光线跟踪的目的是为了模拟自然现象:你能见到各种颜色是因为太阳发射出来的光线,经过各种自然物体的反射或折射后,最终进入你的眼睛。若我们暂时不去计较其他因素,所有的这些光线都应该是直线。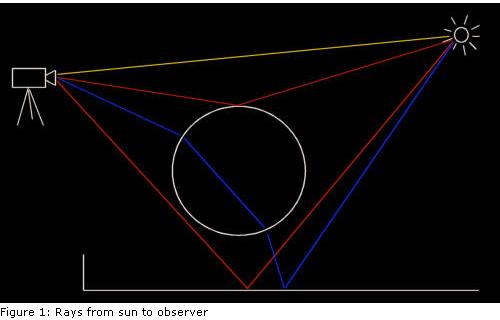
<?xml:namespace prefix = o ns = "urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:office" />
如图所示,黄色的光直接从太阳射入照相机中;红色的光线在跟场景发生发射后到达照相机,而蓝色的光线被玻璃球折射后命中照相机。图中没有画出的是那些无法到达观察者的光线,这些光线也是我们不从光源往照相机进行跟踪的原因,而是采用想反的路径。上图标识的是一种理想情形,因为光线的方向没有影响。
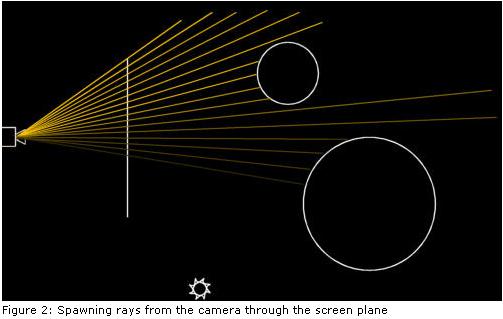
从上面我们得到一个启示:与其等待光源发射一条光线穿过一个目前颜色还是黑色的像素,不如我们自己从照相机发射光线去穿过平面的每个像素,去观察这些光线能击中几何体上的哪些像素。
 //-----------------------------------------------------------
//----------------------------------------------------------- //Rayclassdefinition
//Rayclassdefinition //-----------------------------------------------------------
//----------------------------------------------------------- classRay
classRay

 {
{ public:
public:
 Ray():m_Origin(vector3(0,0,0)),m_Direction(vector3(0,0,0))
Ray():m_Origin(vector3(0,0,0)),m_Direction(vector3(0,0,0)) {};
{}; Ray(vector3&a_Origin,vector3&a_Dir);
Ray(vector3&a_Origin,vector3&a_Dir);
 voidSetOrigin(vector3&a_Origin)
voidSetOrigin(vector3&a_Origin) {m_Origin=a_Origin;}
{m_Origin=a_Origin;}
 voidSetDirection(vector3&a_Direction)
voidSetDirection(vector3&a_Direction) {m_Direction=a_Direction;}
{m_Direction=a_Direction;}
 vector3&GetOrigin()
vector3&GetOrigin() {returnm_Origin;}
{returnm_Origin;}
 vector3&GetDirection()
vector3&GetDirection() {returnm_Direction;}
{returnm_Direction;} private:
private: vector3m_Origin;//光线的起点
vector3m_Origin;//光线的起点 vector3m_Direction;//光线的方向
vector3m_Direction;//光线的方向 };
};
一条光线有它的起点和方向。当从照相机发射光线时,起点一般是一个固定点,并且光线会穿过屏幕表面的像素。
 //-----------------------------------------------------------
//----------------------------------------------------------- //Firesraysinthesceneonescanlineatatime,fromleft
//Firesraysinthesceneonescanlineatatime,fromleft //toright
//toright //-----------------------------------------------------------
//----------------------------------------------------------- boolEngine::Render()
boolEngine::Render()

 {
{ //renderscene
//renderscene vector3o(0,0,-5);
vector3o(0,0,-5); //initializetimer
//initializetimer intmsecs=GetTickCount();
intmsecs=GetTickCount(); //resetlastfoundprimitivepointer
//resetlastfoundprimitivepointer Primitive*lastprim=0;
Primitive*lastprim=0; //renderremaininglines
//renderremaininglines for(inty=m_CurrLine;y<(m_Height-20);y++)
for(inty=m_CurrLine;y<(m_Height-20);y++)

