1.变量名命名规则
# 中文是可以作为变量名的,但不建议
姓名 = "hello"
print(姓名)
# 变量名可以由字母,数字或者下划线;
# 变量名只能以字母或者下划线组成;
# 变量名不能是python的关键字: eg: if, elif, else,
# eg: while, for, break,continue,pass
a_1hello = "hello"
print(a_1hello)
# hell@ = "hello"
# if = "hello"
# while = "hello"
# break = "hello"

2.字符串的定义方式
字符串常用的转义符号:
# \n:换行
# \t: 一个tab键
# \': '
# \": "
# 打印"hello"
# 打印guido's
# 打印"hello guido's python"
print('"hello"')
print("guido's")
print("\"hello guido\'s python\"")
print("%s\t%s" % ("hello", "world"))

s = "hello"
# 索引: 0,1,2,3,4, 索引值是从0开始的;
print(s[0])
print(s[4])
print(s[-1]) # 拿出字符串的最后一个子符;
# 切片
print(s[0:3]) # 切片时规则为s[start:end:step],从start开始,到end-1结束, 步长为step;
print(s[0:4:2])
print(s[:]) # 显示所有子符
print(s[:3]) # 显示前3个子符
print(s[::-1]) # 对于字符串倒序输出;
print(s[1:]) # 除了第一个子符之外, 其他全部显示;
# 重复
print(s*10)
# 连接
print("hello "+"world")
# 成员操作符 s = "hello", in, not in
print('he' in s)
print('aa' in s)
print('he' not in s)

字符串开头和结尾的匹配
# 找出字符串是否以xxxx结尾;
s = "hello.jpg"
print(s.endswith(('.png', '.jpg')))
url1 = "http://www.baidu.com"
url2 = "file:///mnt"
url3 = "https://www.baidu.com"
url4 = "ftp://www.baidu.com"
# 以什么开头;
print(url1.startswith(('https://', 'http://')))
print(url2.startswith("file://"))

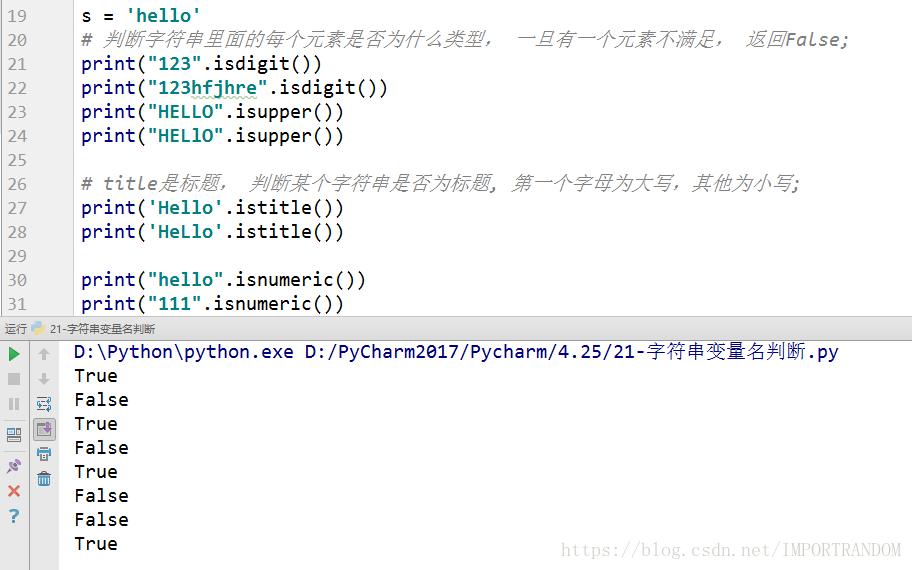
字符串变量名判断
#[[:digit:]]
#[[:upper:]]
#[[:lower:]]
#[[:alnum:]]
#[[:space:]]
s = 'hello'
# 判断字符串里面的每个元素是否为什么类型, 一旦有一个元素不满足, 返回False;
print("123".isdigit())
print("123hfjhre".isdigit())
print("HELLO".isupper())
print("HELlO".isupper())
# title是标题, 判断某个字符串是否为标题, 第一个字母为大写,其他为小写;
print('Hello'.istitle())
print('HeLlo'.istitle())
print("hello".isnumeric())
print("111".isnumeric())
