OCJP题目及解析
每天做一点
1.
11. public static int sum(List list) {
12. int sum = 0;
13. for ( Iterator iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) {
14. int i = ((Integer)iter.next()).intValue();
15. sum += i;
16. }
17. return sum;
18. }
What three changes allow the class to be used with generics and avoid an unchecked warning? (Choose
three.)哪三个改变可以使此类使用泛型,并且没有黄色警告
A. Remove line 14.
B. Replace line 14 with "int i = iter.next();".
C. Replace line 13 with "for (int i : intList) {".
D. Replace line 13 with "for (Iterator iter : intList) {".
E. Replace the method declaration with "sum(List<int> intList)".
F. Replace the method declaration with "sum(List<Integer> intList)".
Answer: A,C,F
知识点:
1)泛型必须使用包装类,而不是基本数据类型,所以选F
2)增强for,使用同样的数据类型i,遍历list中的数据,选C
3)同上,增强for,无需14行的代码
2.
2.A programmer has an algorithm that requires a java.util.List that provides an efficient
implementation of add(0, object), but does NOT need to support quick random access. What supports these requirements.?
需要一个List算法,提供有效的添加,但是不支持快速随机查找
A. java.util.Queue
B. java.util.ArrayList
C. java.util.LinearList
D. java.util.LinkedList
Answer: D
知识点:
A:队列,肯定不行它没有实现list接口。A×
B: ArrayList。有 add方法,支持快速方法有 gen(index)方法 ,底层是用数组实现的。不符合题意:B×
C: C向这个结构,查jdk api根本不存在
D:链表结构,支持add方法。缺点访问速度慢。链表结构,优点:添加删除的速度快。底层是引用实现的 D√
4.
QUESTION 4
Given:
12. import java.util.*;
13. public class Explorer2 {
14. public static void main(String[] args) {
15. TreeSet<Integer> s = new TreeSet<Integer>();
16. TreeSet<Integer> subs = new TreeSet<Integer>();
17. for(int i = 606; i < 613; i++)
18. if(i%2 == 0) s.add(i);
19. subs = (TreeSet)s.subSet(608, true, 611, true);
20. s.add(629);
21. System.out.println(s + " " + subs);
22. }
23. }
What is the result?
A. Compilation fails.
B. An exception is thrown at runtime.
C. [608, 610, 612, 629] [608, 610]
D. [608, 610, 612, 629] [608, 610, 629]
E. [606, 608, 610, 612, 629] [608, 610]
F. [606, 608, 610, 612, 629] [608, 610, 629]
Answer: E
解析:考察 TreeSet的使用, Set集合。无序,但是值不能重复。实现不重复的原因是。执行equals和hashcode方法。subset方法。从608 到611的数字。true包括608和611。填充到子集合中。sub:608,610.
5.
QUESTION 5
Given:
1. public class Score implements Comparable<Score> {
2. private int wins, losses;
3. public Score(int w, int l) { wins = w; losses = l; }
4. public int getWins() { return wins; }
5. public int getLosses() { return losses; }
6. public String toString() {
7. return "<" + wins + "," + losses + ">";
8. }
9. // insert code here
10. }
Which method will complete this class?
A. public int compareTo(Object o){/*more code here*/}
B. public int compareTo(Score other){/*more code here*/}
C. public int compare(Score s1,Score s2){/*more code here*/}
D. public int compare(Object o1,Object o2){/*more code here*/}
Answer: B
解析:可以看一下Comparable原码:泛型跟结构一致。选择B
public interface Comparable<T> {
//里面只有一个compareTo()方法
public int compareTo(T o);
}
6.
QUESTION 6
Given:
11. public class Person {
12. private name;
13. public Person(String name) {
14. this.name = name;
15. }
16. public int hashCode() {
17. return 420;
18. }
19. }
Which statement is true?
A. The time to find the value from HashMap with a Person key depends on the size of the map.
B. Deleting a Person key from a HashMap will delete all map entries for all keys of type Person.
C. Inserting a second Person object into a HashSet will cause the first Person object to be removed as a
duplicate.
D. The time to determine whether a Person object is contained in a HashSet is constant and does NOT
depend on the size of the map.
