务开发者实现ProtocolDriver接口的4个函数之一。
8,r := controller.InitRestRoutes()初始化REST API接口,这些接口对外部提供相关服务,包括读取设备数据或向设备写指令。
9,autoevent.GetManager().StartAutoEvents()启动cache中每个设备模型中的自动测量事件。Device模型中有个AutoEvent字段描述了自动测量的频率与资源。该函数会为每一个自动测量事件创建一个协程,该协程会使用ProtocolDriver接口中的HandleReadCommands读取设备数据并将数据发送至core-data。
10,errChan <- http.ListenAndServe(common.Colon+strconv.Itoa(s.svcInfo.Port), r)启动HTTP Server,至此所有启动工作完成,设备服务开始正常工作。
内部逻辑
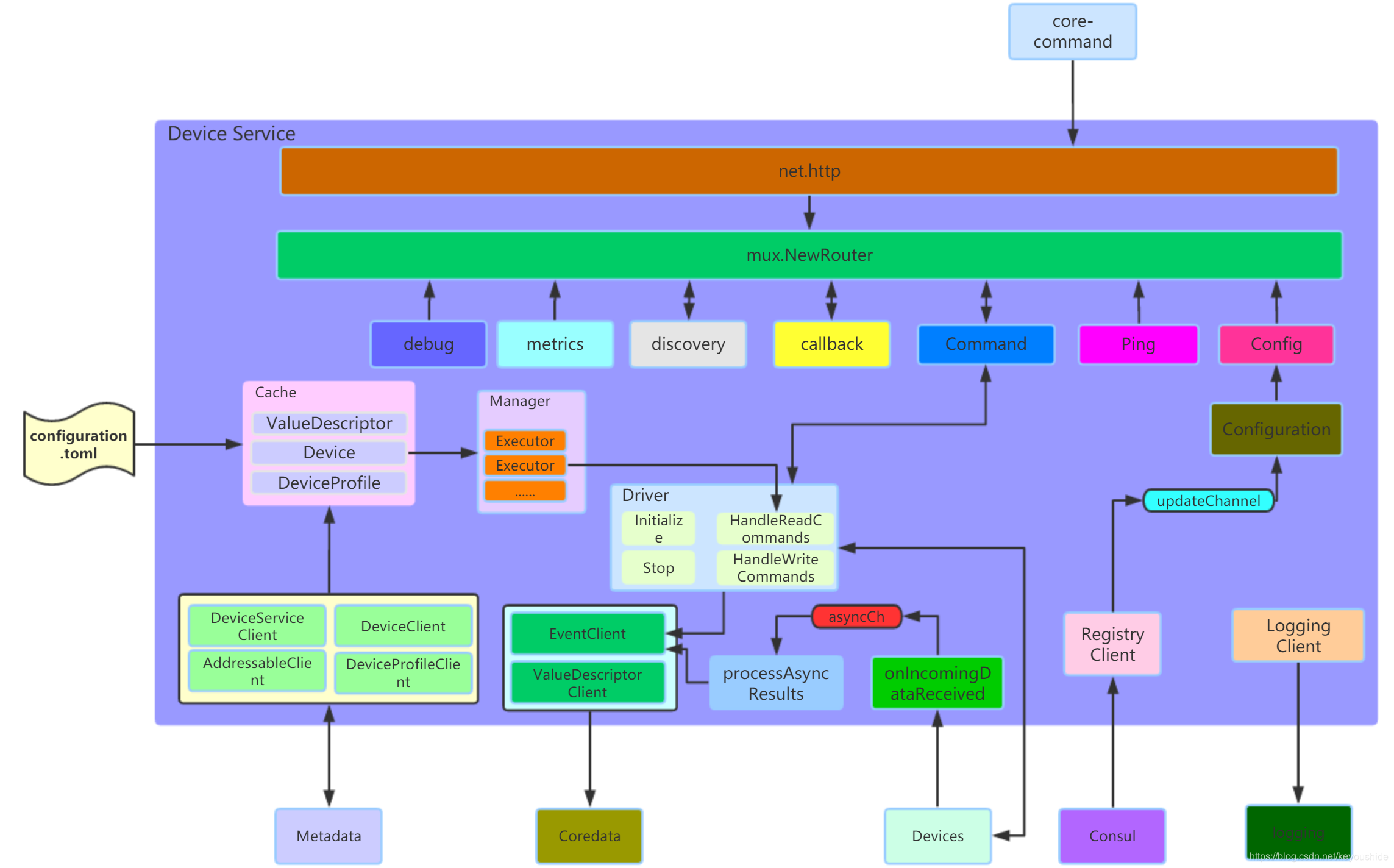
设备服务启动完成后的内部逻辑大致如上图所示,cache分别从metadata和配置文件读取信息,manager为cache中每一个设备创建完成其AutoEvent的Executor,Executor使用Driver中的HandleReadCommands读取设备数据,并将该数据发送给coredata。device-mqtt-go支持异步读取设备数据,因此Driver.Initialize注册onIncomingDataReceived被动接收来自设备的数据并传入asynCh通道,processAsyncResults接收该数据并打包然后传送至coredata。http服务提供7个接口,最重要的便是command,他实现了对物理设备的数据读取与写指令功能。





















 655
655

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








