开发中有时会遇到这样的情况。要求某个调度器去调度一些任务,这些任务放在队列里。任务本身有优先级,调度器要按照优先级去调度队列里的任务,当然也会有新任务不断加入到队列中。
可以类比操作系统调度程序,操作系统要调度某个进程,简单的说会根据某种优先级进行调度(比如某些情况下,先执行时间较短的任务,保证短任务尽快结束。)
所以期望有这样一种数据结构,首先它是一个队列,可以从这个队列中不断取出优先级最高的(也可以认为是最大的或者最小的,因为本质是通过比较决定。)元素。也可以不断的将新元素添加到这个队列。
这种数据结构就叫做优先队列。优先队列的实现方式有很多,但好的实现应该保证关键的操作(如将一个元素放入队列;将优先级最大的元素移出队列等)比较高效。有一种数据结构可以比较高效的实现优先队列,这种数据结构叫二叉堆(binary heap)。
二叉堆形式上是一棵完全二叉树,它的一个重要性质是堆序性,即对于堆中任一个节点n,节点n上的元素e都要小于或等于其子节点(左右两个儿子节点)上的元素。
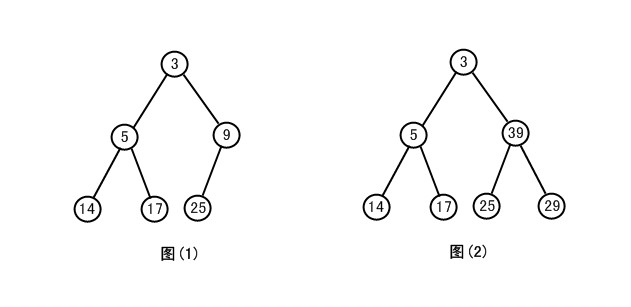
上图中,图(1)和图(2)都是完全二叉树,但只有图(1)是二叉堆,因为图(2)中39大于25和29,不满足堆序性。
接下来看一下,这样的数据结构怎么支持优先队列的操作。
先考虑下获取最小元素的操作,因为最小元素就在树的根节点,所以这个操作只要返回树根节点的元素就行了,操作时间为常数时间。
在看一下添加一个元素的操作,因为二叉堆是一个完全二叉树,所以添加一个元素时首先要将元素添加到完全二叉树的下一个节点上,然后进行一些调整来保证堆序性。
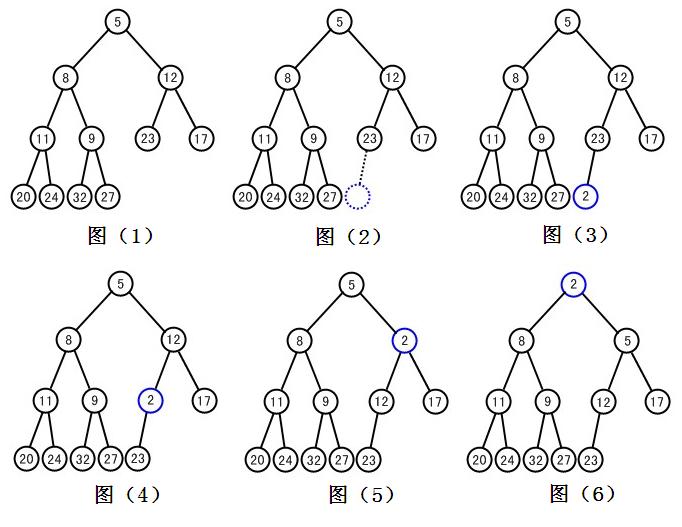
假设要在图(1)中的二叉堆中添加新元素2,图(2)中标出了新元素2要加入的节点,将元素添加到此节点上,就完成了第一步添加操作,如图(3)。接下来是调整操作,为了保证堆序性。首先将新节点与其父节点进行比较(比较元素大小),如果父节点元素小于新节点元素,那么交换新节点和父节点的元素,如图(4)。然后依次类推,继续向上比较,如图(5)、图(6),一直到当前比较节点大于其父节点,或者没有父节点(到达根节点)为止。
可以看到,上图中新添元素向上移动过程中比较次数正好是这个完全二叉树的高,而且上图表示是最差情况(需要比较并移动的次数最多)。所以在二叉堆中新添一个元素的操作时间是O(logN)。
最后看一下移除最小元素的操作(等同于优先级最大元素出队列操作)。因为最小元素就在树根,所以将最小元素移除很简单。但移除之后需要做一系列调整,以保证二叉堆的堆序性。
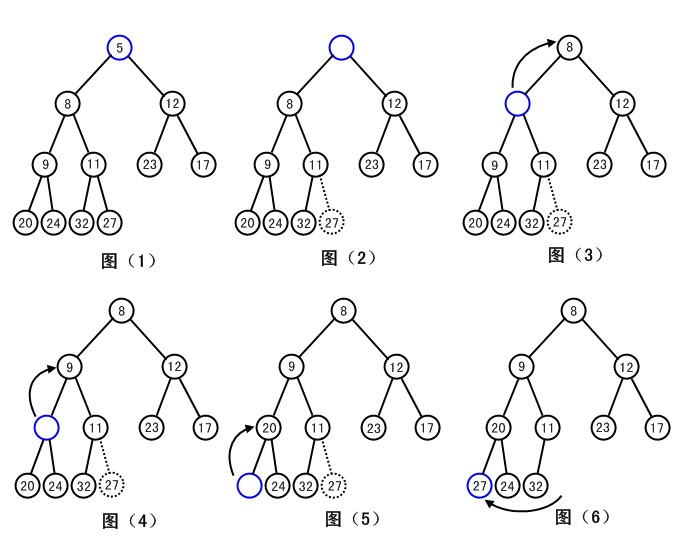