字符串变量名合法性练习题
# 变量名是否合法?
# 变量名可以由字母,数字或者下划线;
# 变量名只能以字母或者下划线开头;
#s = "hello@"
#1. 判断变量名的第一个元素是否为字母或者下划线; s[0]
#2. 如果第一个元素符合条件, 判断除了第一个元素的其他元素;s[1:]
# 1. for循环:依次遍历字符串的每一个元素;
# for i in "hello": # i: 'h', 'e', 'l' s[
# if i.isalpha():
# print(i)
# var = "hello'
# var = input("变量名:")
# # 判断第一个字符是否合法;
# if var[0] == "_" or var[0].isalpha():
# for char in var[1:]: # 判断除了第一个字符之外的其他字符 # char: e,l,l,o
# if char.isalnum() or char == "_":
# continue
# else:
# print('变量名%s不合法' %(var))
# break
# else:
# print('变量名%s合法' %(var))
# else:
# print("变量名不合法:第一个字符错误!")
var = input("变量名:").strip()
# 判断第一个字符是否合法;
if var[0] == "_" or var[0].isalpha():
for char in var[1:]: # 判断除了第一个字符之外的其他字符 # char: e,l,l,o
if not (char.isalnum() or char == "_"):
print('变量名%s不合法' %(var))
break
else:
print('变量名%s合法' %(var))
else:
print("变量名不合法:第一个字符错误!")

字符串搜索与替换
#find(), replace()
s = "hello world hello"
# find找到子串,并返回最小的索引值;
print(s.find("hello"))
print(s.find("world"))
# find找到子串,并返回最大的索引值;
print(s.rfind("hello"))
# 替换字符串中所有的“hello”为"westos"
print(s.replace("hello", "westos"))

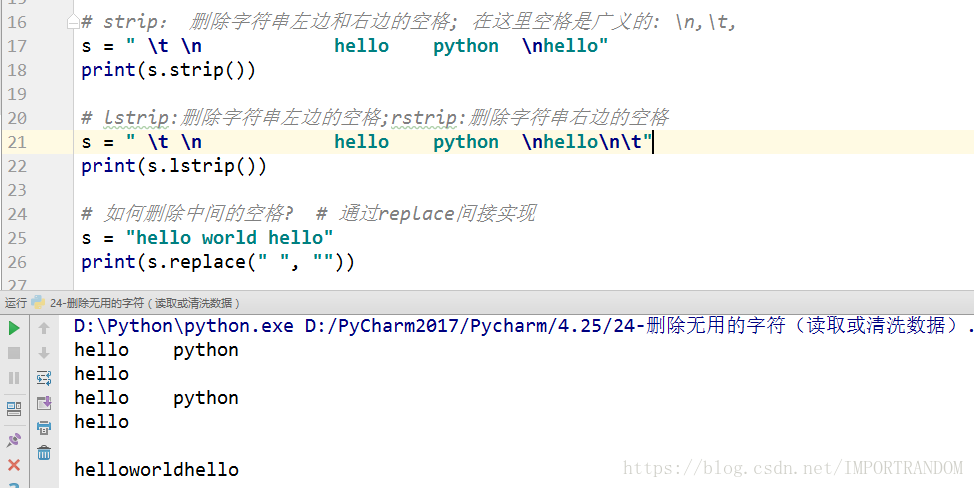
删除无用的字符(读取或清洗数据)
#strip, lstrip, rstrip, replace
