set和map不可以对自定义的数据类型自动排序,但是可以对pair自动排序,默认优先按照first排序,first相等则按照second排序
pair对象
set:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
set<pair<int, int>> s;
s.insert({1, 2});
s.insert({3, 4});
s.insert({1, 1});
for(auto k : s) cout << k.first << " " << k.second << endl;
return 0;
}

map针对其键排序与set同理
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<pair<int, int>, int> s;
s[{1, 2}] = 1;
s[{3, 4}] = 1;
s[{1, 1}] = 0;
for(auto k : s) printf("%d %d %d\n", k.first.first, k.first.second, k.second);
return 0;
}

而若想对自定义的数据类型排序,需要重载"<"运算符
自定义数据类型
set:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct stu
{
int i, j;
bool operator<(const stu & b)const // 类内重载,所以少一个参数,优先按照i从大到小排序,j从大到小次之
{
return i == b.i ? (j > b.j) : (i > b.i);
}
};
int main()
{
set<stu> s;
s.insert({1, 2});
s.insert({3, 4});
s.insert({1, 1});
for(auto k : s) printf("%d %d\n", k.i, k.j);
return 0;
}

map:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct stu
{
int i, j;
bool operator<(const stu & b)const // 类内重载,所以少一个参数,优先按照i从大到小排序,j从大到小次之
{return i == b.i ? (j > b.j) : (i > b.i);}
};
int main()
{
map<stu, int>s;
s[{1, 2}] = 1;
s[{3, 4}] = 1;
s[{1, 1}] = 0;
for(auto k : s) printf("%d %d %d\n", k.first.i, k.first.j, k.second);
return 0;
}
也可以选择手动传入比较函数对象
set:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct stu
{
int i, j;
};
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(const stu &a, const stu & b)const // 重载()
{
return a.i == b.i ? (a.j > b.j) : (a.i > b.i);
}
};
int main()
{
set<stu, cmp> s; // 第二个参数默认是_Compare对象,默认std :: less,将其修改为我们定义的
s.insert({1, 2});
s.insert({3, 4});
s.insert({1, 1});
for(auto k : s) printf("%d %d\n", k.i, k.j);
return 0;
}
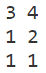
map:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct stu
{
int i, j;
};
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(const stu &a, const stu & b)const // 重载()
{
return a.i == b.i ? (a.j > b.j) : (a.i > b.i);
}
};
int main()
{
map<stu, int, cmp> m; // 第三个参数默认是_Compare对象,默认std :: less,将其修改为我们定义的
m[{1, 2}] = 1;
m[{3, 4}] = 2;
m[{1, 1}] = 3;;
for(auto k : m) printf("%d %d %d\n", k.first.i, k.first.j, k.second);
return 0;
}

有时,需要对map按value值进行排序,此时往往转换为vector
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int, int> s;
s[1] = 4;
s[2] = 3;
s[3] = 1;
vector<pair<int, int>> S;
for (auto i : s) S.push_back(i);
// 将value从大到小排序,lambda表达式
sort(S.begin(), S.end(), [&](pair<int, int>& a, pair<int, int>& b) { return a.second < b.second;});
for(auto k : s) printf("%d %d\n", k.first, k.second);
return 0;
}

另外,set和map底层是基于红黑树的,而unordered_set和unordered_map,都是基于哈希的,因此unordered_set和unordered_map定义时的对象如果是非基本数据类型,要自定义包含哈希函数的对象,处理冲突用的是链地址法
注意,和set和map不同,unordered_set和unordered_map对于pair类型也要自定义哈希对象
可以参考 https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/vevenlcf/article/details/51743058)
set:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class s_hash
{
public:
// 定义为inline提高速度
inline size_t operator()(const pair<int, int> &p)const
{
return p.first^ p.second;
// 哈希函数的设计,链地址法处理冲突
}
};
int main()
{
unordered_set<pair<int, int>, s_hash> s;
s.insert({1, 2});
s.insert({3, 4});
s.insert({1, 1});
for(auto k : s) cout << k.first << " " << k.second << endl;
return 0;
}
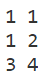
map:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class s_hash
{
public:
// 定义为inline提高速度
inline size_t operator()(const pair<int, int> &p)const
{
return p.first^ p.second;
// 哈希函数的设计
}
};
int main()
{
unordered_map<pair<int, int>, int, s_hash> m;
m[{1, 2}] = 1;
m[{1, 1}] = 2;
m[{3, 4}] = 3;
for(auto k : m) printf("%d %d %d\n", k.first.first, k.first.second, k.second);
return 0;
}






 本文深入探讨了C++ STL中set和map的高级应用技巧,包括自定义数据类型的排序、使用比较函数对象、对map按value排序的方法,以及unordered_set和unordered_map的特殊处理方式。
本文深入探讨了C++ STL中set和map的高级应用技巧,包括自定义数据类型的排序、使用比较函数对象、对map按value排序的方法,以及unordered_set和unordered_map的特殊处理方式。
















 2046
2046

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