当我们移除最小元素时,如图(1)。先将最小元素移除(移除根节点上的元素),并将完全二叉树的最后节点删除,保留其元素(这一步相当于在二叉堆中删除一个元素时,缩短其长度),如图(2)。由于树根没有元素,我们需要把下面的元素向上移动。在移动过程中需要保证堆序性,所以当树根没有元素时,将树根的两个儿子节点中较小的一个中的元素放到树根节点中,如图(3)。现在树根的左子节点元素为空了,我们以同样的方式对其进行处理,直到某个空节点的两个子节点中的元素都大于图(1)中的保留元素27,或者某个空节点没有子节点为止,然后将保留元素27放到这个空节点中。(上图中没有表现出现第一种情况,假设图(4)中空节点下面的两个子节点所带元素为30和34,再想一下上图中的流程)。
这个过程删掉了最小元素同时保证了堆序性,同时也可以看到这个操作的时间也是O(logN)。
以上是二叉堆可支持优先队列的主要操作,从中也可以看到,二叉堆只是把最小元素放在树根节点上,其他元素的顺序是无法保证的。(当然也可以把最大元素放到根节点,因为保证堆序性的过程基于比较。所以有最小堆和最大堆的说法)
有了二叉堆的理论基础,就可以看下java.util.PriorityQueue的源码了。
首先看到PriorityQueue有一个内部数组,用来存储元素。那么一个数组怎么和一个二叉堆(完全二叉树)联系起来呢?我们不妨用上面第二张图中图(1)的二叉堆举个例子。将这个二叉堆中的元素按层级从左到右进行遍历,并放到一个数组里。如下:
由于完全二叉数的特殊性,这个数组里array[n]的左子节点在array[2n+1]位置,右子节点在array[2n+2]位置。array[0]可以认为是根节点。一个树形结构用简单的数组来表示,是不是感觉很爽,嘎嘎。
还有一个重要的内部成员是comparator,通过前面知道二叉堆内部通过比较来保证堆序性,所以通过这个比较器可以大致了解到PriorityQueue内部的比较机制了。PriorityQueue内部做比较时,会先通过comparator进行比较;如果没有提供comparator,那么会根据元素的自然顺序进行比较。
这里注意一下自然顺序。比如我们要在这个优先队列里放基本类型或者String类型,由于在集合里放基本类型必须将集合上的泛型声明为其对应的包装类,当元素加入集合时会自动装箱。那么随便找个包装类看看,就看java.lang.Integer吧:
可以看到这货实现了一个接口java.lang.Comparable。
Comparable接口就定义了一个方法,就是和另一个同类型的元素进行比较。如比另一个元素小,就返回负数;相等就返回零;比另一个元素大就返回正数。当然这里的大小不是狭义的数值的大小,也可以认为是两的对象位置先后等等。
那么来看一下java.lang.Integer的自然顺序是啥?
