
这个系列专注于使用C++和OpenGL在windows平台上开发2D游戏,项目目标是在系列结束后能开发出一个类似俄罗斯方块的游戏。本系列分为3篇文章:
第一部分:涉及win32消息循环,窗口创建和OpenGL的搭建,并且你将会学习如何绘制一些简单的图形。
第二部分:涉及资源处理和简单动画的显示
第三部分:将前面的内容包含进来,并且讨论游戏逻辑。
项目设置
作者做了两项设置:
1)LinkeràInput中,在” Addition Dependencies”中加入”opengl32.lib”,
2)禁掉UNICODE,“c/c++”à” Preprocessor”,在Preprocessor Definitions中将"Inherit from parent or project defaults"不选中。
消息循环
Windows系统为每个应用程序创建一个消息队列,当指定应用程序的窗口上发生一个事件时,系统会把消息推入到这个队列中。你的应用程序应当检索并处理这些消息。这就是所谓的“消息循环“,是win32应用程序的核心。
一个典型的消息循环如下:
 MSGMessage;
MSGMessage; Message.message
=
(
~
WM_QUIT);
Message.message
=
(
~
WM_QUIT); //
LoopuntilaWM_QUITmessageisreceived
//
LoopuntilaWM_QUITmessageisreceived
 while
(Message.message
!=
WM_QUIT)
while
(Message.message
!=
WM_QUIT)

 {
{ if(PeekMessage(&Message,NULL,0,0,PM_REMOVE))
if(PeekMessage(&Message,NULL,0,0,PM_REMOVE))

 {
{ //Ifamessagewaswaitinginthemessagequeue,processit
//Ifamessagewaswaitinginthemessagequeue,processit TranslateMessage(&Message);
TranslateMessage(&Message); DispatchMessage(&Message);
DispatchMessage(&Message); }
} else
else

 {//空闲时
{//空闲时 //Doprocessingstuffhere
//Doprocessingstuffhere
 }
} }
}

TranslateMessage函数的目的是为了将虚键消息(WM_KEYDOWN和WM_KEYUP)为字符消息(WM_CHAR).最后DispatchMessage会将消息定向到正确的窗口处理程序。
 //Theapplicationclass,whichsimplywrapsthemessagequeueandprocess
//Theapplicationclass,whichsimplywrapsthemessagequeueandprocess //thecommandline.
//thecommandline. classCApplication
classCApplication

 {
{ public:
public:
 CApplication()
CApplication() {}
{} CApplication(HINSTANCEhInstance);
CApplication(HINSTANCEhInstance); ~CApplication();
~CApplication();
 //Parsesthecommandlinetoseeiftheapplication
//Parsesthecommandlinetoseeiftheapplication //shouldbeinfullscreenmode.
//shouldbeinfullscreenmode. voidParseCmdLine(LPSTRlpCmdLine);
voidParseCmdLine(LPSTRlpCmdLine); //Createsthemainwindowandstartthemessageloop.
//Createsthemainwindowandstartthemessageloop. voidRun();
voidRun(); voidSetHInst(HINSTANCEhInstance);
voidSetHInst(HINSTANCEhInstance);
 private:
private: HINSTANCEm_hInstance;
HINSTANCEm_hInstance; //Specifiesiftheapplicationhastobestartedinfullscreen
//Specifiesiftheapplicationhastobestartedinfullscreen //mode.Thisoptionissuppliedthroughthecommandline
//mode.Thisoptionissuppliedthroughthecommandline //("-fullscreen"option).
//("-fullscreen"option). boolm_bFullScreen;
boolm_bFullScreen; };
};
ParseCmdLine函数功能非常直观:仅仅简单地检查命令行中是否有参数"-fullscreen",如果有,则设置m_bFullScreen为true,表示窗口模式为全屏模式。
 voidCApplication::Run()
voidCApplication::Run()

 {
{ //Createthemainwindowfirst
//Createthemainwindowfirst CMainWindowmainWindow(800,600,m_bFullScreen);
CMainWindowmainWindow(800,600,m_bFullScreen);
 MSGMessage;
MSGMessage; Message.message=~WM_QUIT;
Message.message=~WM_QUIT; DWORDdwNextDeadLine=GetTickCount()+30;
DWORDdwNextDeadLine=GetTickCount()+30; DWORDdwSleep=30;
DWORDdwSleep=30; boolbUpdate=false;
boolbUpdate=false; //LoopuntilaWM_QUITmessageisreceived
//LoopuntilaWM_QUITmessageisreceived while(Message.message!=WM_QUIT)
while(Message.message!=WM_QUIT)