Answer: A
解析:在hashMap中找到以Person为key的时间取决于map的大小
hashmap不存在重复值。该类重写了hashcode。这个方法永远为真。检验是否重复还有equlas方法。
7.
QUESTION 7
Given:
5. import java.util.*;
6. public class SortOf {
7. public static void main(String[] args) {
8. ArrayList<Integer> a = new ArrayList<Integer>();
9. a.add(1); a.add(5); a.add(3);
11. Collections.sort(a);
12. a.add(2);
13. Collections.reverse(a);
14. System.out.println(a);
15. }
16. }
What is the result?
A. [1, 2, 3, 5]
B. [2, 1, 3, 5]
C. [2, 5, 3, 1]
D. [5, 3, 2, 1]
E. [1, 3, 5, 2]
F. Compilation fails.
G. An exception is thrown at runtime.
Answer: C
使用了工具类Collections.sort排序
reverse反转这个顺序
8.
QUESTION 8
Given
11. public interface Status {
12. /* insert code here */ int MY_VALUE = 10;
13. } Which three are valid on line
12?
(Choose three.)
A. final
B. static
C. native
D. public
E. private
F. abstract
G. protected
Answer: ABD
interface接口
固定写法:public static final ??=??;
9.
QUESTION 9
Given:
5. class Atom {
6. Atom() { System.out.print("atom "); }
7. }
8. class Rock extends Atom {
9. Rock(String type) { System.out.print(type); }
10. }
11. public class Mountain extends Rock {
12. Mountain() {
13. super("granite ");
14. new Rock("granite ");
15. }
16. public static void main(String[] a) { new Mountain(); }
17. }
What is the result?
A. Compilation fails.
B. atom granite
C. granite granite
D. atom granite granite
E. An exception is thrown at runtime.
F. atom granite atom granite
Answer: F
构造子类优先构造父类;
10.
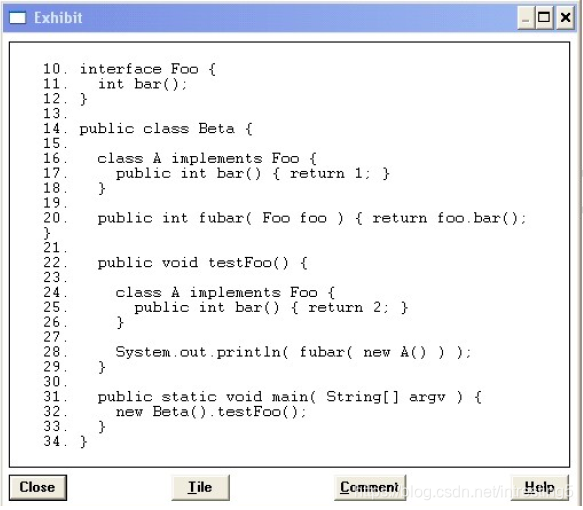
QUESTION 10
Click the Exhibit button. Which three statements are true? (Choose three.)
A. Compilation fails.
B. The code compiles and the output is 2.
C. If lines 16, 17 and 18 were removed, compilation would fail.
D. If lines 24, 25 and 26 were removed, compilation would fail.
E. If lines 16, 17 and 18 were removed, the code would compile and the output would be 2.
F. If lines 24, 25 and 26 were removed, the code would compile and the output would be 1.
Answer: BEF
11.
QUESTION 11
Given:
10. class Line {
11. public class Point { public int x,y;}
12. public Point getPoint() { return new Point(); }
13. }
14. class Triangle {
15. public Triangle() {
16. // insert code here
17. }
18. }
Which code, inserted at line 16, correctly retrieves a local instance of a Point object?
A. Point p = Line.getPoint();
B. Line.Point p = Line.getPoint();
C. Point p = (new Line()).getPoint();
D. Line.Point p = (new Line()).getPoint();
Answer: D
内部类的实例化操作。由于不是静态的A B×。同级内部类。选择D
12.
QUESTION 12
Given:
11. class Alpha {
12. public void foo() { System.out.print("Afoo "); }
13. }
14. public class Beta extends Alpha {
15. public void foo() { System.out.print("Bfoo "); }
16. public static void main(String[] args) {
17. Alpha a = new Beta();
18. Beta b = (Beta)a;
19. a.foo();
20. b.foo();
21. }
22. }
What is the result?
