在Web应用中如何使用Spring框架?
在回答这个问题之前,让我们先回顾一下在非Web中使用Spring框架的方式:
package xyz.huning.spring4.helloworld;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建Spring的IOC容器
// ApplicationContext代表IOC容器,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从 类路径下加载配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("helloworld.xml");
// 2. 从IOC容器中获取bean
Helloworld helloworld = context.getBean("helloWorld", Helloworld.class);
helloworld.say();
// 3. 关闭IOC容器
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)context).close();
}
}
不错,我们是通过new一个ApplicationContext的对象,让后加载配置文件来完成的。那么,在Web应有中我们又该如何实现呢?要回答这个问题,我们需要弄清楚一下一个问题:
1) Spring 的配置文件有什么不同?
2) 用什么方式创建IOC容器?
3) 在什么时候创建IOC容器?
4) 在 Web 应用的其他组件中如何来访问 IOC 容器?
5) 如何加载Spring配置文件?
Spring 的配置文件有什么不同?
因为配置文件中是对bean的配置,并不涉及IOC容器在哪里使用。因此,在Web应用中的配置文件和非Web应用中没有区别。
用什么方式创建IOC容器?
非 WEB 应用在 main 方法中直接创建,即在程序启动的时候创建。那么Web应用也应该在程序启动的时候创建,那Web应用是在什么时候启动程序的呢?
显然是在WEB 应用被服务器加载时启动的,因此,应该在 Web 应用被服务器加载时就创建 IOC 容器。查看ServletAPI后,发现在 ServletContextListener接口的
contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent evt) 方法中创建 IOC 容器是最佳时机。
在 Web 应用的其他组件中如何来访问 IOC 容器?
考虑到Web容器中存在四中作用域:applIcation(整个应用,对应servlet中ServletContext),session(会话,对应servlet中HttpSession),request(一次请求,对应servlet中HttpServletRequest)和page(当前页面)。
为了在所有范围内访问到IOC容器,在 ServletContextListener接口的contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent evt) 方法中创建 IOC 容器后, 可以把其放在ServletContext(即 application 域)的一个属性中。
如何加载Spring配置文件?
如果使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext来创建IOC容器,则Spring配置文件放置于Classpath类路径中即可。为了增加应用的灵活性,可以利用web.xml中的初始化参数“context-param”来传入配置文件名称。然后使用
ServletContext接口的getInitParameter(String arg)来获取。以此来达到可配置的效果。
示例(源代码见附件)
1. 创建JavaWeb工程xyz.huning.web.spring4.custom
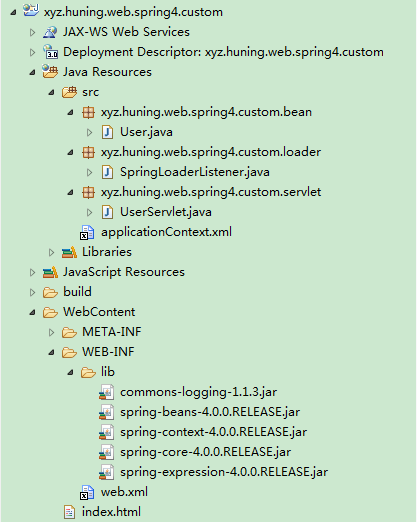
2. 添加模型类
package xyz.huning.web.spring4.custom.bean;
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", password="
+ password + "]";
}
}
3. 配置模型bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="user1" class="xyz.huning.web.spring4.custom.bean.User"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="username" value="BluceLi"></property> <property name="password" value="123456"></property> </bean> </beans>
4. 添加ServletContextListener
package xyz.huning.web.spring4.custom.loader;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringLoaderListener implements ServletContextListener {
public static final String APPLICATION_CONTEXT = "xyz.huning.web.spring4.custom.loader.ctx";
private ServletContext servletContext;
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent evt) {
servletContext = evt.getServletContext();
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = (ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)servletContext.getAttribute(APPLICATION_CONTEXT);
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent evt) {
servletContext = evt.getServletContext();
String springCfgFile = servletContext.getInitParameter("springCfgFile");
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(springCfgFile);
servletContext.setAttribute(APPLICATION_CONTEXT, ctx);
}
}
5. 添加测试Servlet
package xyz.huning.web.spring4.custom.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import xyz.huning.web.spring4.custom.bean.User;
import xyz.huning.web.spring4.custom.loader.SpringLoaderListener;
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8200917637630894695L;
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ApplicationContext ctx = (ApplicationContext)getServletContext().getAttribute(SpringLoaderListener.APPLICATION_CONTEXT);
User user1 = ctx.getBean("user1", User.class);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(response.getOutputStream());
pw.print(user1);
pw.flush();
pw.close();
}
}
6. 添加web.xml并配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <context-param> <param-name>springCfgFile</param-name> <param-value>applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>xyz.huning.web.spring4.custom.loader.SpringLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <servlet> <servlet-name>userServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>xyz.huning.web.spring4.custom.servlet.UserServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>userServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/userServlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> </web-app>
7. 配置tomcat添加目标工程后启动
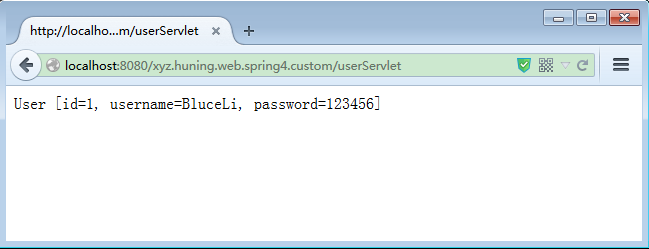
8. 在浏览器中输入地址:http://localhost:8080/xyz.huning.web.spring4.custom/userServlet
9. 查看返回结果





 本文详细介绍了在Web应用中如何使用Spring框架,包括配置文件的区别、创建IOC容器的最佳时机、访问IOC容器的方法以及加载配置文件的策略。通过示例代码展示了如何在JavaWeb工程中实现Spring框架的应用。
本文详细介绍了在Web应用中如何使用Spring框架,包括配置文件的区别、创建IOC容器的最佳时机、访问IOC容器的方法以及加载配置文件的策略。通过示例代码展示了如何在JavaWeb工程中实现Spring框架的应用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