 {
{ //Waituntilamessagecomesinoruntilthetimeoutexpires.The
//Waituntilamessagecomesinoruntilthetimeoutexpires.The //timeoutisrecalculatedsothatthisfunctionwillreturnat
//timeoutisrecalculatedsothatthisfunctionwillreturnat //leastevery30msec.
//leastevery30msec. DWORDdwResult=MsgWaitForMultipleObjectsEx(0,NULL,dwSleep,QS_ALLEVENTS,0);
DWORDdwResult=MsgWaitForMultipleObjectsEx(0,NULL,dwSleep,QS_ALLEVENTS,0); if(dwResult!=WAIT_TIMEOUT)
if(dwResult!=WAIT_TIMEOUT)

 {
{ //Ifthefunctionreturnedwithnotimeout,itmeansthata
//Ifthefunctionreturnedwithnotimeout,itmeansthata //messagehasbeenreceived,soprocessit.
//messagehasbeenreceived,soprocessit. if(PeekMessage(&Message,NULL,0,0,PM_REMOVE))
if(PeekMessage(&Message,NULL,0,0,PM_REMOVE))

 {
{ //Ifamessagewaswaitinginthemessagequeue,processit
//Ifamessagewaswaitinginthemessagequeue,processit TranslateMessage(&Message);
TranslateMessage(&Message); DispatchMessage(&Message);
DispatchMessage(&Message); }
}
 //Ifthecurrenttimeisclose(orpast)tothe
//Ifthecurrenttimeisclose(orpast)tothe //deadline,theapplicationshouldbeprocessed.
//deadline,theapplicationshouldbeprocessed. if(GetTickCount()>=dwNextDeadLine-1)
if(GetTickCount()>=dwNextDeadLine-1) bUpdate=true;
bUpdate=true; }
} else
else //Onatimeout,theapplicationshouldbeprocessed.
//Onatimeout,theapplicationshouldbeprocessed. bUpdate=true;
bUpdate=true;
 //Checkiftheapplicationshouldbeprocessed
//Checkiftheapplicationshouldbeprocessed if(bUpdate)
if(bUpdate)

 {
{ DWORDdwCurrentTime=GetTickCount();
DWORDdwCurrentTime=GetTickCount(); //Updatethemainwindow
//Updatethemainwindow mainWindow.Update(dwCurrentTime);
mainWindow.Update(dwCurrentTime); //Drawthemainwindow
//Drawthemainwindow mainWindow.Draw();
mainWindow.Draw();
 dwNextDeadLine=dwNextDeadLine+30;
dwNextDeadLine=dwNextDeadLine+30; dwSleep=30;
dwSleep=30; }
} else
else dwSleep=dwNextDeadLine-GetCurrentTime();
dwSleep=dwNextDeadLine-GetCurrentTime(); }
} }
}
函数第一行创建主窗口。和常见的消息循环不同,由于在2D游戏中并不需要很快地刷新屏幕,以固定地速率(这里是30毫秒)刷新,对于绘制动画和其他处理已经足够了。
作者在这里使用的技巧就是出于这个目的,他使用了MsgWaitForMultipleObjectsEx函数来等待任何事件的发生,再判断是30毫秒的时限已到,还是有事件要处理,若是后者,则先处理事件,在处理完后,若此时也已经接近30毫秒的时限的话,就重绘界面,若是超时发生了,则说明30毫秒时限已到,需要去刷新界面了。若这两种情况都没有的话,这个函数不会消耗 CPU周期,线程只是被挂起,不参与调度。
主窗口
创建窗口
 CMainWindow::CMainWindow(
int
iWidth,
int
iHeight,
bool
bFullScreen)
CMainWindow::CMainWindow(
int
iWidth,
int
iHeight,
bool
bFullScreen) :m_hWindow(NULL),m_hDeviceContext(NULL),m_hGLContext(NULL),
:m_hWindow(NULL),m_hDeviceContext(NULL),m_hGLContext(NULL), m_bFullScreen(bFullScreen)
m_bFullScreen(bFullScreen)