A. Afoo Afoo
B. Afoo Bfoo
C. Bfoo Afoo
D. Bfoo Bfoo
E. Compilation fails.
F. An exception is thrown at runtime.
Answer: D
父类可以调用任一子类,创建的是子类的对象。
多态强制转换, 调用的还是Beta。所以是D项。
13.
13.Click the Exhibit button.
Which statement is true about the classes and interfaces in the exhibit?
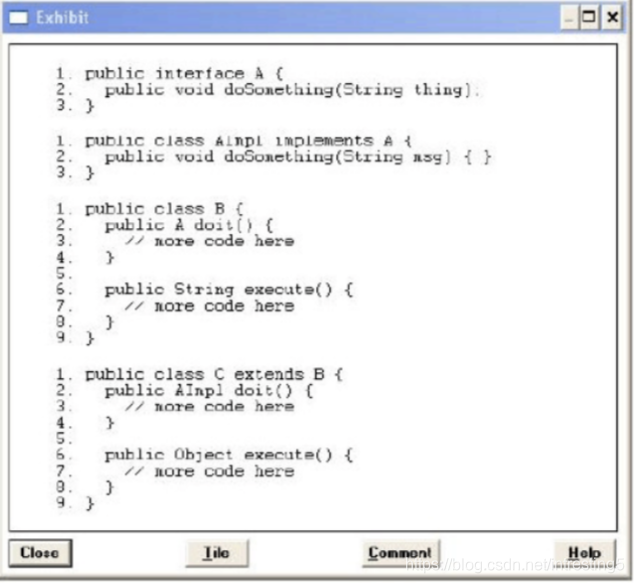
A. Compilation will succeed for all classes and interfaces.
B. Compilation of class C will fail because of an error in line 2.
C. Compilation of class C will fail because of an error in line 6.
D. Compilation of class AImpl will fail because of an error in line 2.
Answer: C
继承后重写方法使,返回值可以更改。
但是改变后的类型必须是修改前类型的子类型。
14.
14.Which two code fragments correctly create and initialize a static array of int elements? (Choose two.)
A. static final int[] a = { 100,200 };
B. static final int[] a;
static { a=new int[2]; a[0]=100; a[1]=200;
}
C. static final int[] a = new int[2]{ 100,200 }
;
D. static final int[] a;
static void init() { a = new int[3]; a[0]=100; a[1]=200; }
Answer: A,B
题目:哪两个代码片段正确地创建和初始化了一个静态的int元素数组?(选择两个。)
嗯,记住三种初始化方式,不要搞混了。
static final int[] a = { 100,200 };
static final int[] a;
static final int[] b = new int[2];
15.
15.Given:
10. interface Foo { int bar(); }
11. public class Sprite {
12. public int fubar( Foo foo ) { return foo.bar(); }
13. public void testFoo() {
14. fubar(
15. // insert code here 16.
16. );
17. }
18.
}
Which code, inserted at line 15, allows the class Sprite to compile?
A. Foo { public int bar() { return 1; }
B. new Foo { public int bar() { return 1;
}
C. new Foo() { public int bar() { return 1;
}
D. new class Foo { public int bar() { return 1; }
Answer: C
首先的话知道fubar()里面放的是Foo的一个对象。所以是new Foo();接口中的方法是未定义的,所以要重写他的方法
16.
16.Given:
1. class Alligator {
2. public static void main(String[] args) {
3. int []x[] = {{1,2}, {3,4,5}, {6,7,8,9}};
4. int [][]y = x;
5. System.out.println(y[2][1]);
6. }
7.
}
What is the result?A. 2 B. 3
C. 4
D. 6
E. 7
F. Compilation fails. Answer: E
我是这么理解的:int []x[],首先将x[]看成一个整体a,int [] a,就是一个一维数组。将2代入取出a[2]={6,7,8,9},即y[2][]={6,7,8,9},把1代入取出的就是7了。
17.
