一,异常
程序出现的不正常的情况
java中的异常类有以下类型
Throwable ->(Error,Exception->(RuntimeException,非RuntimeException))
可以看出Throwable是所有异常类的父类
Error是严重问题,不需要处理
RuntimeException在编译时检查不出来,但执行会出问题
非RuntimeException编译时不会编译通过
二,try...catch...
它不会中断程序的执行
//Throwable的成员方法(所有异常的祖宗类,方法所有异常都可以用)
//getMassage()返回错误的原因
//toString()返回错误类型和原因
//printStackTrace()返回错误类型、原因和错误位置
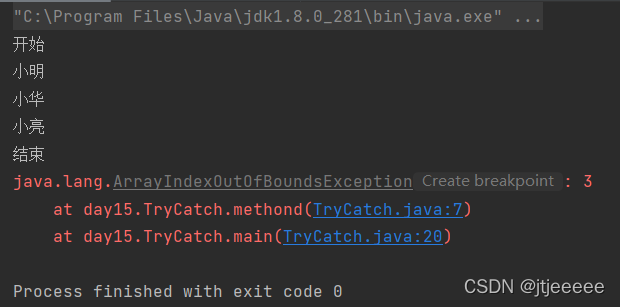
public class TryCatch {
public static void methond(String[] str){
try{
for(int i=0;i<=str.length+1;i++){
System.out.println(str[i]);
}
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException a){
// toString()返回错误类型和原因
// System.out.println(a.toString());
// getMassage()返回错误的原因
// System.out.println(a.getMessage());
// printStackTrace()返回错误类型、原因和错误位置
a.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开始");
String[] str={"小明","小华","小亮"};
methond(str);
System.out.println("结束");
}
}
它没有中断执行
三,throws
将异常抛出去,并不会实际处理问题而是让调用者处理,如果调用者不处理,将会用默认处理方案
四,自定义异常
| throws | throw |
| 用在方法声明后面,跟的是异常类名 | 用在方法体内,跟的是异常对象名 |
| 表示抛出异常由该方案的调用者处理 | 表示抛出异常,由方法体内的语句处理 |
| 表示可能出现异常 | 执行throw一定有异常 |
事例
学生类
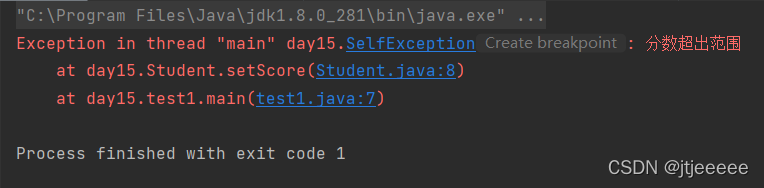
public class Student{
public String name;
public int score;
public void setScore(int score) throws SelfException {
if(score>100){
// 可以看出throw抛出的实际是一个对象
throw new SelfException("分数超出范围");
}else{
this.score=score;
System.out.println("正确");
}
}
}
自定义异常类SelfException
public class SelfException extends Exception{
public SelfException(){};
public SelfException(String message){
// 这个message参数会一直追溯到祖宗类,效果就是作为错误原因输出出来
super(message);
}
}
测试类
public class TryCatch {
public static void methond(String[] str){
try{
for(int i=0;i<=str.length+1;i++){
System.out.println(str[i]);
}
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException a){
// toString()返回错误类型和原因
// System.out.println(a.toString());
// getMassage()返回错误的原因
// System.out.println(a.getMessage());
// printStackTrace()返回错误类型、原因和错误位置
a.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开始");
String[] str={"小明","小华","小亮"};
methond(str);
System.out.println("结束");
}
}
结果:




















 5534
5534

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