 {//逐条扫描线处理
{//逐条扫描线处理 m_SX=m_WX1;
m_SX=m_WX1; //renderpixelsforcurrentline
//renderpixelsforcurrentline for(intx=0;x<m_Width;x++)
for(intx=0;x<m_Width;x++)

 {//对当前扫描线上的所有像素点处理
{//对当前扫描线上的所有像素点处理 //fireprimaryray
//fireprimaryray Coloracc(0,0,0);
Coloracc(0,0,0); vector3dir=vector3(m_SX,m_SY,0)-o;//发射出的光线的方向
vector3dir=vector3(m_SX,m_SY,0)-o;//发射出的光线的方向 NORMALIZE(dir);
NORMALIZE(dir); Rayr(o,dir);
Rayr(o,dir); floatdist;
floatdist; Primitive*prim=Raytrace(r,acc,1,1.0f,dist);
Primitive*prim=Raytrace(r,acc,1,1.0f,dist); intred=(int)(acc.r*256);
intred=(int)(acc.r*256); intgreen=(int)(acc.g*256);
intgreen=(int)(acc.g*256); intblue=(int)(acc.b*256);
intblue=(int)(acc.b*256); if(red>255)red=255;
if(red>255)red=255; if(green>255)green=255;
if(green>255)green=255; if(blue>255)blue=255;
if(blue>255)blue=255; m_Dest[m_PPos++]=(red<<16)+(green<<8)+blue;
m_Dest[m_PPos++]=(red<<16)+(green<<8)+blue; m_SX+=m_DX;
m_SX+=m_DX; }
} m_SY+=m_DY;
m_SY+=m_DY; //seeifwe'vebeenworkingtolongalready
//seeifwe'vebeenworkingtolongalready if((GetTickCount()-msecs)>100)
if((GetTickCount()-msecs)>100)

 {
{ //returncontroltowindowssothescreengetsupdated
//returncontroltowindowssothescreengetsupdated m_CurrLine=y+1;
m_CurrLine=y+1; returnfalse;
returnfalse; }
} }
} //alldone
//alldone returntrue;
returntrue; }
}
注意这段代码:
 vector3o(0,0,-5);
vector3o(0,0,-5); vector3dir=vector3(m_SX,m_SY,0)-o;
vector3dir=vector3(m_SX,m_SY,0)-o; NORMALIZE(dir);
NORMALIZE(dir); Rayr(o,dir);
Rayr(o,dir);
一条光线起始点在’o’,方向朝向屏幕平面上的一个位置,并且方向进行了单位化处理,从而建立了这条光线。
屏幕平面指的是一个漂浮在虚拟世界的一个矩形,用来表示屏幕。代码中它以原点为中心,宽为8个单位,高为6个单位,这对于800*600的分辨率是合适的。你可以对这个平面做各种处理:若你将它移开照相机,则光线的宽度就变窄,从而物体会在屏幕上变大。若你旋转这个平面(且照相机以它为中心),你会得到虚拟世界的另一种视图。
接下来,我们需要一个场景来进行光线跟踪。一个场景中包含各种元素:如球体和平面等几何物体。你也可以使用三角面片,并且用这些三角面片来构造其他各种元素。
元素Sphere和PlanePrim是从Primitive继承下来的,每个元素都有一个Material,并且都实现了方法Intersect和GetNormal.
 //-----------------------------------------------------------
//----------------------------------------------------------- //Sceneclassdefinition
//Sceneclassdefinition //-----------------------------------------------------------
//-----------------------------------------------------------
 classScene
classScene