17.Given:
22. StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder("123");
23. String s1 = "123";
24. // insert code here
25. System.out.println(sb1 + " " + s1)
;
Which code fragment, inserted at line 24, outputs "123abc 123abc" ?A. sb1.append("abc"); s1.append("abc")
;
B. sb1.append("abc"); s1.concat("abc")
;
C. sb1.concat("abc"); s1.append("abc")
;
D. sb1.concat("abc"); s1.concat("abc")
;
E. sb1.append("abc"); s1 = s1.concat("abc")
;
F. sb1.concat("abc"); s1 = s1.concat("abc")
;
G. sb1.append("abc"); s1 = s1 + s1.concat("abc") ;
H. sb1.concat("abc"); s1 = s1 + s1.concat("abc") ;
Answer: E
解析:String的赋值原理是创建一个新的对象(new String())来储存。比如说
String a=“tt”;
a=“xx”;
这两个a不是同一个a,后面的a是重新new出来的,而之前的a会被回收。
这边的concat方法也是如此,s1.concat(“abc”)之后,获得一个字符串“123abc”,这个字符串不会直接加到s1中,需要一个新的容器来储存,所以要写成s1 = s1.concat(“abc”),这边的s1也同样和之前的s1不是同一个;而StringBuilder类的追加是直接追加在同一个对象中。所以直接用sb1.append(“abc”);
18.
18.Given that the current directory is empty, and that the user has read and write permissions, and the following:
11. import java.io.*;
12. public class DOS {
13. public static void main(String[] args) {
14. File dir = new File("dir");
15. dir.mkdir();
16. File f1 = new File(dir, "f1.txt");
17. try {
18. f1.createNewFile();
19. } catch (IOException e) { ; }
20. File newDir = new File("newDir");
21. dir.renameTo(newDir);
22. }
23.
}
Which statement is true?
A. Compilation fails.
B. The file system has a new empty directory named dir.
C. The file system has a new empty directory named newDir.
D. The file system has a directory named dir, containing a file f1.txt.
E. The file system has a directory named newDir, containing a file f1.txt. Answer: E
????
19.
19.Given:
11. class Converter {
12. public static void main(String[] args) {
13. Integer i = args[0];
14. int j = 12;
15. System.out.println("It is " + (j==i) + " that j==i.");
16. }
17. }
What is the result when the programmer attempts to compile the code and run it with the command java Converter 12?
A. It is true that j==i.
B. It is false that j==i.
C. An exception is thrown at runtime.
D. Compilation fails because of an error in line 13. Answer: D
解析:当程序员试图编译代码并使用命令Java转换器12运行代码时,结果是什么?
“String[] args”,arg[0]是字符类型不能放入Integer类型的I中。
20.
20.Given:
11. String test = "Test A. Test B. Test C.";
12. // insert code here
13. String[] result = test.split(regex);
Which regular expression, inserted at line 12, correctly splits test into "Test A", "Test B", and "Test C"?
A. String regex = "";
B. String regex = " ";
C. String regex = ".*";
D. String regex = "\\s";
E. String regex = "\\.\\s*";
F. String regex = "\\w[ \.] +";
Answer: E
根据题意要用“. ”分割字符串,在最后一个"Test C.“中要去掉”."
要用到正则表达式首先匹配一个点用“.”,匹配0个或多个空格用“\s*”
因为\在正则中有特殊意义,所有需要转义,写成了\
21.
21.Given:
5. import java.util.Date;
6. import java.text.DateFormat;
21. DateFormat df;
22. Date date = new Date();
23. // insert code here
24. String s = df.format(date);
Which code fragment, inserted at line 23, allows the code to compile? A. df = new DateFormat();
B. df = Date.getFormat();
C. df = date.getFormat();
D. df = DateFormat.getFormat();
E. df = DateFormat.getInstance();
Answer: E
???
22.
22.Given a class Repetition:
1. package utils;
2.
2. public class Repetition {
3. public static String twice(String s) { return s + s; }
4. } and given another class Demo:
1. // insert code here
2.
6. public class Demo {
7. public static void main(String[] args) {
8. System.out.println(twice("pizza"));
9. }
10. }
Which code should be inserted at line 1 of Demo.java to compile and run Demo to print "pizzapizza"?
