1.8 Elasticsearch-排序、分页、_source 过滤
1.8.1 排序(sort)
在 Elasticsearch 中,默认按照 _score 倒序排列。业务上经常需要显式指定排序字段与顺序,语法与 SQL 的 ORDER BY 非常接近。
单字段排序
GET /shop/_search
{
"query": {"match": {"title": "手机"}},
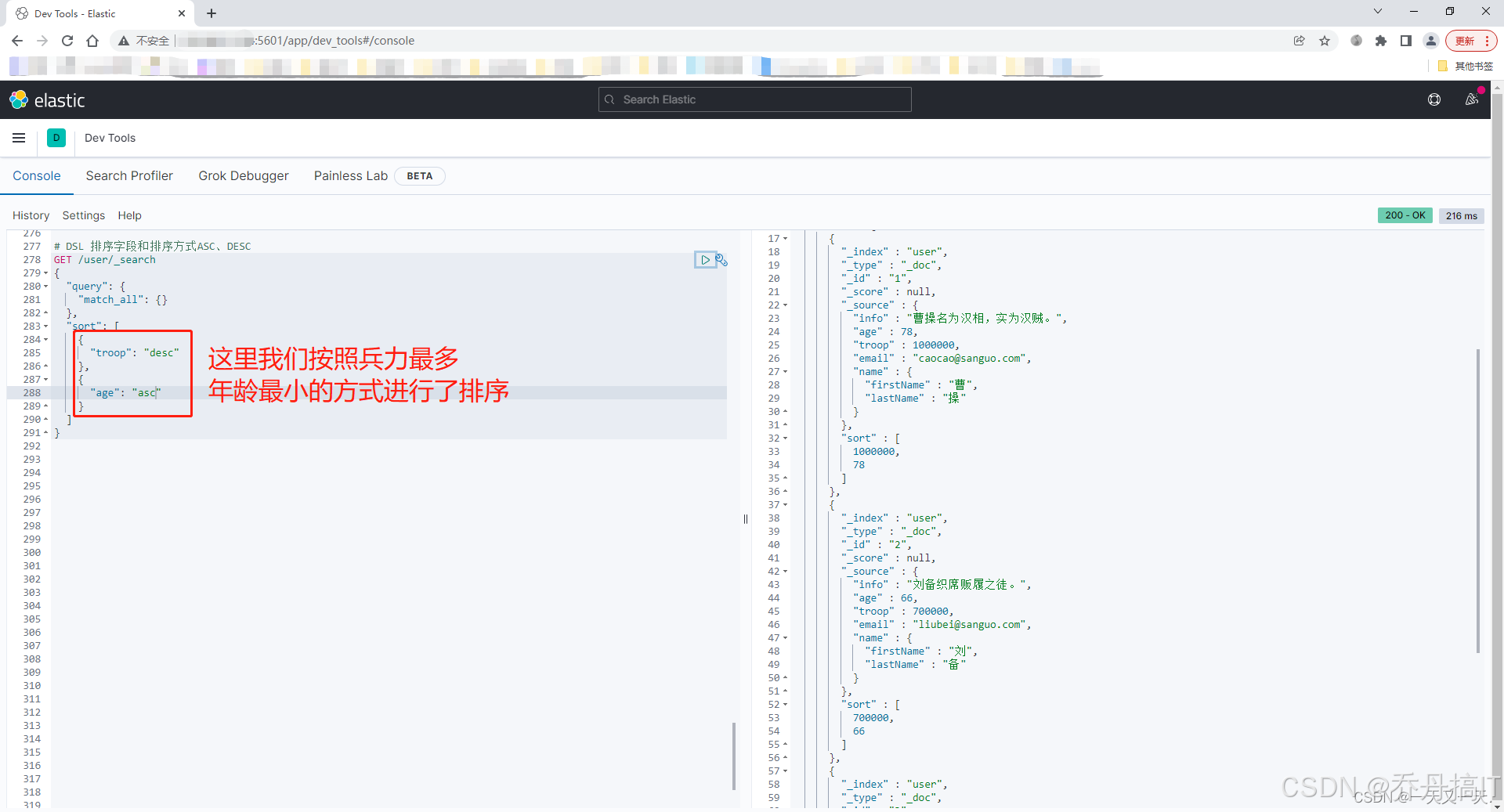
"sort": [
{"price": {"order": "asc"}}
]
}
order 取值:asc | desc。
多字段排序
当第一排序字段值相同时,依次取后续字段做次级排序:
"sort": [
{"in_stock": {"order": "desc"}},
{"price": {"order": "asc"}}
]
geo_distance 排序
地理位置场景按距离升序排列,越近越靠前:
"sort": [
{
"_geo_distance": {
"location": {"lat": 31.2, "lon": 121.5},
"order": "asc",
"unit": "km",
"distance_type": "arc"
}
}
]
返回结果每条命中的 sort 数组里会多出一个 distance 值,单位为 km。
script 排序
字段值需要二次计算再排序时,可用 painless 脚本:
"sort": [
{
"_script": {
"type": "number",
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": "doc['sales'].value * 0.8 + doc['comment_score'].value * 0.2"
},
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
脚本排序会禁用 track_total_hits 优化,大数据集请评估性能。
排序注意事项
- 排序字段必须开启
doc_values(默认开启);text类型需用field.keyword多字段。 - 对
text类型直接排序会抛出异常Fielddata is disabled on text fields by default. - 排序字段值缺失的文档,默认排在最后,可通过
missing参数调整:{"price": {"order": "asc", "missing": "_first"}}
1.8.2 分页(from/size)
Elasticsearch 使用 from 偏移量 + size 返回条数实现浅分页,与 MySQL 的 LIMIT from, size 等价。
GET /shop/_search
{
"query": {"match_all": {}},
"from": 0,
"size": 20,
"sort": [{"_id": "asc"}]
}
from从 0 开始计数。- 默认单次最多返回 10 000 条结果,受集群参数
index.max_result_window限制;超过会报Result window is too large。
深度分页成本
每次请求,协调节点都需要从每个分片取 (from + size) 条记录做全局排序,内存与 CPU 随 from 线性增长。深度翻页推荐:
- scroll 快照游标,适合离线导出:
返回POST /shop/_search?scroll=2m { "size": 1000, "sort": ["_doc"] }_scroll_id,后续用POST /_search/scroll循环拉取。 - search_after 实时滚动,适合业务端连续翻页:
利用上一页最后一条的排序值作为游标,避免随机跳页,性能稳定。GET /shop/_search { "size": 20, "sort": [{"price": "asc"}, {"_id": "asc"}], "search_after": [1999, "product-12345"] }
1.8.3 _source 过滤
默认情况下,Elasticsearch 会把整条原始 JSON (_source) 原样返回。若索引文档很大且只需要部分字段,可在请求体里显式过滤,减少网络带宽与序列化开销。
includes/excludes 语法
GET /shop/_search
{
"_source": {
"includes": ["title", "price", "in_stock"],
"excludes": ["description", "internal_note"]
},
"query": {"match_all": {}}
}
支持通配符:
"includes": ["title", "meta.*"]
关闭 _source
极端场景下可直接禁掉:
"_source": false
此时返回体里不再有 _source 字段,只能通过 docvalue_fields 或 stored_fields 拿特定字段。
与 stored_fields 区别
_source是保存整条原始文档,存储开销一次、取回一次。stored_fields需要字段在 mapping 里显式设置"store": true,适合超大字段、只要少量列的场景;否则优先用_source过滤。
综合示例
查询手机类商品,按价格升序取第 3 页(每页 10 条),只返回商品标题、价格、库存、距离当前用户的位置,并过滤掉描述字段:
GET /shop/_search
{
"_source": {
"includes": ["title", "price", "in_stock"]
},
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {"match": {"category": "手机"}},
"filter": {"geo_distance": {"distance": "10km", "location": {"lat": 31.2, "lon": 121.5}}}
}
},
"sort": [
{"price": "asc"},
{
"_geo_distance": {
"location": {"lat": 31.2, "lon": 121.5},
"order": "asc",
"unit": "km"
}
}
],
"from": 20,
"size": 10
}
返回结果每条命中仅包含 title、price、in_stock,并在 sort 数组中给出 _geo_distance 计算出的距离值,前端可直接渲染,避免多余字段传输。
小结
排序、分页与 _source 过滤是搜索接口最常用却也最容易踩坑的三件套:
- 排序字段类型、缺失值、脚本性能都要提前核对;
- 深度分页务必改用
search_after或scroll; - 大字段列表页一定利用
_source过滤,减少 70%+ 的网络包大小。
掌握这三板斧,才能在 Elasticsearch 高并发场景下游刃有余。
更多技术文章见公众号: 大城市小农民























 3566
3566

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