比较的问题不是重点,就说到这儿。总之能了解PriorityQueue里怎么比较元素即可。
其他的属性都没什么可说的。接下来是一系列构造方法,也没什么可说的。
下面看一下添加元素的操作。
add方法中调用了offer,offer方法中首先是一些判断,在必要的时候进行内部数组的扩容。然后将元素e添加到数组的下一个空位(下标为size),当数组中本来没有元素时,说明添加的第一个元素,直接放到queue[0](根节点)上。否则,要调用一个siftUp的方法。看方法名称和我们上面提到的二叉堆添加一个元素后向上移动的动作很像吧,看看实现:
在siftUp里首先检查有没有比较器,没有的话就使用自然顺序的方式比较,所以在siftUpComparable方法里会看到一个Comparable类型的强转。至于siftUpUsingComparator和siftUpComparable方法里的逻辑都是一样的,看一个就行了。
那就看siftUpUsingComparator吧。首先构造一个while循环,k>0是条件(因为根节点下标是0)。由上面的提到的内部数组的特性可知(queue[k]的左右子节点的位置是2k+1和2k+2),当前位置节点的父节点的位置是(k - 1) >>> 1(相当于k除以2)。然后得到父节点的元素并和当前要添加的元素进行比较。如果当前元素x小于k位置的父元素e,那么把父元素放到k位置,并把k指向父节点位置,继续循环。知道当前元素x大于k位置的父元素,或者k=0(到达根节点),那么将当前元素x放到k位置。基本上实现了上面提到的二叉堆的添加逻辑。
获取最小(大)元素的方法一目了然。
看一下移除最小(大)元素的方法,也就是出队列的方法。
对比上面提到的二叉堆的移除操作逻辑。E result = (E) queue[0]确定了要返回的是根节点元素;E x = (E) queue[s]拿到了二叉堆最后位置的元素;queue[s] = null移除最后的节点。接下来就是最后的元素该放在哪的问题了,二叉堆里只能一个元素的时候,直接返回;否则调用siftDown方法。
siftDown就是向下移动,保证堆序的逻辑了。直接看siftDownUsingComparator的代码吧。先通过size >>> 1得到一个half值,然后在k < half的条件下做循环。因为在内部数组的特殊性下,如果k>=half,那么k位置的节点不存在子节点。然后得到k位置的左子节点位置,并得到其元素c。然后获取其右子节点(如果有的话),并和左子节点进行比较,如果右子节点的元素小于左子结点的元素,那么将child指向右子结点的下标并将c指向右子结点的元素,然后和x比较(也就是用两个子节点中最小的和x比较)。如果c小于当前元素x,那么用c来填补k位置,并将k指向较小的子节点的位置,继续循环。直到c大于等于x,或者k位置没有子节点,那么将x填入k位置。
再看下另外几个基于siftUp和siftDown的方法。
这个方法表示删除某个下标的元素。因为删除后还要做移动操作来保证堆序性,所以在删除的位置上先拿数组中最后一个元素进行siftDown,如果没有任何移动,再进行siftUp。
这个操作也比较重要,它将一个普通数组构建成一个二叉堆。有了上面的分析代码很好理解,感兴趣的话可以画图来理解一下过程。这个操作以线性平均时间完成。
这里有一个有趣的问题,前面提到二叉堆不保证最大元素(或最小元素)之外元素的顺序。但我们想一下,如果用构建二叉堆的方法将一个数组构建成一个二叉堆,然后移除最大(或最小)元素n次(数组长度为n),并将每次移除的元素放到另外一个数组中(或者放到本数组中每次的废弃位置也可以),那么这个数组不就排好序了么!这种方法叫做堆排序,由于构建一个堆要平均O(N)时间,再加上遍历N次,每次O(logN)的操作时间,所以堆排序的时间复杂度是O(NlogN)。
好了,其他的代码也应该很容易看懂了。java.util.PriorityQueue就总结到这里!