A. import utils.*;
B. static import utils.*;
C. import utils.Repetition.*;
D. static import utils.Repetition.*;
E. import utils.Repetition.twice();
F. import static utils.Repetition.twice;
G. static import utils.Repetition.twice;
Answer: F
直接使用了方法。F这个选项直接引用到具体的某一方法。
这个static是因为方法是静态的。
23.
23.A UNIX user named Bob wants to replace his chess program with a new one, but he is not sure where the old one is installed. Bob is currently able to run a Java chess program starting from his home directory /home/bob using the command: java -classpath /test:/home/bob/downloads/*.jar
games.Chess Bob's CLASSPATH is set (at login time) to: /usr/lib:/home/bob/classes:/opt/java/lib:/opt/java/lib/*.jar What is a possible location for the
Chess.class file?
A. /test/Chess.class
B. /home/bob/Chess.class
C. /test/games/Chess.class
D. /usr/lib/games/Chess.class
E. /home/bob/games/Chess.class
F. inside jarfile /opt/java/lib/Games.jar (with a correct manifest)
G. inside jarfile /home/bob/downloads/Games.jar (with a correct manifest) Answer: C
24.
24.Given:
3. interface Animal { void makeNoise(); }
4. class Horse implements Animal {
5. Long weight = 1200L;
6. public void makeNoise() { System.out.println("whinny"); }
7. }
8. public class Icelandic extends Horse {
9. public void makeNoise() { System.out.println("vinny"); }
10. public static void main(String[] args) {
11. Icelandic i1 = new Icelandic();
12. Icelandic i2 = new Icelandic();
13. Icelandic i3 = new Icelandic();
14. i3 = i1; i1 = i2; i2 = null; i3 = i1;
15. }
16.
}
When line 15 is reached, how many objects are eligible for the garbage collector?A. 0 B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
F. 6 Answer: E
我的理解是,首先i1,i2,i3三个对象是确定的,由于有继承关系,在构造子类之前先构造父类,在加载父类的时候 Long weight = 1200L;初始化了weight这个对象,weight这个对象只创建一次,因为后面两次在常量池中找到1200L,所以会引用过去,所以答案是E。
25.
25.Click the Exhibit button. Given the fully-qualified class names: com.foo.bar.Dog com.foo.bar.blatz.Book com.bar.Car com.bar.blatz.Sun Which graph represents the correct directory structure for a JAR file from which those classes can be used by the compiler and JVM?
A. Jar A B. Jar B C. Jar C D. Jar D E. Jar E Answer: A
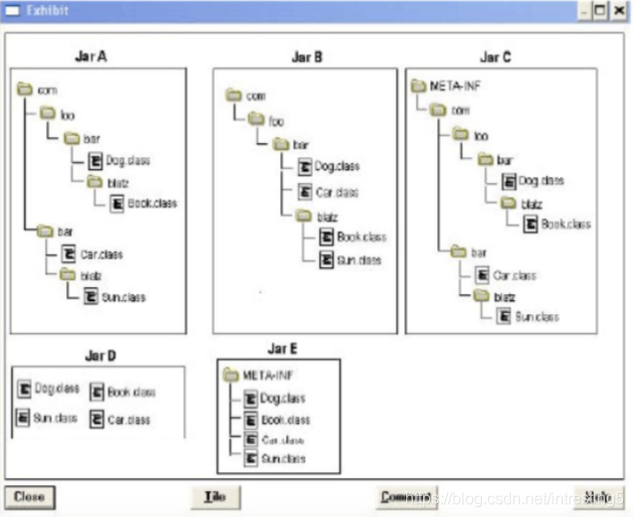
太糊,看的脑阔疼,跳过哈哈
26.
26.Given classes defined in two different files:
1. package util;
2. public class BitUtils {
3. private static void process(byte[] b) {}
4. }
6. package app;
2
. public class SomeApp
{
7. public static void main(String[] args)
{
8. byte[] bytes = new byte[256]
;
9. // insert code here
6.
}
7.
}
What is required at line 5 in class SomeApp to use the process method of BitUtils?A. process(bytes) ;
B. BitUtils.process(bytes)
;
C. app.BitUtils.process(bytes)
;
D. util.BitUtils.process(bytes)
;
E. import util.BitUtils.*; process(bytes)
;
F. SomeApp cannot use the process method in BitUtils.
Answer: F
首先这两个类在不同的包,要调用的方法是一个静态方法,所以可以通过类名加.方法,由于没有引用包所以在调用时,使用(包名.类名.方法)调用,所以一开始我选的D,是因为我默认为这两个包在同一个文件夹中,但是看题目!!两个不同的文件夹中!!不同文件夹是不能互相调用的。
27.