# strip: 删除字符串左边和右边的空格; 在这里空格是广义的: \n,\t,
s = " \t \n hello python \nhello"
print(s.strip())
# lstrip:删除字符串左边的空格;rstrip:删除字符串右边的空格
s = " \t \n hello python \nhello\n\t"
print(s.lstrip())
# 如何删除中间的空格? # 通过replace间接实现
s = "hello world hello"
print(s.replace(" ", ""))
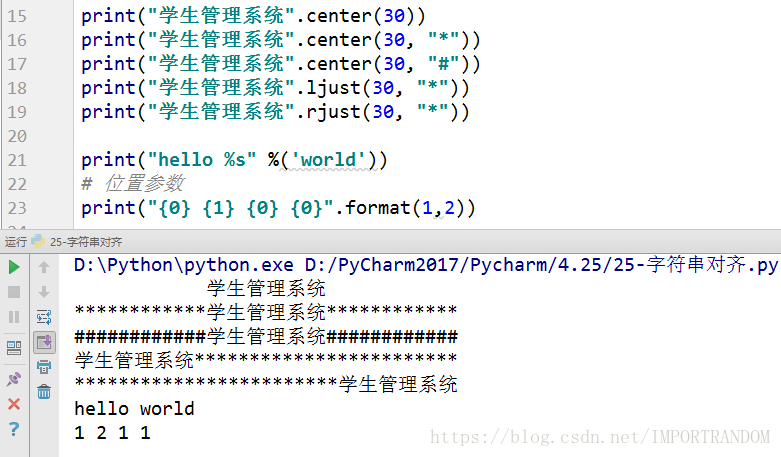
字符串对齐
#ljust, rjust, center, format
print("学生管理系统".center(30))
print("学生管理系统".center(30, "*"))
print("学生管理系统".center(30, "#"))
print("学生管理系统".ljust(30, "*"))
print("学生管理系统".rjust(30, "*"))
print("hello %s" %('world'))
# 位置参数
print("{0} {1} {0} {0}".format(1,2))
字符串统计
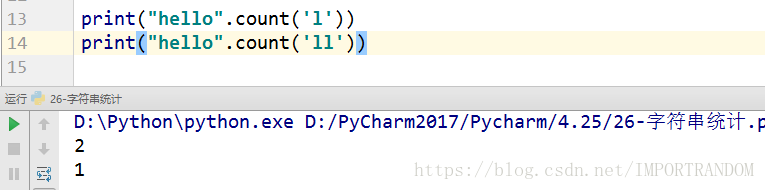
字符串统计练习
# 给定一个字符串来代表一个学生的出勤纪录,这个纪录仅包含以下三个字符:
# 'A' : Absent,缺勤
# 'L' : Late,迟到
# 'P' : Present,到场
# 如果一个学生的出勤纪录中不超过一个'A'(缺勤)并且不超过两个连续的'L'(迟到),
# 那么这个学生会被奖赏。
# 你需要根据这个学生的出勤纪录判断他是否会被奖赏。
# 示例 1:
# 输入: "PPALLP"
# 输出: True
# 示例 2:
# 输入: "PPALLL"
# 输出: False
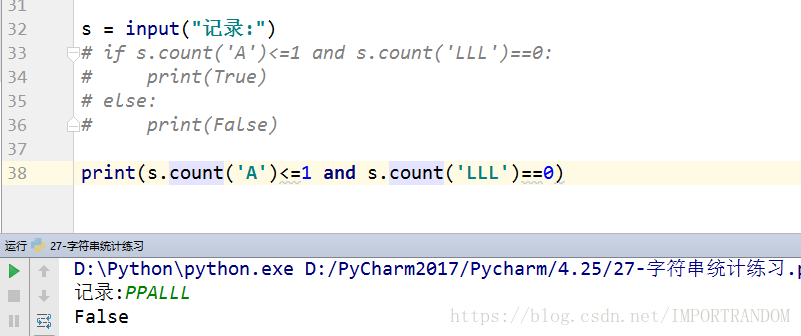
s = input("记录:")
# if s.count('A')<=1 and s.count('LLL')==0:
# print(True)
# else:
# print(False)
print(s.count('A')<=1 and s.count('LLL')==0)
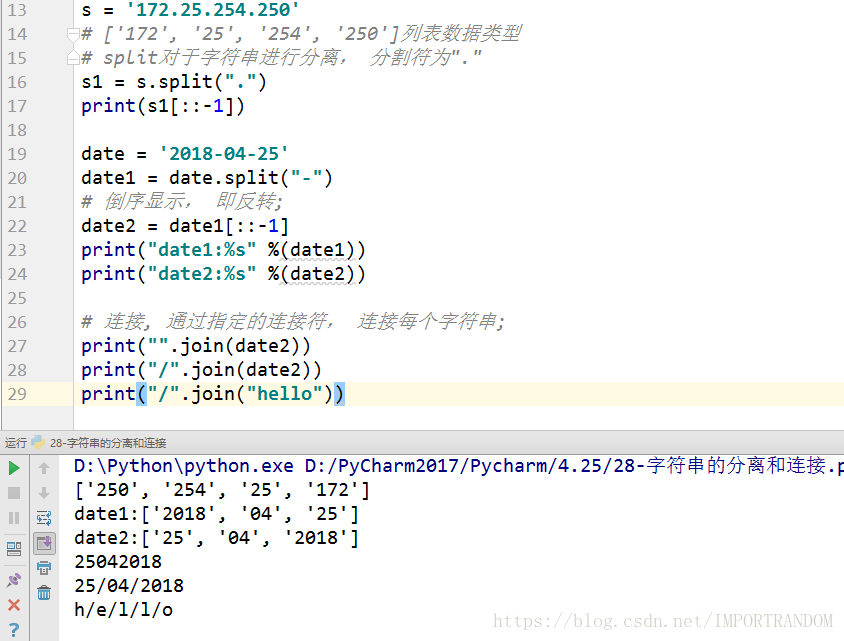
字符串的分离和连接
s = '172.25.254.250'
# ['172', '25', '254', '250']列表数据类型
# split对于字符串进行分离, 分割符为"."
s1 = s.split(".")