可以类比操作系统调度程序,操作系统要调度某个进程,简单的说会根据某种优先级进行调度(比如某些情况下,先执行时间较短的任务,保证短任务尽快结束。)
所以期望有这样一种数据结构,首先它是一个队列,可以从这个队列中不断取出优先级最高的(也可以认为是最大的或者最小的,因为本质是通过比较决定。)元素。也可以不断的将新元素添加到这个队列。
这种数据结构就叫做优先队列。优先队列的实现方式有很多,但好的实现应该保证关键的操作(如将一个元素放入队列;将优先级最大的元素移出队列等)比较高效。有一种数据结构可以比较高效的实现优先队列,这种数据结构叫二叉堆(binary heap)。
二叉堆形式上是一棵完全二叉树,它的一个重要性质是堆序性,即对于堆中任一个节点n,节点n上的元素e都要小于或等于其子节点(左右两个儿子节点)上的元素。

上图中,图(1)和图(2)都是完全二叉树,但只有图(1)是二叉堆,因为图(2)中39大于25和29,不满足堆序性。
接下来看一下,这样的数据结构怎么支持优先队列的操作。
先考虑下获取最小元素的操作,因为最小元素就在树的根节点,所以这个操作只要返回树根节点的元素就行了,操作时间为常数时间。
在看一下添加一个元素的操作,因为二叉堆是一个完全二叉树,所以添加一个元素时首先要将元素添加到完全二叉树的下一个节点上,然后进行一些调整来保证堆序性。

假设要在图(1)中的二叉堆中添加新元素2,图(2)中标出了新元素2要加入的节点,将元素添加到此节点上,就完成了第一步添加操作,如图(3)。接下来是调整操作,为了保证堆序性。首先将新节点与其父节点进行比较(比较元素大小),如果父节点元素小于新节点元素,那么交换新节点和父节点的元素,如图(4)。然后依次类推,继续向上比较,如图(5)、图(6),一直到当前比较节点大于其父节点,或者没有父节点(到达根节点)为止。
可以看到,上图中新添元素向上移动过程中比较次数正好是这个完全二叉树的高,而且上图表示是最差情况(需要比较并移动的次数最多)。所以在二叉堆中新添一个元素的操作时间是O(logN)。
最后看一下移除最小元素的操作(等同于优先级最大元素出队列操作)。因为最小元素就在树根,所以将最小元素移除很简单。但移除之后需要做一系列调整,以保证二叉堆的堆序性。

当我们移除最小元素时,如图(1)。先将最小元素移除(移除根节点上的元素),并将完全二叉树的最后节点删除,保留其元素(这一步相当于在二叉堆中删除一个元素时,缩短其长度),如图(2)。由于树根没有元素,我们需要把下面的元素向上移动。在移动过程中需要保证堆序性,所以当树根没有元素时,将树根的两个儿子节点中较小的一个中的元素放到树根节点中,如图(3)。现在树根的左子节点元素为空了,我们以同样的方式对其进行处理,直到某个空节点的两个子节点中的元素都大于图(1)中的保留元素27,或者某个空节点没有子节点为止,然后将保留元素27放到这个空节点中。(上图中没有表现出现第一种情况,假设图(4)中空节点下面的两个子节点所带元素为30和34,再想一下上图中的流程)。
这个过程删掉了最小元素同时保证了堆序性,同时也可以看到这个操作的时间也是O(logN)。
以上是二叉堆可支持优先队列的主要操作,从中也可以看到,二叉堆只是把最小元素放在树根节点上,其他元素的顺序是无法保证的。(当然也可以把最大元素放到根节点,因为保证堆序性的过程基于比较。所以有最小堆和最大堆的说法)
有了二叉堆的理论基础,就可以看下java.util.PriorityQueue的源码了。

- public class PriorityQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
- implements java.io.Serializable {
- private static final long serialVersionUID = -7720805057305804111L;
- private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;
- /**
- * Priority queue represented as a balanced binary heap: the two
- * children of queue[n] are queue[2*n+1] and queue[2*(n+1)]. The
- * priority queue is ordered by comparator, or by the elements'
- * natural ordering, if comparator is null: For each node n in the
- * heap and each descendant d of n, n <= d. The element with the
- * lowest value is in queue[0], assuming the queue is nonempty.
- */
- private transient Object[] queue;
- /**
- * The number of elements in the priority queue.
- */
- private int size = 0;
- /**
- * The comparator, or null if priority queue uses elements'
- * natural ordering.
- */
- private final Comparator<? super E> comparator;
- /**
- * The number of times this priority queue has been
- * <i>structurally modified</i>. See AbstractList for gory details.
