编译ONNX模型
下面描述使用Relay如何部署ONNX模型:
#安装onnx,https://github.com/onnx/onnx
pip install onnx --user
首先导入所需要的python包:
import onnx
import numpy as np
import tvm
import tvm.relay as relay
from tvm.contrib.download import download_testdata
加载预训练ONNX模型
model_url = ''.join(['https://gist.github.com/zhreshold/', 'bcda4716699ac97ea44f791c24310193/raw/','93672b029103648953c4e5ad3ac3aadf346a4cdc/','super_resolution_0.2.onnx'])
model_path = download_testdata(model_url, 'super_resolution.onnx', module='onnx')
#从硬盘加载supe_resolution.onnx
onnx_model = onnx.load(model_path)
加载一张测试图像
from PIL import Image
img_url = 'https://github.com/dmlc/mxnet.js/blob/master/data/cat.png?raw=true'
img_path = download_testdata(img_url, 'cat.png', module='data')
img = Image.open(img_path).resize((224,224))
img_ycbcr = img.convert("YCbCr")
img_y, img_cb, img_cr = img_ycbcr.split()
x = np.array(img_y)[np.newaxis, np.newaxis, :, :]
使用relay编译模型
target = 'llvm'
input_name = '1'
shape_dict = {input_name: x.shape}
sym, params = relay.frontend.from_onnx(onnx_model, shape_dict)
with relay.build_config(opt_level = 1):
intrp = relay.build_module.create_executor('graph',sym, tvm.cpu(0), target)
在TVM上执行
dtype = 'float32'
tvm_output = intrp.evaluate(sym)(tvm.nd.array(x.astype(dtype)),**params).asnumpy()
显示结果
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
out_y = Image.fromarray(np.uint8((tvm_output[0,0]).clip(0, 255)),model='L')
out_cb = img_cb.resize(out_y.size, Image.BICUBIC)
out_cr = img_cr.resize(out_y.size, Image.BICUBIC)
result = Image.merge('YCbCr', [out_y, out_cb, out_cr]).convert('RGB')
canvas = np.full((672,672*2,3),255)
canvas[0:224, 0:224, :] = np.asarray(img)
canvas[:, 672:, :] = np.asarray(result)
plt.imshow(canvas.astype(np.uint8))
plt.show()




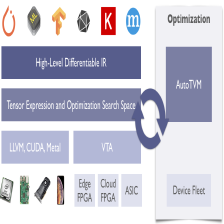
 本文是TVM Compiler的中文教程,详细介绍了如何加载预训练的ONNX模型,加载测试图像,通过Relay进行模型编译,并在TVM上执行,最后展示执行结果。
本文是TVM Compiler的中文教程,详细介绍了如何加载预训练的ONNX模型,加载测试图像,通过Relay进行模型编译,并在TVM上执行,最后展示执行结果。
















 91
91

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








