1.将时间序列转换为监督数据
关键函数df.shift()
- 实际上df.shift()函数可以将当前列的值拷贝并按照输入的参数(表示step)来填充NaN
from pandas import DataFrame
df = DataFrame()
df['t'] = [x for x in range(10)]
print(df)
from pandas import DataFrame
df = DataFrame()
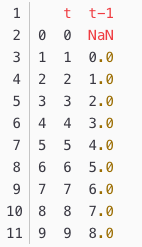
df['t'] = [x for x in range(10)]
df['t-1'] = df['t'].shift(1)
print(df)
运行示例,我们发现数据集中有了两列的值,第一个是原来的列和一个新的shift()函数产生的列。
我们可以看到,将序列向前移动一步,我们构造出了一个原始的监督学习问题,尽管X和y的顺序是错误的。 忽略行标签的那一列,由于NaN值,第一行需要被丢弃。 第二行显示第二列(输入或X)中的输入值0.0和第一列(输出或y)中的值1。
from pandas import DataFrame
df = DataFrame()
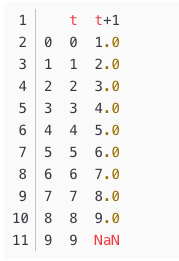
df['t'] = [x for x in range(10)]
df['t+1'] = df['t'].shift(-1)
print(df)
运行该示例,显示了一个最后一行值为NaN的新列。
我们可以看到,原始列可以作为输入(X),第二个新列作为输出值(y)。 那就是输入值0可以用来预测1的输出值。
def series_to_supersived(data,n_in=1,n_out=1,dropnan=True):
"""
Frame a time series as a supervised learning dataset.
Arguments:
data: Sequence of observations as a list or NumPy array.
n_in: Number of lag observations as input (X).
n_out: Number of observations as output (y).
dropnan: Boolean whether or not to drop rows with NaN values.
Returns:
Pandas DataFrame of series framed for supervised learning.
"""
# judge whether the data is list if not then get the data's column
n_vars = 1 if type(data) is list else data.shape[1]
# if the data is list list(data) = ['col1','col2'...]
# if not then get the len of col
df = DataFrame(data)
cols,names = list(),list()
#input sequence(t-n,...t-1)
for i in range(n_in,0,-1):#[n_in,0] step is :-1
cols.append(df.shift(i))
# api df.shift(i) 表示将从第一行开始到i rows变为NaN
# append:对行数进行累加
names += [('var%d(t-%d)' % (j+1,i)) for j in range(n_vars)]
#forecast sequence (t,t+1,...t+n)
for i in range(0,n_out):
cols.append(df.shift(-i))
if i == 0:
names += [('var%d(t)' % (j+1)) for j in range(n_vars)]
else:
names += [('var%d(t+%d)' % (j+1,i)) for j in range(n_vars)]
# put it all together concat
agg = concat(cols,axis=1)
agg.columns = names # columns
#drop rows with Nan values
if dropnan:
agg.dropna(inplace=True)
return agg
- 以上代码大概过程是分别做时间序列列表&列名(根据时间序列) 第一个for循环通过
df.shift()求过去的序列 第二个for 是求未来的序列 接着将其合并 最后丢弃nan的rows - 小测试
>>> df.shift()
A a b c
A
0 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0
2 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0
>>> df.shift(1)
A a b c
A
0 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0
2 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0
>>> df
A a b c
A
0 0 1 2 3
1 4 5 6 7
2 8 9 10 11
>>> df.shift(3)
A a b c
A
0 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1 NaN NaN NaN NaN
2 NaN NaN NaN NaN
>>> x = list()
>>> x
[]
>>> x = df.shift(1)
>>> x
A a b c
A
0 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0
2 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0
>>> x.append(df.shift(2))
A a b c
A
0 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0
2 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0
0 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1 NaN NaN NaN NaN
2 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0
>>> x.append(df.shift(3))
A a b c
A
0 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0
2 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0
0 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1 NaN NaN NaN NaN
2 NaN NaN NaN NaN
2.LabelEncoder()
LabelEncoder()对输入的数据进行加密参考文档
>>> from sklearn import preprocessing
>>> le = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()
>>> le.fit([1,2,2,6])
LabelEncoder()
>>> le.classes_
array([1, 2, 6])
>>> le.transform([1,1,2,6])
array([0, 0, 1, 2])
>>> le.inverse_transform([0,0,1,2])
array([1, 1, 2, 6])
>>> a = le.fit_transform([0,0,1.2])
>>> a
array([0, 0, 1])
3.MinMaxScaler()
def cs_to_sl():
#load data
dataset = read_csv('pollution.csv',header=0,index_col=0)
values = dataset.values
#integer encode direction
encoder = LabelEncoder()
#api LabelEncoder() with [0,n] take the inverse transform 加密进行
values[:,4] = encoder.fit_transform(values[:,4])
#ensure all data is float
values = values.astype('float32')
#normalize feature
scaler =MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0,1))
#scaler = MinMaxScaler(copy=True, feature_range=(0, 1)) method
#api 将属性缩放到一个指定范围 标准化 purpose:1、对于方差非常小的属性可以增强其稳定性。2、维持稀疏矩阵中为0的条目。
#https://www.cnblogs.com/chaosimple/p/4153167.html - reference
scaled = scaler.fit_transform(values)
# handeled dataset :scaled
# frame as supervised learning
reframed = series_to_supersived(scaled,1,1)
#drop columns we dont want to predict
reframed.drop(reframed.columns[[9,10,11,12,13,14,15]], axis=1, inplace=True)
print (reframed.head(10))
return reframed,scaler
4.split data sets
- small demo:
>>> df1 = df.values
>>> df1
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 15, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 51, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 22, 11]])
>>> df1.shape
(3, 5)
>>> train_df1 = df1[:,:-1]
>>> test_df1 = df1[:,-1]
>>> train_df1
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 15],
[ 4, 5, 6, 51],
[ 8, 9, 10, 22]])
>>> train_df1.shape
(3, 4)
>>> test_df1.shape
(3,)
>>> train_df1.shape[1]
4
- train_test func:
def train_test(reframed):
# split into train and test sets
values = reframed.values
n_train_hours = 365 * 24
train = values[:n_train_hours, :]
test = values[n_train_hours:, :]
# split into input and outputs
#left the last one element
train_X, train_y = train[:, :-1], train[:, -1]
test_X, test_y = test[:, :-1], test[:, -1]
# reshape input to be 3D [samples, timesteps, features]
# train_X:[] except 倒数一列 test_X:倒数一列
#train_X.shape[1]:num_col train_X.shape[0]:num_row
train_X = train_X.reshape((train_X.shape[0], 1, train_X.shape[1]))
# test_X.shape[0]:num_rows test_X.shape[1]:num_cols
test_X = test_X.reshape((test_X.shape[0], 1, test_X.shape[1]))
print(train_X.shape, train_y.shape, test_X.shape, test_y.shape)
return train_X,train_y,test_X,test_y





 本文介绍如何使用Pandas的df.shift()函数将时间序列数据转换为适合监督学习的数据集,包括构建输入和输出序列,以及如何处理NaN值。同时,探讨了LabelEncoder()和MinMaxScaler()在数据预处理中的应用,以及如何划分训练集和测试集。
本文介绍如何使用Pandas的df.shift()函数将时间序列数据转换为适合监督学习的数据集,包括构建输入和输出序列,以及如何处理NaN值。同时,探讨了LabelEncoder()和MinMaxScaler()在数据预处理中的应用,以及如何划分训练集和测试集。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