- */
- private transient int modCount = 0;
首先看到PriorityQueue有一个内部数组,用来存储元素。那么一个数组怎么和一个二叉堆(完全二叉树)联系起来呢?我们不妨用上面第二张图中图(1)的二叉堆举个例子。将这个二叉堆中的元素按层级从左到右进行遍历,并放到一个数组里。如下:
- [5,8,12,11,9,23,17,20,24,32,27]
由于完全二叉数的特殊性,这个数组里array[n]的左子节点在array[2n+1]位置,右子节点在array[2n+2]位置。array[0]可以认为是根节点。一个树形结构用简单的数组来表示,是不是感觉很爽,嘎嘎。
还有一个重要的内部成员是comparator,通过前面知道二叉堆内部通过比较来保证堆序性,所以通过这个比较器可以大致了解到PriorityQueue内部的比较机制了。PriorityQueue内部做比较时,会先通过comparator进行比较;如果没有提供comparator,那么会根据元素的自然顺序进行比较。
这里注意一下自然顺序。比如我们要在这个优先队列里放基本类型或者String类型,由于在集合里放基本类型必须将集合上的泛型声明为其对应的包装类,当元素加入集合时会自动装箱。那么随便找个包装类看看,就看java.lang.Integer吧:
- public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer> {
可以看到这货实现了一个接口java.lang.Comparable。
- public interface Comparable<T> {
- public int compareTo(T o);
- }
Comparable接口就定义了一个方法,就是和另一个同类型的元素进行比较。如比另一个元素小,就返回负数;相等就返回零;比另一个元素大就返回正数。当然这里的大小不是狭义的数值的大小,也可以认为是两的对象位置先后等等。
那么来看一下java.lang.Integer的自然顺序是啥?
- public int compareTo(Integer anotherInteger) {
- int thisVal = this.value;
- int anotherVal = anotherInteger.value;
- return (thisVal<anotherVal ? -1 : (thisVal==anotherVal ? 0 : 1));
- }
比较的问题不是重点,就说到这儿。总之能了解PriorityQueue里怎么比较元素即可。
其他的属性都没什么可说的。接下来是一系列构造方法,也没什么可说的。
- /**
- * Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} with the specified initial
- * capacity that orders its elements according to their
- * {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering}.
- *
- * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity for this priority queue
- * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code initialCapacity} is less
- * than 1
- */
- public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity) {
- this(initialCapacity, null);
- }
- /**
- * Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} with the specified initial capacity
- * that orders its elements according to the specified comparator.
- *
- * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity for this priority queue
- * @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this
- * priority queue. If {@code null}, the {@linkplain Comparable
- * natural ordering} of the elements will be used.
- * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code initialCapacity} is
- * less than 1
- */
- public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity,
- Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
- // Note: This restriction of at least one is not actually needed,
- // but continues for 1.5 compatibility
- if (initialCapacity < 1)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException();
- this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity];
- this.comparator = comparator;
- }
- /**
- * Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} containing the elements in the
- * specified collection. If the specified collection is an instance of
- * a {@link SortedSet} or is another {@code PriorityQueue}, this
- * priority queue will be ordered according to the same ordering.
- * Otherwise, this priority queue will be ordered according to the
- * {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} of its elements.
- *
- * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed
- * into this priority queue
- * @throws ClassCastException if elements of the specified collection
- * cannot be compared to one another according to the priority
- * queue's ordering
- * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection or any
- * of its elements are null
- */
- public PriorityQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {
- initFromCollection(c);
- if (c instanceof SortedSet)
- comparator = (Comparator<? super E>)
- ((SortedSet<? extends E>)c).comparator();
- else if (c instanceof PriorityQueue)
- comparator = (Comparator<? super E>)
- ((PriorityQueue<? extends E>)c).comparator();
- else {
- comparator = null;
- heapify();
- }
- }
- /**
- * Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} containing the elements in the
- * specified priority queue. This priority queue will be
- * ordered according to the same ordering as the given priority
- * queue.
- *
- * @param c the priority queue whose elements are to be placed
- * into this priority queue
- * @throws ClassCastException if elements of {@code c} cannot be
- * compared to one another according to {@code c}'s
- * ordering
- * @throws NullPointerException if the specified priority queue or any
- * of its elements are null
- */
- public PriorityQueue(PriorityQueue<? extends E> c) {
- comparator = (Comparator<? super E>)c.comparator();
- initFromCollection(c);
- }
- /**
- * Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} containing the elements in the
- * specified sorted set. This priority queue will be ordered
- * according to the same ordering as the given sorted set.
