package Interface;
public interface ICLinked {
void addFirst(int data);
void addLast(int data);
boolean addindex(int index,int data);
boolean contains(int key);
int remove(int key);
void removeAllKey(int key);
int getLength();
void display();
void clear();
}
package DS;
import Interface.ICLinked;
public class MyHeadSingleListImpl implements ICLinked {
class Node {
private int data;
private Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
public Node() {
this.data = -1;
this.next = null;
}
}
private Node head;
private MyHeadSingleListImpl() {
this.head = new Node();
this.head.next = this.head;
}
@Override
public void addFirst(int data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
node.next = this.head.next;
this.head.next = node;
}
@Override
public void addLast(int data) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != this.head) {
cur = cur.next;
}
Node node = new Node(data);
node.next = this.head;
cur.next = node;
}
@Override
public boolean addindex(int index, int data) {
if (index < 0 || index > getLength()) {
return false;
}
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return true;
} else if (index == getLength()) {
addLast(data);
return true;
}
Node cur = this.head.next;
int count = 1;
while (count != index) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
Node node = new Node(data);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(int key) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != this.head) {
if (cur.data == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if (cur.data == key) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public Node SearchPrev(int key) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != this.head) {
if (cur.next.data == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public int remove(int key) {
if(this.head == null ){
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("单链表为空");
}
Node prev = SearchPrev(key);
if (prev == null) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("没有前驱!");
}
if (this.head.data == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return key;
}
Node delete = prev.next;
prev.next = delete.next;
return delete.data;
}
@Override
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if (this.head == null || this.head.next == this.head) {
return;
}
if (this.head.data == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
Node prev = this.head;
Node cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != this.head) {
if (cur.data == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = prev.next;
} else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
@Override
public int getLength() {
Node cur = this.head;
int length = 0;
while (cur.next != this.head) {
length++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return length;
}
@Override
public void display() {
Node cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != this.head) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
@Override
public void clear() {
}
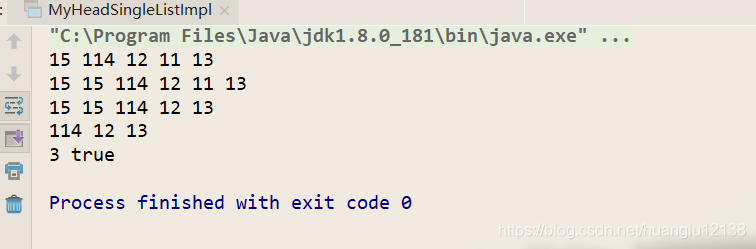
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyHeadSingleListImpl m = new MyHeadSingleListImpl();
m.addLast(13);
m.addFirst(11);
m.addFirst(12);
m.addFirst(114);
m.addFirst(15);
m.display();
m.addindex(1,15);
m.display();
m.remove(11);
m.display();
m.removeAllKey(15);
m.display();
System.out.println(m.getLength()+" "+m.contains(12));
}
}








 本文介绍了一种带头结点的循环单链表的数据结构实现,包括头插法、尾插法、任意位置插入等核心操作,并实现了查找、删除等功能。
本文介绍了一种带头结点的循环单链表的数据结构实现,包括头插法、尾插法、任意位置插入等核心操作,并实现了查找、删除等功能。
















 1283
1283

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