print(s1[::-1])
date = '2018-04-25'
date1 = date.split("-")
# 倒序显示, 即反转;
date2 = date1[::-1]
print("date1:%s" %(date1))
print("date2:%s" %(date2))
# 连接, 通过指定的连接符, 连接每个字符串;
print("".join(date2))
print("/".join(date2))
print("/".join("hello"))
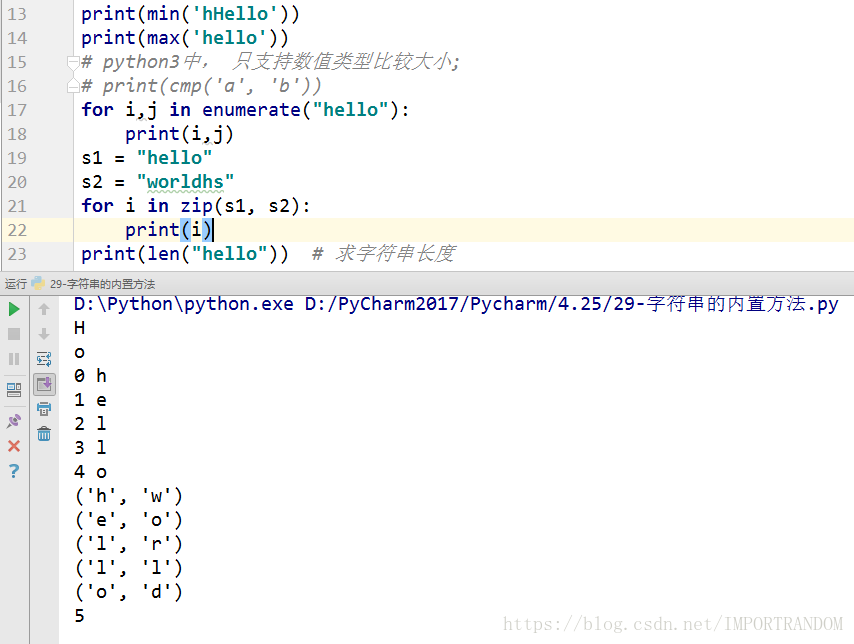
字符串的内置方法
print(min('hHello'))
print(max('hello'))
# python3中, 只支持数值类型比较大小;
# print(cmp('a', 'b'))
for i,j in enumerate("hello"):
print(i,j)
s1 = "hello"
s2 = "worldhs"
for i in zip(s1, s2):
print(i)
print(len("hello")) # 求字符串长度
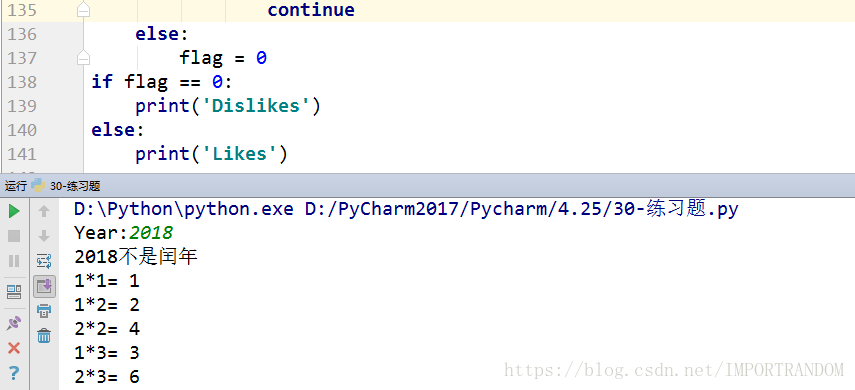
10.练习题
1. 用户键盘输入一年份, 判断是否为闰年?