- *
- * @param c the sorted set whose elements are to be placed
- * into this priority queue
- * @throws ClassCastException if elements of the specified sorted
- * set cannot be compared to one another according to the
- * sorted set's ordering
- * @throws NullPointerException if the specified sorted set or any
- * of its elements are null
- */
- public PriorityQueue(SortedSet<? extends E> c) {
- comparator = (Comparator<? super E>)c.comparator();
- initFromCollection(c);
- }
下面看一下添加元素的操作。
- /**
- * Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
- *
- * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
- * @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be
- * compared with elements currently in this priority queue
- * according to the priority queue's ordering
- * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
- */
- public boolean add(E e) {
- return offer(e);
- }
- /**
- * Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
- *
- * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
- * @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be
- * compared with elements currently in this priority queue
- * according to the priority queue's ordering
- * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
- */
- public boolean offer(E e) {
- if (e == null)
- throw new NullPointerException();
- modCount++;
- int i = size;
- if (i >= queue.length)
- grow(i + 1);
- size = i + 1;
- if (i == 0)
- queue[0] = e;
- else
- siftUp(i, e);
- return true;
- }
add方法中调用了offer,offer方法中首先是一些判断,在必要的时候进行内部数组的扩容。然后将元素e添加到数组的下一个空位(下标为size),当数组中本来没有元素时,说明添加的第一个元素,直接放到queue[0](根节点)上。否则,要调用一个siftUp的方法。看方法名称和我们上面提到的二叉堆添加一个元素后向上移动的动作很像吧,看看实现:
- /**
- * Inserts item x at position k, maintaining heap invariant by
- * promoting x up the tree until it is greater than or equal to
- * its parent, or is the root.
- *
- * To simplify and speed up coercions and comparisons. the
- * Comparable and Comparator versions are separated into different
- * methods that are otherwise identical. (Similarly for siftDown.)
- *
- * @param k the position to fill
- * @param x the item to insert
- */
- private void siftUp(int k, E x) {
- if (comparator != null)
- siftUpUsingComparator(k, x);
- else
- siftUpComparable(k, x);
- }
- private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) {
- Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x;
- while (k > 0) {
- int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
- Object e = queue[parent];
- if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0)
- break;
- queue[k] = e;
- k = parent;
- }
- queue[k] = key;
- }
- private void siftUpUsingComparator(int k, E x) {
- while (k > 0) {
- int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
- Object e = queue[parent];
- if (comparator.compare(x, (E) e) >= 0)
- break;
- queue[k] = e;
- k = parent;
- }
- queue[k] = x;
- }
在siftUp里首先检查有没有比较器,没有的话就使用自然顺序的方式比较,所以在siftUpComparable方法里会看到一个Comparable类型的强转。至于siftUpUsingComparator和siftUpComparable方法里的逻辑都是一样的,看一个就行了。
那就看siftUpUsingComparator吧。首先构造一个while循环,k>0是条件(因为根节点下标是0)。由上面的提到的内部数组的特性可知(queue[k]的左右子节点的位置是2k+1和2k+2),当前位置节点的父节点的位置是(k - 1) >>> 1(相当于k除以2)。然后得到父节点的元素并和当前要添加的元素进行比较。如果当前元素x小于k位置的父元素e,那么把父元素放到k位置,并把k指向父节点位置,继续循环。知道当前元素x大于k位置的父元素,或者k=0(到达根节点),那么将当前元素x放到k位置。基本上实现了上面提到的二叉堆的添加逻辑。
获取最小(大)元素的方法一目了然。
- public E peek() {
- if (size == 0)
- return null;
- return (E) queue[0];
- }
看一下移除最小(大)元素的方法,也就是出队列的方法。
- public E poll() {
- if (size == 0)
- return null;
- int s = --size;
- modCount++;
- E result = (E) queue[0];
- E x = (E) queue[s];
- queue[s] = null;
- if (s != 0)
- siftDown(0, x);
- return result;
- }
对比上面提到的二叉堆的移除操作逻辑。E result = (E) queue[0]确定了要返回的是根节点元素;E x = (E) queue[s]拿到了二叉堆最后位置的元素;queue[s] = null移除最后的节点。接下来就是最后的元素该放在哪的问题了,二叉堆里只能一个元素的时候,直接返回;否则调用siftDown方法。
- /**
- * Inserts item x at position k, maintaining heap invariant by
- * demoting x down the tree repeatedly until it is less than or
- * equal to its children or is a leaf.