27.Given:
11. public class ItemTest {
12. private final int id;
13. public ItemTest(int id) { this.id = id; }
14. public void updateId(int newId) { id = newId; }
15.
16. public static void main(String[] args) {
17. ItemTest fa = new ItemTest(42);
18. fa.updateId(69);
19. System.out.println(fa.id);
20. }
21.
}
What is the result?A. Compilation fails.
B. An exception is thrown at runtime.
C. The attribute id in the ItemTest object remains unchanged.
D. The attribute id in the ItemTest object is modified to the new value.
E. A new ItemTest object is created with the preferred value in the id attribute.
Answer: A
final关键字在变量上不可更改,后续复制的话编译不会通过,所以选A。
28.
28.Given:
13. public class Pass {
14. public static void main(String [] args) {
15. int x = 5;
16. Pass p = new Pass();
17. p.doStuff(x);
18. System.out.print(" main x = " + x);
19. }
20.
21. void doStuff(int x) {
22. System.out.print(" doStuff x = " + x++);
23. }
24.
}
What is the result?A. Compilation fails. B. An exception is thrown at runtime. C. doStuff x = 6 main x =
6
D. doStuff x = 5 main x =
5
E. doStuff x = 5 main x =
6
F. doStuff x = 6 main x =
5
Answer: D
首先创建了自己的对象,调用doStuff方法“X++”,先用在加,先用所以doStuff x = 5,其次函数内为形参,不会对实参更改,所以main x =5。
29.
29.Given:
1. public class GC {
2. private Object o;
3. private void doSomethingElse(Object obj) { o = obj; }
4. public void doSomething() {
5. Object o = new Object();
6. doSomethingElse(o);
7. o = new Object();
8. doSomethingElse(null);
9. o = null;
10. }
11. }
When the doSomething method is called, after which line does the Object created in line 5 become available for garbage collection?
A. Line 5
B. Line 6
C. Line 7 D. Line 8 E. Line 9 F. Line 10 Answer: D
题目:当调用dosomething方法时,第5行中创建的对象在哪一行之后可用于垃圾收集?
首先可以这么理解,对象是什么,对象是内存中的某一块,在创建新的对象时就会创建的。
那么什么时候会被回收,不在使用这块内存时就会被回收。
第5行:在内存中分配出一块内存,名字叫做o,方便起见,就叫o(1);
第6行:将这块内存引用给成员变量 o,方便起见就叫o(2)。o(1)o(2)引用同一个内存。
第7行:new 创建了o,就叫o(3)吧,会重新开辟内存来储存(内存2号),此时o(3)会覆盖o(1),但是不会回收这块内存,因为这块内存还被o(2)所使用。
第8行:将o(2)的指针指向了null,那么这块内存就没人使用了,系统就会自动回收了。
第9行:o(3)也被指向了null,所以内存2号也被回收了。
30.
30.Given:
11. public static void test(String str) {
12. int check = 4;
13. if (check = str.length()) {
14. System.out.print(str.charAt(check -= 1) +", ");
15. } else {
16. System.out.print(str.charAt(0) + ", ");
17. }
18. }
19. and the invocation:
20. test("four");
21. test("tee");
22. test("to");
What is the result?
A. r, t, t,
B. r, e, o,
C. Compilation fails.
D. An exception is thrown at runtime.
Answer: C
解析:注意它是单等于,不是判等。编译错误
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43





 这篇博客详细解析了OCJP(Oracle Certified Java Programmer)考试的多个题目,涵盖泛型、集合、多态、继承、接口、字符串操作等多个知识点,帮助考生理解和准备考试。
这篇博客详细解析了OCJP(Oracle Certified Java Programmer)考试的多个题目,涵盖泛型、集合、多态、继承、接口、字符串操作等多个知识点,帮助考生理解和准备考试。
















 1048
1048

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