# - 如果是闰年, 则输出xxx是闰年;
# - 如果不是闰年, 则输出xxx不是闰年;
# 判断闰年的方法:
# 1). 能被4整除但不能被100整除;
# 2). 能被400整除;
year = int(input("Year:"))if (year % 4 == 0 and year %100 !=0) or (year % 400 == 0):
print("%s是闰年" %(year))
else:
print("%s不是闰年" %(year))
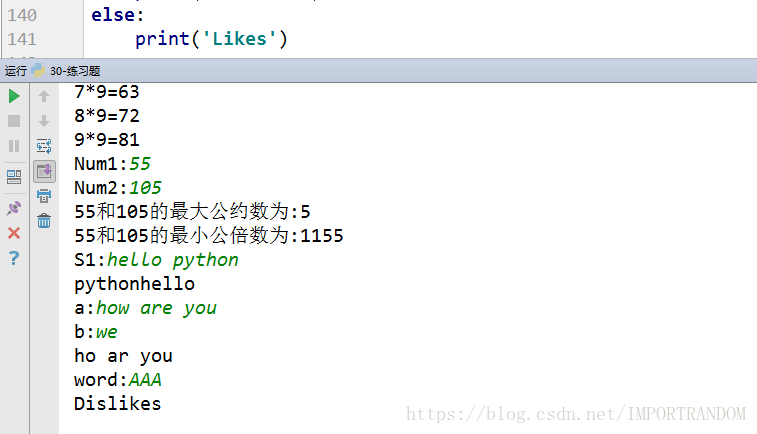
2. for循环嵌套:打印9*9乘法表;
for i in range(1,10):
for j in range(1,i+1):
print("{}*{}={:2}" .format(j,i,i*j), end='')
print('')
3. 输入两个数,求这两个数的最大公约数和最小公倍数;
num1 = int(input('Num1:'))
num2 = int(input('Num2:'))
min_num = min(num1, num2)
for i in range(1, min_num + 1):
if num1 % i == 0 and num2 % i == 0:
res = i
lcm = int((num1 * num2) / res)
print("%s和%s的最大公约数为:%s" % (num1, num2, res))
print("%s和%s的最小公倍数为:%s" % (num1, num2, lcm))
4. (2017-小米-句子反转)
# - 题目描述:
# > 给定一个句子(只包含字母和空格), 将句子中的单词位置反转,单词用空格分割, 单词之间只有一个空格,前后没有空格。 比如: (1)
# “hello xiao mi”-> “mi xiao hello”
# - 输入描述:
# > 输入数据有多组,每组占一行,包含一个句子(句子长度小于1000个字符)
# - 输出描述:
# > 对于每个测试示例,要求输出句子中单词反转后形成的句子
# - 示例1:
# - 输入
# hello xiao mi
# - 输出
# mi xiao hello
s = input('S1:')
s=s.split(' ')
a = s[::-1]
print('' .join(a))
5. # (2017-好未来-笔试编程题)--练习
# - 题目描述:
# 输入两个字符串,从第一字符串中删除第二个字符串中所有的字符。例如,输入”They
# are students.”和”aeiou”,则删除之后的第一个字符串变成”Thy r stdnts.”
# - 输入描述:
# 每个测试输入包含2个字符串
# - 输出描述:
# 输出删除后的字符串
# - 示例1:
# 输入
# They are students.
# aeiou
# 输出
# Thy r stdnts.
a = input('a:')
b = input('b:')
x = ""
for i in a:
if i in b:
pass
else:
x+=i
print(x)
6. # (2017-网易-笔试编程题)-字符串练习
# 小易喜欢的单词具有以下特性:
# 1.单词每个字母都是大写字母
# 2.单词没有连续相等的字母
# 列可能不连续。
# 例如:
# 小易不喜欢"ABBA",因为这里有两个连续的'B'
# 小易不喜欢"THETXH",因为这里包含子序列"THTH"
# 小易喜欢"A", "ABA"和"ABCBA"这些单词
# 给你一个单词,你要回答小易是否会喜欢这个单词。
# - 输入描述:
# 输入为一个字符串,都由大写字母组成,长度小于100
# - 输出描述:
# 如果小易喜欢输出"Likes", 不喜欢输出"Dislikes"
# 示例1:
# 输入
# AAA
# 输出
# Dislikes
d = input('word:')