- *
- * @param k the position to fill
- * @param x the item to insert
- */
- private void siftDown(int k, E x) {
- if (comparator != null)
- siftDownUsingComparator(k, x);
- else
- siftDownComparable(k, x);
- }
- private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) {
- Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x;
- int half = size >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf
- while (k < half) {
- int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least
- Object c = queue[child];
- int right = child + 1;
- if (right < size &&
- ((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0)
- c = queue[child = right];
- if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0)
- break;
- queue[k] = c;
- k = child;
- }
- queue[k] = key;
- }
- private void siftDownUsingComparator(int k, E x) {
- int half = size >>> 1;
- while (k < half) {
- int child = (k << 1) + 1;
- Object c = queue[child];
- int right = child + 1;
- if (right < size &&
- comparator.compare((E) c, (E) queue[right]) > 0)
- c = queue[child = right];
- if (comparator.compare(x, (E) c) <= 0)
- break;
- queue[k] = c;
- k = child;
- }
- queue[k] = x;
- }
siftDown就是向下移动,保证堆序的逻辑了。直接看siftDownUsingComparator的代码吧。先通过size >>> 1得到一个half值,然后在k < half的条件下做循环。因为在内部数组的特殊性下,如果k>=half,那么k位置的节点不存在子节点。然后得到k位置的左子节点位置,并得到其元素c。然后获取其右子节点(如果有的话),并和左子节点进行比较,如果右子节点的元素小于左子结点的元素,那么将child指向右子结点的下标并将c指向右子结点的元素,然后和x比较(也就是用两个子节点中最小的和x比较)。如果c小于当前元素x,那么用c来填补k位置,并将k指向较小的子节点的位置,继续循环。直到c大于等于x,或者k位置没有子节点,那么将x填入k位置。
再看下另外几个基于siftUp和siftDown的方法。
- /**
- * Removes the ith element from queue.
- *
- * Normally this method leaves the elements at up to i-1,
- * inclusive, untouched. Under these circumstances, it returns
- * null. Occasionally, in order to maintain the heap invariant,
- * it must swap a later element of the list with one earlier than
- * i. Under these circumstances, this method returns the element
- * that was previously at the end of the list and is now at some
- * position before i. This fact is used by iterator.remove so as to
- * avoid missing traversing elements.
- */
- private E removeAt(int i) {
- assert i >= 0 && i < size;
- modCount++;
- int s = --size;
- if (s == i) // removed last element
- queue[i] = null;
- else {
- E moved = (E) queue[s];
- queue[s] = null;
- siftDown(i, moved);
- if (queue[i] == moved) {
- siftUp(i, moved);
- if (queue[i] != moved)
- return moved;
- }
- }
- return null;
- }
这个方法表示删除某个下标的元素。因为删除后还要做移动操作来保证堆序性,所以在删除的位置上先拿数组中最后一个元素进行siftDown,如果没有任何移动,再进行siftUp。
- /**
- * Establishes the heap invariant (described above) in the entire tree,
- * assuming nothing about the order of the elements prior to the call.
- */
- private void heapify() {
- for (int i = (size >>> 1) - 1; i >= 0; i--)
- siftDown(i, (E) queue[i]);
- }
这个操作也比较重要,它将一个普通数组构建成一个二叉堆。有了上面的分析代码很好理解,感兴趣的话可以画图来理解一下过程。这个操作以线性平均时间完成。
这里有一个有趣的问题,前面提到二叉堆不保证最大元素(或最小元素)之外元素的顺序。但我们想一下,如果用构建二叉堆的方法将一个数组构建成一个二叉堆,然后移除最大(或最小)元素n次(数组长度为n),并将每次移除的元素放到另外一个数组中(或者放到本数组中每次的废弃位置也可以),那么这个数组不就排好序了么!这种方法叫做堆排序,由于构建一个堆要平均O(N)时间,再加上遍历N次,每次O(logN)的操作时间,所以堆排序的时间复杂度是O(NlogN)。
好了,其他的代码也应该很容易看懂了。java.util.PriorityQueue就总结到这里!





 本文深入探讨了Java PriorityQueue的数据结构实现,包括优先队列的底层原理、操作方法及性能分析,帮助开发者掌握如何利用PriorityQueue高效地管理具有优先级的任务队列。
本文深入探讨了Java PriorityQueue的数据结构实现,包括优先队列的底层原理、操作方法及性能分析,帮助开发者掌握如何利用PriorityQueue高效地管理具有优先级的任务队列。

















 411
411

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