 {
{ RegisterWindowClass();
RegisterWindowClass();
 RECTWindowRect;
RECTWindowRect; WindowRect.top=WindowRect.left=0;
WindowRect.top=WindowRect.left=0; WindowRect.right=iWidth;
WindowRect.right=iWidth; WindowRect.bottom=iHeight;
WindowRect.bottom=iHeight;
 //WindowExtendedStyle
//WindowExtendedStyle DWORDdwExStyle=0;
DWORDdwExStyle=0; //WindowsStyle
//WindowsStyle DWORDdwStyle=0;
DWORDdwStyle=0;
 if(m_bFullScreen)
if(m_bFullScreen)

 {
{ DEVMODEdmScreenSettings;
DEVMODEdmScreenSettings; memset(&dmScreenSettings,0,sizeof(dmScreenSettings));
memset(&dmScreenSettings,0,sizeof(dmScreenSettings)); dmScreenSettings.dmSize=sizeof(dmScreenSettings);
dmScreenSettings.dmSize=sizeof(dmScreenSettings); dmScreenSettings.dmPelsWidth=iWidth;
dmScreenSettings.dmPelsWidth=iWidth; dmScreenSettings.dmPelsHeight=iHeight;
dmScreenSettings.dmPelsHeight=iHeight; dmScreenSettings.dmBitsPerPel=32;
dmScreenSettings.dmBitsPerPel=32; dmScreenSettings.dmFields=DM_PELSWIDTH|DM_PELSHEIGHT|DM_BITSPERPEL;
dmScreenSettings.dmFields=DM_PELSWIDTH|DM_PELSHEIGHT|DM_BITSPERPEL;
 //Changethedisplaysettingstofullscreen.Onerror,throw
//Changethedisplaysettingstofullscreen.Onerror,throw //anexception.
//anexception. if(ChangeDisplaySettings(&dmScreenSettings,CDS_FULLSCREEN)
if(ChangeDisplaySettings(&dmScreenSettings,CDS_FULLSCREEN) !=DISP_CHANGE_SUCCESSFUL)
!=DISP_CHANGE_SUCCESSFUL)

 {
{ throwCException("Unabletoswithtofullscreenmode");
throwCException("Unabletoswithtofullscreenmode"); }
}
 dwExStyle=WS_EX_APPWINDOW;
dwExStyle=WS_EX_APPWINDOW; dwStyle=WS_POPUP;
dwStyle=WS_POPUP; //Infullscreenmode,wehidethecursor.
//Infullscreenmode,wehidethecursor. ShowCursor(FALSE);
ShowCursor(FALSE); }
} else
else

 {
{ dwExStyle=WS_EX_APPWINDOW|WS_EX_WINDOWEDGE;
dwExStyle=WS_EX_APPWINDOW|WS_EX_WINDOWEDGE; dwStyle=WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW;
dwStyle=WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW; }
}
 //Adjustthewindowtothetruerequestedsize
//Adjustthewindowtothetruerequestedsize AdjustWindowRectEx(&WindowRect,dwStyle,FALSE,dwExStyle);
AdjustWindowRectEx(&WindowRect,dwStyle,FALSE,dwExStyle); //Nowcreatethemainwindow
//Nowcreatethemainwindow m_hWindow=CreateWindowEx(dwExStyle,TEXT(WINDOW_CLASSNAME),
m_hWindow=CreateWindowEx(dwExStyle,TEXT(WINDOW_CLASSNAME), TEXT("Tutorial1"),
TEXT("Tutorial1"), WS_CLIPSIBLINGS|WS_CLIPCHILDREN|dwStyle,
WS_CLIPSIBLINGS|WS_CLIPCHILDREN|dwStyle, 0,0,WindowRect.right-WindowRect.left,
0,0,WindowRect.right-WindowRect.left, WindowRect.bottom-WindowRect.top,
WindowRect.bottom-WindowRect.top, NULL,NULL,
NULL,NULL, GetModuleHandle(NULL),
GetModuleHandle(NULL), this);
this); if(m_hWindow==NULL)
if(m_hWindow==NULL) throwCException("Cannotcreatethemainwindow");
throwCException("Cannotcreatethemainwindow");
 CreateContext();
CreateContext(); InitGL();
InitGL(); ShowWindow(m_hWindow,SW_SHOW);
ShowWindow(m_hWindow,SW_SHOW); //CallOnSizemanuallybecauseinfullscreenmodeitwillbe
//CallOnSizemanuallybecauseinfullscreenmodeitwillbe //calledonlywhenthewindowiscreated(whichistooearly
//calledonlywhenthewindowiscreated(whichistooearly //becauseOpenGLisnotinitializedyet).
//becauseOpenGLisnotinitializedyet). OnSize(iWidth,iHeight);
OnSize(iWidth,iHeight); }
}