 {
{ public:
public:
 Scene():m_Primitives(0),m_Primitive(0)
Scene():m_Primitives(0),m_Primitive(0) {};
{}; ~Scene();
~Scene(); voidInitScene();
voidInitScene();
 intGetNrPrimitives()
intGetNrPrimitives() {returnm_Primitives;}
{returnm_Primitives;}
 Primitive*GetPrimitive(inta_Idx)
Primitive*GetPrimitive(inta_Idx) {returnm_Primitive[a_Idx];}
{returnm_Primitive[a_Idx];} private:
private: intm_Primitives;
intm_Primitives; Primitive**m_Primitive;//保存的是指向各种元素的指针
Primitive**m_Primitive;//保存的是指向各种元素的指针 };
};
 voidScene::InitScene()
voidScene::InitScene()

 {
{ m_Primitive=newPrimitive*[100];//最多100个立体元素
m_Primitive=newPrimitive*[100];//最多100个立体元素 //groundplane
//groundplane m_Primitive[0]=newPlanePrim(vector3(0,1,0),4.4f);
m_Primitive[0]=newPlanePrim(vector3(0,1,0),4.4f); m_Primitive[0]->SetName("plane");
m_Primitive[0]->SetName("plane"); m_Primitive[0]->GetMaterial()->SetReflection(0);
m_Primitive[0]->GetMaterial()->SetReflection(0); m_Primitive[0]->GetMaterial()->SetDiffuse(1.0f);
m_Primitive[0]->GetMaterial()->SetDiffuse(1.0f); m_Primitive[0]->GetMaterial()->SetColor(Color(0.4f,0.3f,0.3f));
m_Primitive[0]->GetMaterial()->SetColor(Color(0.4f,0.3f,0.3f)); //bigsphere
//bigsphere m_Primitive[1]=newSphere(vector3(1,-0.8f,3),2.5f);
m_Primitive[1]=newSphere(vector3(1,-0.8f,3),2.5f); m_Primitive[1]->SetName("bigsphere");
m_Primitive[1]->SetName("bigsphere"); m_Primitive[1]->GetMaterial()->SetReflection(0.6f);
m_Primitive[1]->GetMaterial()->SetReflection(0.6f); m_Primitive[1]->GetMaterial()->SetColor(Color(0.7f,0.7f,0.7f));
m_Primitive[1]->GetMaterial()->SetColor(Color(0.7f,0.7f,0.7f)); //smallsphere
//smallsphere m_Primitive[2]=newSphere(vector3(-5.5f,-0.5,7),2);
m_Primitive[2]=newSphere(vector3(-5.5f,-0.5,7),2); m_Primitive[2]->SetName("smallsphere");
m_Primitive[2]->SetName("smallsphere"); m_Primitive[2]->GetMaterial()->SetReflection(1.0f);
m_Primitive[2]->GetMaterial()->SetReflection(1.0f); m_Primitive[2]->GetMaterial()->SetDiffuse(0.1f);
m_Primitive[2]->GetMaterial()->SetDiffuse(0.1f); m_Primitive[2]->GetMaterial()->SetColor(Color(0.7f,0.7f,1.0f));
m_Primitive[2]->GetMaterial()->SetColor(Color(0.7f,0.7f,1.0f)); //lightsource1
//lightsource1 m_Primitive[3]=newSphere(vector3(0,5,5),0.1f);
m_Primitive[3]=newSphere(vector3(0,5,5),0.1f); m_Primitive[3]->Light(true);
m_Primitive[3]->Light(true); m_Primitive[3]->GetMaterial()->SetColor(Color(0.6f,0.6f,0.6f));
m_Primitive[3]->GetMaterial()->SetColor(Color(0.6f,0.6f,0.6f)); //lightsource2
//lightsource2 m_Primitive[4]=newSphere(vector3(2,5,1),0.1f);
m_Primitive[4]=newSphere(vector3(2,5,1),0.1f); m_Primitive[4]->Light(true);
m_Primitive[4]->Light(true); m_Primitive[4]->GetMaterial()->SetColor(Color(0.7f,0.7f,0.9f));
m_Primitive[4]->GetMaterial()->SetColor(Color(0.7f,0.7f,0.9f)); //setnumberofprimitives
//setnumberofprimitives m_Primitives=5;
m_Primitives=5; }
}
这个方法中我们加入了一个地表平面,两个球体以及2个光源。
现在就开始跟踪光线了,首先来看下处理的伪代码:
 Foreachpixel
Foreachpixel

