1. 前言
本文主要参考了ELF格式解析的学习笔记,此笔记中详细介绍了ELF的基本格式,并对其中的各个部分进行了详细的说明。其中<<详解ELF重定位原理>>又对ELF重定位的原理进行了一个简要说明,本文主要用一个程序实例解释了elf的基本组成及可重定位原理。
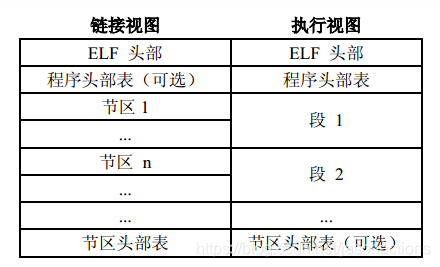
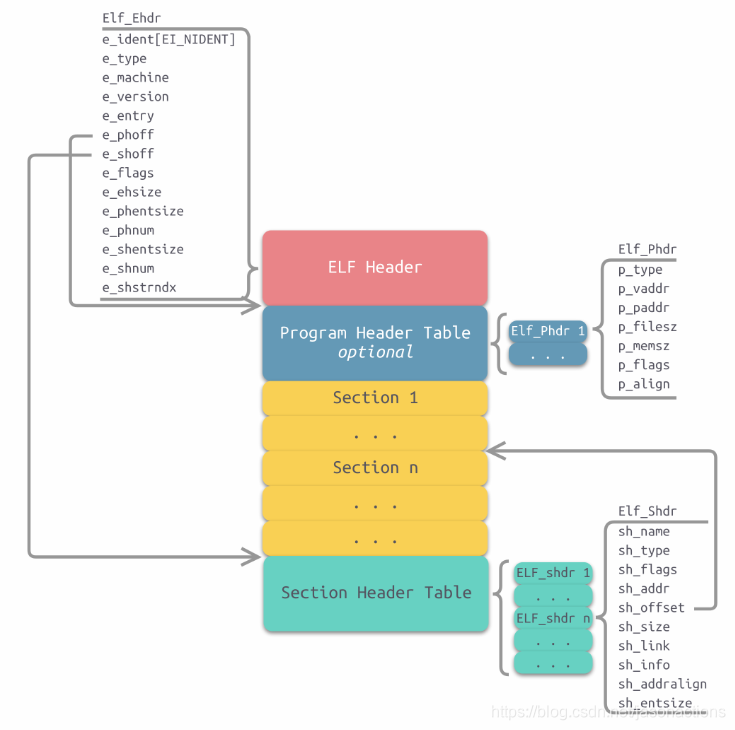
如上可理解为elf的总体布局,主要引用自 《ELF格式解析》学习笔记(一)
2. 实例代码
//main.c
#include "part.h"
extern int g_int1, g_int2;
extern char *g_str1, *g_str2;
int main()
{
int i = 0;
char *str = "abc";
func_1(i);
func_2(str);
g_int1 = 9;
g_str1 = "defg";
printf("Global integer is %d and %d, global string is %s and %s.\n", g_int1, g_int2,
g_str1, g_str2);
return i;
}
//part.c
#include "part.h"
int g_int1, g_int2 = 5;
char *g_str1, *g_str2 = "xyz";
void func_1(int i)
{
int j;
j = i;
printf("func_1 : j = %d\n", j);
}
void func_2(char *str)
{
printf("func_2 : str = %s\n", str);
}
//part.h
#ifndef _PART_H_
#define _PART_H_
void func_1(int i);
void func_2(char *str);
#endif
//Makefile
all: main_s main_d
main_s: main.o part.o
gcc main.o part.o -o main_s
main_d: main.o libpart.so
gcc main.o -L. -lpart -o main_d
libpart.so: part.o
gcc --shared part.o -o libpart.so
main.o: main.c
gcc -c main.c -o main.o
part.o: part.c
gcc -c part.c -o part.o
clean:
rm -f *.o *.so main_s main_d
3. 重定位原理说明
以main函数调用func_1函数的重定位为例,说明重定位的原理。
编译后生成如下的文件
ubuntu@VM-0-9-ubuntu:~/test/elf_test$ ls
libpart.so main.c main_d main.o main_s Makefile part.c part.h part.o
查看main.o的信息:
ubuntu@VM-0-9-ubuntu:~/test/elf_test$ readelf -a main.o
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: REL (Relocatable file)
Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x0
Start of program headers: 0 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 1304 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 0 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 0
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 13
Section header string table index: 12
Section Headers:
[Nr] Name Type Address Offset
Size EntSize Flags Link Info Align
[ 0] NULL 




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1215
1215

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