在构造函数中,检查完是否需要进入全屏模式后,通过调用ChangeDisplaySettings来切换到全屏模式,然后调用AdjustWindowRectEx来调整矩形的大小,但这个函数在全屏模式下没什么作用,最后CreateContext和InitGL对OpenGL进行初始化。
 LRESULTCMainWindow::OnEvent(HWNDHandle,UINTMessage,WPARAMwParam,LPARAMlParam)
LRESULTCMainWindow::OnEvent(HWNDHandle,UINTMessage,WPARAMwParam,LPARAMlParam)

 {
{ if(Message==WM_CREATE)
if(Message==WM_CREATE)

 {
{ //Getthecreationparameters.
//Getthecreationparameters. CREATESTRUCT*pCreateStruct=reinterpret_cast<CREATESTRUCT*>(lParam);
CREATESTRUCT*pCreateStruct=reinterpret_cast<CREATESTRUCT*>(lParam);
 //Setasthe"userdata"parameterofthewindow
//Setasthe"userdata"parameterofthewindow SetWindowLongPtr(Handle,GWLP_USERDATA,
SetWindowLongPtr(Handle,GWLP_USERDATA, reinterpret_cast<long>(pCreateStruct->lpCreateParams));
reinterpret_cast<long>(pCreateStruct->lpCreateParams)); }
}
 //GettheCMainWindowinstancecorrespondingtothewindowhandle
//GettheCMainWindowinstancecorrespondingtothewindowhandle CMainWindow*pWindow=reinterpret_cast<CMainWindow*>
CMainWindow*pWindow=reinterpret_cast<CMainWindow*> (GetWindowLongPtr(Handle,GWLP_USERDATA));
(GetWindowLongPtr(Handle,GWLP_USERDATA)); if(pWindow)
if(pWindow) pWindow->ProcessEvent(Message,wParam,lParam);
pWindow->ProcessEvent(Message,wParam,lParam);
 returnDefWindowProc(Handle,Message,wParam,lParam);
returnDefWindowProc(Handle,Message,wParam,lParam); }
}

由于OnEvent函数是静态的,因此就没法访问非静态成员,为了解决这个问题,在调用CreateWindowEx创建窗口时最后一个参数传的是this指针。传给窗口处理过程的第一个消息是WM_CREATE,当接收到这个消息时,wParam参数中包含一个CREATESTRUCT指针,它里面包含了额外的数据,在这里是指向CMainWindow的指针。但遗憾的是,不是每个消息都有这个结构,所以要保存起来供后面使用。因此调用SetWindowLongPtr,它的目的是为一个特定的窗口保存一些用户数据(GWLP_USERDATA)。在这里,作者保存了到类实例的指针。当接收到其他消息时,我们只是简单地通过GetWindowLongPtr来取回这个指针,然后访问非静态函数ProcessEvent,而这个函数负责具体的消息处理。
 void
CMainWindow::ProcessEvent(UINTMessage,WPARAMwParam,LPARAMlParam)
void
CMainWindow::ProcessEvent(UINTMessage,WPARAMwParam,LPARAMlParam)

 {
{ switch(Message)
switch(Message)

 {
{ //Quitwhenweclosethemainwindow
//Quitwhenweclosethemainwindow caseWM_CLOSE:
caseWM_CLOSE: PostQuitMessage(0);
PostQuitMessage(0); break;
break; caseWM_SIZE:
caseWM_SIZE: OnSize(LOWORD(lParam),HIWORD(lParam));
OnSize(LOWORD(lParam),HIWORD(lParam)); break;
break; caseWM_KEYDOWN:
caseWM_KEYDOWN: break;
break; caseWM_KEYUP:
caseWM_KEYUP: break;
break; }
} }
}

异常处理
 class
CException:
public
std::exception
class
CException:
public
std::exception