 {
{ Constructrayfromcamerathroughpixel
Constructrayfromcamerathroughpixel Findfirstprimitivehitbyray
Findfirstprimitivehitbyray Determinecoloratintersectionpoint
Determinecoloratintersectionpoint Drawcolor
Drawcolor }
}
为了确定光线命中的最近的一个元素,我们必须对其所有可能的交点做测试。

 //-----------------------------------------------------------
//----------------------------------------------------------- //Naiveraytracing:Intersectstheraywitheveryprimitive
//Naiveraytracing:Intersectstheraywitheveryprimitive //inthescenetodeterminetheclosestintersection
//inthescenetodeterminetheclosestintersection //-----------------------------------------------------------
//----------------------------------------------------------- Primitive*Engine::Raytrace(Ray&a_Ray,Color&a_Acc,inta_Depth,floata_RIndex,float&a_Dist)
Primitive*Engine::Raytrace(Ray&a_Ray,Color&a_Acc,inta_Depth,floata_RIndex,float&a_Dist)

 {
{ if(a_Depth>TRACEDEPTH)return0;
if(a_Depth>TRACEDEPTH)return0; //traceprimaryray
//traceprimaryray a_Dist=1000000.0f;
a_Dist=1000000.0f; vector3pi;
vector3pi; Primitive*prim=0;
Primitive*prim=0; intresult;
intresult; //findthenearestintersection
//findthenearestintersection for(ints=0;s<m_Scene->GetNrPrimitives();s++)
for(ints=0;s<m_Scene->GetNrPrimitives();s++)

 {
{ Primitive*pr=m_Scene->GetPrimitive(s);
Primitive*pr=m_Scene->GetPrimitive(s); intres;
intres; if(res=pr->Intersect(a_Ray,a_Dist))
if(res=pr->Intersect(a_Ray,a_Dist))

 {
{ prim=pr;
prim=pr; result=res;//0=miss,1=hit,-1=hitfrominsideprimitive
result=res;//0=miss,1=hit,-1=hitfrominsideprimitive }
} }
} //nohit,terminateray
//nohit,terminateray if(!prim)return0;
if(!prim)return0; //handleintersection
//handleintersection if(prim->IsLight())
if(prim->IsLight())

 {
{ //wehitalight,stoptracing
//wehitalight,stoptracing a_Acc=Color(1,1,1);
a_Acc=Color(1,1,1); }
} else
else

 {
{ //determinecoloratpointofintersection
//determinecoloratpointofintersection pi=a_Ray.GetOrigin()+a_Ray.GetDirection()*a_Dist;
pi=a_Ray.GetOrigin()+a_Ray.GetDirection()*a_Dist; //tracelights
//tracelights for(intl=0;l<m_Scene->GetNrPrimitives();l++)
for(intl=0;l<m_Scene->GetNrPrimitives();l++)

 {
{ Primitive*p=m_Scene->GetPrimitive(l);
Primitive*p=m_Scene->GetPrimitive(l); if(p->IsLight())
if(p->IsLight())

 {
{ Primitive*light=p;
Primitive*light=p; //calculatediffuseshading
//calculatediffuseshading vector3L=((Sphere*)light)->GetCentre()-pi;
vector3L=((Sphere*)light)->GetCentre()-pi; NORMALIZE(L);
NORMALIZE(L); vector3N=prim->GetNormal(pi);
vector3N=prim->GetNormal(pi); if(prim->GetMaterial()->GetDiffuse()>0)
if(prim->GetMaterial()->GetDiffuse()>0)

 {
{ floatdot=DOT(N,L);
floatdot=DOT(N,L); if(dot>0)
if(dot>0)

 {
{ floatdiff=dot*prim->GetMaterial()->GetDiffuse();
floatdiff=dot*prim->GetMaterial()->GetDiffuse(); //adddiffusecomponenttoraycolor
//adddiffusecomponenttoraycolor a_Acc+=diff*prim->GetMaterial()->GetColor()*light->GetMaterial()->GetColor();
a_Acc+=diff*prim->GetMaterial()->GetColor()*light->GetMaterial()->GetColor(); }
} }
} }
} }
} }
} //returnpointertoprimitivehitbyprimaryray
//returnpointertoprimitivehitbyprimaryray returnprim;
returnprim; }
}
其中这段代码:

 //findthenearestintersection
//findthenearestintersection for(ints=0;s<m_Scene->GetNrPrimitives();s++)
for(ints=0;s<m_Scene->GetNrPrimitives();s++)

 {//对所有的元素做测试
{//对所有的元素做测试 Primitive*pr=m_Scene->GetPrimitive(s);
Primitive*pr=m_Scene->GetPrimitive(s); intres;
intres; if(res=pr->Intersect(a_Ray,a_Dist))
if(res=pr->Intersect(a_Ray,a_Dist))

 {//找到第一个命中的元素
{//找到第一个命中的元素 prim=pr;
prim=pr; result=res;//0=miss,1=hit,-1=hitfrominsideprimitive
result=res;//0=miss,1=hit,-1=hitfrominsideprimitive }
} }
}
对场景中的所以元素做循环处理,为每个元素调用其Intersect方法,这个方法以一条光线为参数,返回一个整数表明是命中还是没有命中,以及相交的距离是在体内还是体外。除此以外还会记录下最近相交的记录。
一旦我们知道光线命中的是那个元素,那么就可以来计算光线的颜色了。若只是简单地使用元素的材质颜色就太简单了,并且结果颜色也很枯燥。因此,我们使用两个点光源来计算散射阴影。
 //determinecoloratpointofintersection
//determinecoloratpointofintersection pi=a_Ray.GetOrigin()+a_Ray.GetDirection()*a_Dist;
pi=a_Ray.GetOrigin()+a_Ray.GetDirection()*a_Dist; //tracelights
//tracelights for(intl=0;l<m_Scene->GetNrPrimitives();l++)
for(intl=0;l<m_Scene->GetNrPrimitives();l++)

 {
{ Primitive*p=m_Scene->GetPrimitive(l);
Primitive*p=m_Scene->GetPrimitive(l); if(p->IsLight())
if(p->IsLight())

 {
{ Primitive*light=p;
Primitive*light=p; //calculatediffuseshading
//calculatediffuseshading vector3L=((Sphere*)light)->GetCentre()-pi;
vector3L=((Sphere*)light)->GetCentre()-pi; NORMALIZE(L);
NORMALIZE(L); vector3N=prim->GetNormal(pi);
vector3N=prim->GetNormal(pi); if(prim->GetMaterial()->GetDiffuse()>0)
if(prim->GetMaterial()->GetDiffuse()>0)

 {
{ floatdot=DOT(N,L);//点积
floatdot=DOT(N,L);//点积 if(dot>0)
if(dot>0)

 {
{ floatdiff=dot*prim->GetMaterial()->GetDiffuse();
floatdiff=dot*prim->GetMaterial()->GetDiffuse(); //adddiffusecomponenttoraycolor
//adddiffusecomponenttoraycolor a_Acc+=diff*prim->GetMaterial()->GetColor()*light->GetMaterial()->GetColor();
a_Acc+=diff*prim->GetMaterial()->GetColor()*light->GetMaterial()->GetColor(); }
} }
} }
}
这段代码计算从相交点(pi)到光源(L)的向量,并用这个向量和相交点的单位向量的叉积来计算出光源的亮度。这个计算出的亮度是元素朝向光源的那一点被光源照亮,而其他点就是阴暗的了。叉积大于0为了防止面与光源反向。

好了,这一篇就到这里了,没有反射,没有折射,更没有加入阴影,这些东东在后续的文章中会慢慢加入的,而这只是最简单的一个光线跟踪而已




 本文介绍光线跟踪的基本原理,包括光线的定义、如何从摄像机发射光线并计算光线与场景元素的交点,以及如何通过考虑光源来计算交点处的颜色。
本文介绍光线跟踪的基本原理,包括光线的定义、如何从摄像机发射光线并计算光线与场景元素的交点,以及如何通过考虑光源来计算交点处的颜色。
















 485
485

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








