Flip Game
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 30172 | Accepted: 13094 |
Description
Flip game is played on a rectangular 4x4 field with two-sided pieces placed on each of its 16 squares. One side of each piece is white and the other one is black and each piece is lying either it's black or white side up. Each round you flip 3 to 5 pieces, thus changing the color of their upper side from black to white and vice versa. The pieces to be flipped are chosen every round according to the following rules:
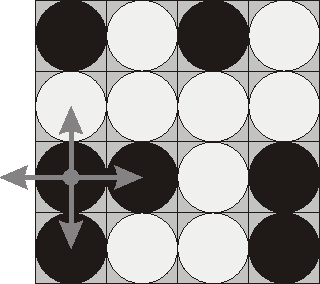 Consider the following position as an example:
Consider the following position as an example:
bwbw
wwww
bbwb
bwwb
Here "b" denotes pieces lying their black side up and "w" denotes pieces lying their white side up. If we choose to flip the 1st piece from the 3rd row (this choice is shown at the picture), then the field will become:
bwbw
bwww
wwwb
wwwb
The goal of the game is to flip either all pieces white side up or all pieces black side up. You are to write a program that will search for the minimum number of rounds needed to achieve this goal.
- Choose any one of the 16 pieces.
- Flip the chosen piece and also all adjacent pieces to the left, to the right, to the top, and to the bottom of the chosen piece (if there are any).
 Consider the following position as an example:
Consider the following position as an example:
bwbw
wwww
bbwb
bwwb
Here "b" denotes pieces lying their black side up and "w" denotes pieces lying their white side up. If we choose to flip the 1st piece from the 3rd row (this choice is shown at the picture), then the field will become:
bwbw
bwww
wwwb
wwwb
The goal of the game is to flip either all pieces white side up or all pieces black side up. You are to write a program that will search for the minimum number of rounds needed to achieve this goal.
Input
The input consists of 4 lines with 4 characters "w" or "b" each that denote game field position.
Output
Write to the output file a single integer number - the minimum number of rounds needed to achieve the goal of the game from the given position. If the goal is initially achieved, then write 0. If it's impossible to achieve the goal, then write the word "Impossible" (without quotes).
Sample Input
bwwb bbwb bwwb bwww
Sample Output
4
Source
题意就是4*4的棋盘,每个格子黑白两色,每次翻一个格子周围四个也会翻。问最少翻几个能使棋盘变成一个颜色。
就是模拟加上dfs
#include<string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
char a[5][5];
int qp[6][6];
int flag=0,s;
void shuru()//从1到4,相当于棋盘周围又加了一圈;
{
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=4;j++)
{
scanf("%c",&a[i][j]);
if(a[i][j]=='b')qp[i][j]=1;
if(a[i][j]=='w')qp[i][j]=0;
}
getchar();
}
}
int wanc()
{
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=4;j++)
{
if(qp[i][j]!=qp[1][1])return 0;
}
return 1;
}
void f(int x,int y)
{
qp[x][y]=!qp[x][y];
qp[x+1][y]=!qp[x+1][y];
qp[x][y+1]=!qp[x][y+1];
qp[x-1][y]=!qp[x-1][y];
qp[x][y-1]=!qp[x][y-1];
}
void dfs(int x,int y,int step)
{
if(step==s)//搜索的步数等于当前步数
{
flag=wanc();return;
}
if(flag||x==5)return;//x==5表示第一行这四个搜完了
f(x,y);//翻一次
if(y<4)dfs(x,y+1,step+1);//如果这一列没搜完,搜这一列的下一行,因为刚才翻了一次,所以step+1;
else dfs(x+1,1,step+1);//如果搜完了,就从下一行的第一列开始搜
f(x,y);//翻回来,相当于这个格子没翻,所以下面step不加一
if(y<4)dfs(x,y+1,step);
else dfs(x+1,1,step);
return ;
}
int main()
{
shuru();
for(s=0;s<=16;s++)
{
dfs(1,1,0);
if(flag)break;
}
if(flag)printf("%d\n",s);
else printf("Impossible\n");
}




 本文介绍了一个4x4棋盘翻转游戏的算法实现,目标是在最少的步骤内将所有棋子翻转成同一颜色。采用深度优先搜索(DFS)策略模拟每一步翻转,并记录达到目标状态所需的最小翻转次数。
本文介绍了一个4x4棋盘翻转游戏的算法实现,目标是在最少的步骤内将所有棋子翻转成同一颜色。采用深度优先搜索(DFS)策略模拟每一步翻转,并记录达到目标状态所需的最小翻转次数。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