 {
{ public:
public:
 constchar*what()const
constchar*what()const {returnm_strMessage.c_str();}
{returnm_strMessage.c_str();}

 CException(conststd::string&strMessage=""):m_strMessage(strMessage)
CException(conststd::string&strMessage=""):m_strMessage(strMessage) {}
{}
 virtual~CException()
virtual~CException() {}
{}
 std::stringm_strMessage;
std::stringm_strMessage; }
;
}
;
使用的实例:
 CApplicationtheApp;
CApplicationtheApp;
 int
WINAPIWinMain(HINSTANCEInstance,HINSTANCEhPrevInstance,LPSTRlpCmdLine,INT)
int
WINAPIWinMain(HINSTANCEInstance,HINSTANCEhPrevInstance,LPSTRlpCmdLine,INT)

 {
{ try
try

 {
{ //Createtheapplicationclass,
//Createtheapplicationclass, //parsethecommandlineand
//parsethecommandlineand //starttheapp.
//starttheapp. theApp.SetHInst(Instance);
theApp.SetHInst(Instance); theApp.ParseCmdLine(lpCmdLine);
theApp.ParseCmdLine(lpCmdLine); theApp.Run();
theApp.Run(); }
} catch(CException&e)
catch(CException&e)

 {
{ MessageBox(NULL,e.what(),"Error",MB_OK|MB_ICONEXCLAMATION);
MessageBox(NULL,e.what(),"Error",MB_OK|MB_ICONEXCLAMATION); }
}
 return0;
return0; }
}

初始化OpenGL
CreateContext用来初始化绘制上下文,使得OpenGL基本元素可以在窗口上绘制:
 void
CMainWindow::CreateContext()
void
CMainWindow::CreateContext()

 {
{ //Describesthepixelformatofthedrawingsurface
//Describesthepixelformatofthedrawingsurface PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTORpfd;
PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTORpfd; memset(&pfd,0,sizeof(PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTOR));
memset(&pfd,0,sizeof(PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTOR)); pfd.nSize=sizeof(PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTOR);
pfd.nSize=sizeof(PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTOR); pfd.nVersion=1;//VersionNumber
pfd.nVersion=1;//VersionNumber pfd.dwFlags=PFD_DRAW_TO_WINDOW|//Drawstoawindow
pfd.dwFlags=PFD_DRAW_TO_WINDOW|//Drawstoawindow PFD_SUPPORT_OPENGL|//TheformatmustsupportOpenGL
PFD_SUPPORT_OPENGL|//TheformatmustsupportOpenGL PFD_DOUBLEBUFFER;//Supportfordoublebuffering
PFD_DOUBLEBUFFER;//Supportfordoublebuffering pfd.iPixelType=PFD_TYPE_RGBA;//UsesanRGBApixelformat
pfd.iPixelType=PFD_TYPE_RGBA;//UsesanRGBApixelformat pfd.cColorBits=32;//32bitscolors
pfd.cColorBits=32;//32bitscolors
 if(!(m_hDeviceContext=GetDC(m_hWindow)))
if(!(m_hDeviceContext=GetDC(m_hWindow))) throwCException("Unabletocreaterenderingcontext");
throwCException("Unabletocreaterenderingcontext");
 intPixelFormat;
intPixelFormat; //DoWindowsfindamatchingpixelformat?
//DoWindowsfindamatchingpixelformat? if(!(PixelFormat=ChoosePixelFormat(m_hDeviceContext,&pfd)))
if(!(PixelFormat=ChoosePixelFormat(m_hDeviceContext,&pfd))) throwCException("Unabletocreaterenderingcontext");
throwCException("Unabletocreaterenderingcontext"); //Setthenewpixelformat
//Setthenewpixelformat if(!SetPixelFormat(m_hDeviceContext,PixelFormat,&pfd))
if(!SetPixelFormat(m_hDeviceContext,PixelFormat,&pfd)) throwCException("Unabletocreaterenderingcontext");
throwCException("Unabletocreaterenderingcontext"); //CreatetheOpenGLrenderingcontext
//CreatetheOpenGLrenderingcontext if(!(m_hGLContext=wglCreateContext(m_hDeviceContext)))
if(!(m_hGLContext=wglCreateContext(m_hDeviceContext))) throwCException("Unabletocreaterenderingcontext");
throwCException("Unabletocreaterenderingcontext"); //Activatetherenderingcontext
//Activatetherenderingcontext if(!wglMakeCurrent(m_hDeviceContext,m_hGLContext))
if(!wglMakeCurrent(m_hDeviceContext,m_hGLContext)) throwCException("Unabletocreaterenderingcontext");
throwCException("Unabletocreaterenderingcontext"); }
}

