1 Basic Knowledge
| downstream sublink | The collection of lanes between the DFP Tx and the UFP Rx. |
|---|---|
| DPP | Data Packet Payload. Contains the data packet’s data and a 32 -bit CRC. |
| DP | Data Packet which consists of a Data Packet Header(DPH) followed by a Data Packet Payload(DPP). |
| Gen X | Gen X is a generic term used to refer to any of the combinations Gen 1, Gen 2 orGen 1/Gen 2 when the topic is specific to the phy layers but does not need to bespecific to either Gen 1 or Gen 2 |
| Gen X x Y | X refers to the rate of signaling on the wire (Gen 1, Gen 2, etc.) and Y refers to the number of lanes. |
| LMP | Link Management Packet. A type of header packet used to communicate information between a pair of link partners. |
| LTSSM | Link Training and Status State Machine |
| transaction | The IN consists of an ACK TP with a response of NRDY TP, DP, or STALL TP. The OUT consists of a DP with a response of NRDY TP, an ACK TP, or STALL TP. |
| transfer | One or more bus transactions to move information between a software client and its function. |
- The USB 3.2 system architecture is comprised of two simultaneously active buses: a USB 2.0 bus and an Enhanced SuperSpeed bus.
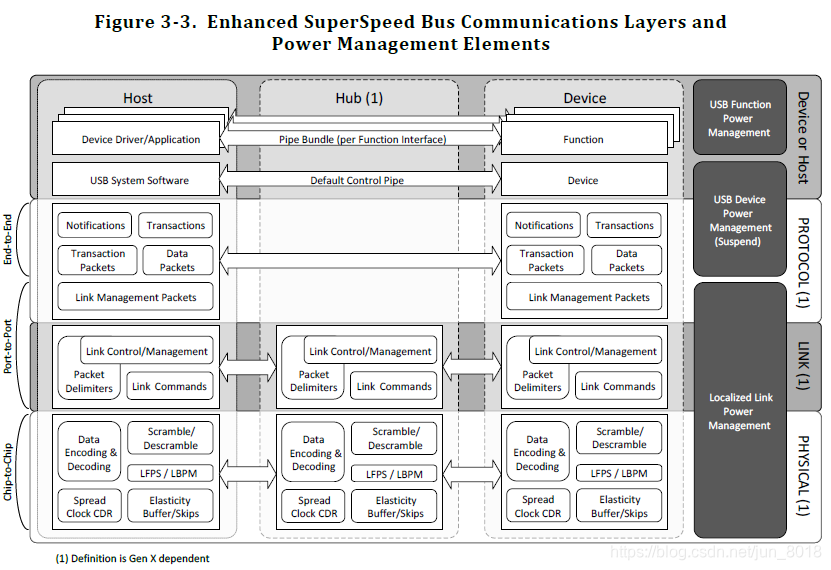
- The nominal signaling data rate for Gen 1 physical layer is 5 Gbps. A Gen 1 transmitter encodes data and control characters into symbols using an 8b/10b code.
- The nominal signaling data rate for the Gen 2 physical layer is 10 Gbps. A Gen 2 transmitter frames data and control bytes (referred to as Symbols) by prepending a 4-bit block identifier to 16 symbols (128 bits) to create a 128b/132b block.
- For links that operate at Gen 1x1 speed (5 Gbps and 8b/10b line encoding) the raw throughput is 500 MB/sec.
- For links that operate at Gen 2x1 speed (10 Gbps and 128b/132b line encoding) the raw throughput is approximately 1.2 GB/sec.





 本文详细介绍了USB3.2系统的架构,包括其双总线设计:USB2.0和增强型超高速总线。文章对比了USB2.0与增强型超高速总线在交易、流模式、批量传输能力及广播方式上的不同,深入解析了数据爆发、IN/OUT传输、控制传输、批量传输、中断传输和等时传输等概念。同时,还阐述了四种基本包类型:链路管理包、交易包、数据包和等时时间戳包的特性。
本文详细介绍了USB3.2系统的架构,包括其双总线设计:USB2.0和增强型超高速总线。文章对比了USB2.0与增强型超高速总线在交易、流模式、批量传输能力及广播方式上的不同,深入解析了数据爆发、IN/OUT传输、控制传输、批量传输、中断传输和等时传输等概念。同时,还阐述了四种基本包类型:链路管理包、交易包、数据包和等时时间戳包的特性。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1023
1023

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