flag = 1
lenth = len(d)
for x in d:
if x >= "A" and x<="Z":
for i in range(lenth - 1):
if d[i] == d[i+1]:
flag = 0
for i in range(lenth - 3):
d1 =d.find(d[i],i+2)
if d1 == -1:
continue
else:
flag = 0
if flag == 0:
print('Dislikes')
else:
print('Likes')
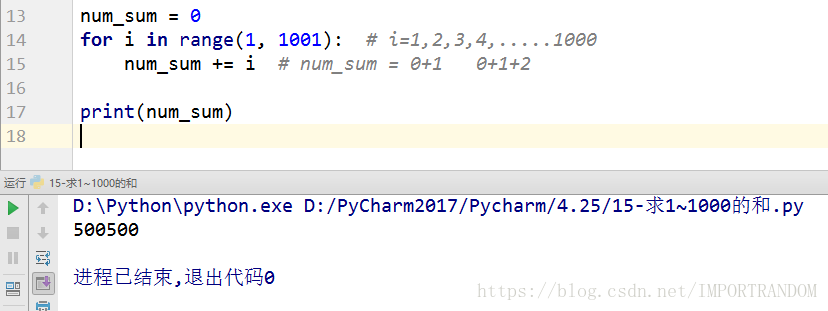
7.求1~1000的和
num_sum = 0
for i in range(1, 1001): # i=1,2,3,4,.....1000
num_sum += i # num_sum = 0+1 0+1+2
print(num_sum)
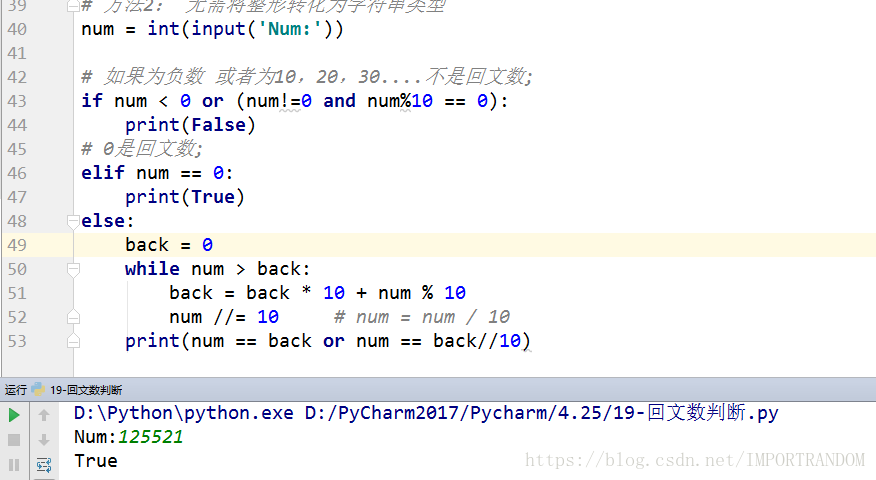
8.回文数判断
# 题目要求:
#判断一个整数是否是回文数。回文数是指正序(从左向右)和倒序(从右向左)读都是一样的整数。
# 示例:
#示例 1:
# 输入: 121
# 输出: true
#示例 2:
# 输入: -121
# 输出: false # 解释: 从左向右读, 为 -121 。 从右向左读, 为 121- 。因此它不是一个回文数。
#示例 3:
# 输入: 10
# 输出: false
# 解释: 从右向左读, 为 01 。因此它不是一个回文数。
#进阶:
#你能不将整数转为字符串来解决这个问题吗?
# 方法1:
# # 121 == 121
# num = input('Num:')
# print(num == num[::-1])
# 方法2: 无需将整形转化为字符串类型num = int(input('Num:'))
# 如果为负数 或者为10,20,30....不是回文数;
if num < 0 or (num!=0 and num%10 == 0):
print(False)
# 0是回文数;
elif num == 0:
print(True)
else:
back = 0
while num > back:
back = back * 10 + num % 10
num //= 10 # num = num / 10
print(num == back or num == back//10)





 本文介绍了Python字符串的定义、转义符号、操作方法,包括索引、切片、重复和连接等。同时,讲解了字符串的成员操作、开头和结尾的匹配,以及变量名的合法性判断。还提供了字符串搜索与替换、删除无用字符、对齐、统计和分离连接的实例。最后,通过示例展示了字符串在实际问题中的应用,如闰年判断、回文数检测等。
本文介绍了Python字符串的定义、转义符号、操作方法,包括索引、切片、重复和连接等。同时,讲解了字符串的成员操作、开头和结尾的匹配,以及变量名的合法性判断。还提供了字符串搜索与替换、删除无用字符、对齐、统计和分离连接的实例。最后,通过示例展示了字符串在实际问题中的应用,如闰年判断、回文数检测等。
















 333
333

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