函数的第一部分填充PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTOR结构体:缓冲区用来绘制到窗口上,支持OpenGL,使用双缓存(为了避免闪烁)。然后调用ChoosePixelFormat来检查像素格式是否支持,这个函数返回一个像素格式索引(若没有找到匹配的,则返回0)。一旦存在这样的像素格式索引,则通过SetPixelFormat来设置新像素格式。然后调用wglCreateContext创建OpenGL绘制上下文,最后,调用wglMakeCurrent,这指明线程接下来的OpenGL调用会绘制在这个设备上下文上。
InitGL函数很简单:
 void
CMainWindow::InitGL()
void
CMainWindow::InitGL()

 {
{ //Enable2Dtexturing
//Enable2Dtexturing glEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
glEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D); //Chooseasmoothshadingmodel
//Chooseasmoothshadingmodel glShadeModel(GL_SMOOTH);
glShadeModel(GL_SMOOTH); //Settheclearcolortoblack
//Settheclearcolortoblack glClearColor(0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0);
glClearColor(0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0); }
}

再看OnSize函数
 void
CMainWindow::OnSize(GLsizeiwidth,GLsizeiheight)
void
CMainWindow::OnSize(GLsizeiwidth,GLsizeiheight)

 {
{ //SetsthesizeoftheOpenGLviewport
//SetsthesizeoftheOpenGLviewport glViewport(0,0,width,height);
glViewport(0,0,width,height);
 //Selecttheprojectionstackandapply
//Selecttheprojectionstackandapply //anorthographicprojection
//anorthographicprojection glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity();
glLoadIdentity(); glOrtho(0.0,width,height,0.0,-1.0,1.0);
glOrtho(0.0,width,height,0.0,-1.0,1.0); glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); }
}

正交投影
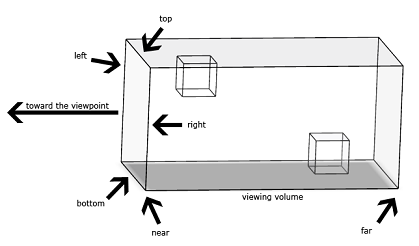
透视投影

绘制简单图形
 void
CMainWindow::Draw()
void
CMainWindow::Draw()

 {
{ //Clearthebuffer
//Clearthebuffer glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
 //Heregoesthedrawingcode
//Heregoesthedrawingcode glBegin(GL_QUADS);
glBegin(GL_QUADS); glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0);glVertex3i(50,200,0);
glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0);glVertex3i(50,200,0); glColor3f(0.0,1.0,0.0);glVertex3i(250,200,0);
glColor3f(0.0,1.0,0.0);glVertex3i(250,200,0); glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0);glVertex3i(250,350,0);
glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0);glVertex3i(250,350,0); glColor3f(1.0,1.0,1.0);glVertex3i(50,350,0);
glColor3f(1.0,1.0,1.0);glVertex3i(50,350,0); glEnd();
glEnd();
 glBegin(GL_TRIANGLES);
glBegin(GL_TRIANGLES); glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0);glVertex3i(400,350,0);
glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0);glVertex3i(400,350,0); glColor3f(0.0,1.0,0.0);glVertex3i(500,200,0);
glColor3f(0.0,1.0,0.0);glVertex3i(500,200,0); glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0);glVertex3i(600,350,0);
glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0);glVertex3i(600,350,0); glEnd();
glEnd();
 SwapBuffers(m_hDeviceContext);
SwapBuffers(m_hDeviceContext); }
}





 本文介绍了一个使用C++和OpenGL在Win32平台上开发2D游戏的教程系列,重点讲解了消息循环、窗口创建、OpenGL环境搭建等内容,并演示了如何绘制简单图形。
本文介绍了一个使用C++和OpenGL在Win32平台上开发2D游戏的教程系列,重点讲解了消息循环、窗口创建、OpenGL环境搭建等内容,并演示了如何绘制简单图形。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








