定义和概念:
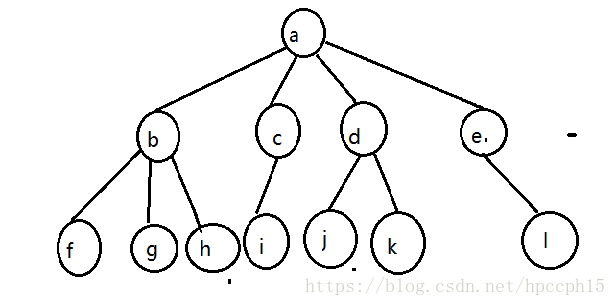
- 树的一种定义方式是递归的方式:一棵树是一些节点的集合,这个集合可以是空集 ,若不是空集,则树由称作根的节点及0个或多个子树组成,如图,由根节点a和四棵子树组成,而每一个子树也有其自己的根节点和子树。
- 根节点子树的根称为根节点的儿子,如图a节点的儿子是b,c,d,e,节点e的儿子是 l,l 的父亲是e。
- 没有儿子的节点称为树叶,如图f g h i j k l都是树叶。
- 有同一个父亲的节点之间互为兄弟。
- 结点的深度:从该节点到树根的路径长度,根节点的深度为0,如图b的深度为1.
- 树的深度:最深的树叶的深度。如图该树的深度是2。
- 节点的高:从该节点出发到最深的树叶的路经长,如图,b的高是1,a的高是2. 显然,树叶的高为0.
- 树的高:总是等于树的深度。
树的实现:
由于声明每一个节点都必须要表示出每个节点的数据还要有该节点指向的儿子的链,然而实现树的数据结构建立每一个儿子的链接是不可行的,可建立第一个儿子的链接,然后使其指向其下一兄弟。如图所示,将上图转换之后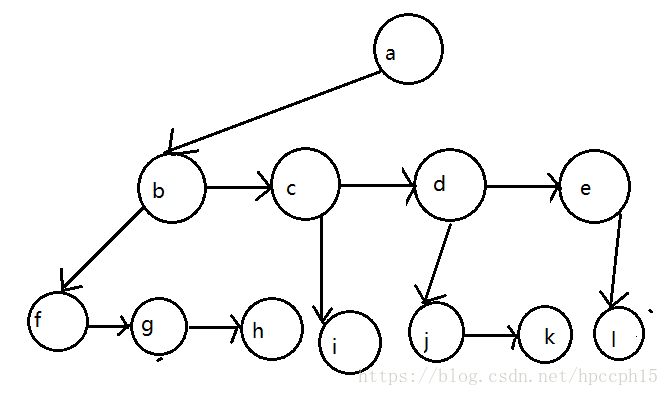
class TreeNode
{
Object element;
TreeNode firstChild;//第一个儿子
TreeNode nextSibling;//下一个兄弟
}树的遍历:
- 先序遍历:根—->左儿子—->右儿子
- 中序遍历: 左儿子—->根—->右儿子
- 后序遍历: 左儿子—->右儿子—->根
二叉树:
每个节点不能有多余两个儿子的树。
实现:
class BinaryNode
{
Object element;
BinaryNode left;
BInaryNode right;
}二叉查找树(重点):
1.二叉查找树的性质:对于树中的每一个节点x,它的左子树中的所有值都比x小,它的右子树的所有值都比x大。
2.同样使用递归实现。
private static class BInaryNode<AnyType>
{
AnyType element;
BinaryType<AnyType> left;
BinaryType<AnyType> right;
BinaryNode(AnyType theElement)
{
this(theElement,null,null);
}
BinaryNode(AnyType theElement,BinaryNode<AnyType> lt,BinaryNode<AnyType> rt)
{
element = theElement;//节点数据
left = lt;//左孩子
right = rt;//右孩子
}
} 3.二叉查找树的架构
public class BinarySearchTree<AnyType extends Comparable<? super AnyType>>
//二叉查找树要求所有项都能排序,所以继承了Comparable接口。
{
private static class BinaryNode<AnyType>
{
//通过递归可实现二叉查找树的节点类,并将该类作为内部类。
}
private BinaryNode<AnyType> root;//该架构唯一的数据域就是对根节点的引用
public BinarySearch()
{
root = null;//空树为null
}
public void makeEmpty(){root = null;}
public blooean isEmpty(){return root == null;}
public boolean contains(AnyType x){return contains(x,root);}
public AnyType findMin()
{
if(isEmpty()) throw new UnderflowException();
return findMin(root).element;
}
public AnyType findMax()
{
if(isEmpty()) throw new UnderflowException();
return findMax(root).element;
}
public void insert(AnyType x){root = insert(x,root);}//插入数据后重置根节点的引用
public void remove(AnyType x){root = remove(x,root);}//删除数据后重置根节点的引用
private boolean contains(AnyType x,BinaryNode<AnyType t>)
{
if(t == null)return false;
int compareResult = x.compareTo(t.element);//因为继承了compareable所以可通过compareTo()比较。
if(compareResult<0)
return contains(x,t.left);//如果插入值小于根节点,再比较左孩子
else if(compareResult>0)
return contains(x,t.right);//如果插入值大于根节点,比较右孩子
else
return true;如果等于返回true
}
private BinaryNode<AnyType> findMin(BinaryNode t)
{
if(t == null)
return null;
else if(t.left == null)
return t;
return findMin(t.left);//通过递归实现查找
}
private BinaryNode<AnyType> findMax(AnyType t)
{
if(t!=null)
while(t.right!=null)
t = t.right;
return t;//非递归查找
}
private BinaryNode<AnyType> insert(AnyType x,BinaryNode t)
{
if(t = null)
return new BinaryNode(x,null,null);
int compareResult = x.compareTo(t.element);
if(compareResult<0)
t.left = insert(x,t.left);//如果比根节点小,则在左子树中插入,引用的是左子树的根节点,由于插入后左子树的结构发生变化,所以重置左子树跟节点的引用。
else if(compareResult>0)
t.right = insert(x,t.right);//与左同理
else
;//相等的话什么都不用做
return t;
}
private BinaryNode<AnyType> remove(AnyType x,BinaryNode<AnyType> t)
{//删除节点的逻辑要搞清楚
if(t == null)
return t;
int compareResult = x.compareTo(t.element);
if(compareResult<0)
t.left = remove(x,t.left);
else if(compareResult>0)
t.right = remove(x,t.right);
else if(t.left!=null&&t.right!=null)//找到要删除的节点,但是该节点左右都有孩子
{
t.element = findMIn(t.right).element;
t.right = remove(t.element,t.right);
}
else//只有一个孩子
t = (t.left!=null)?t.left:t.right;
return t;
}
}




 本文详细介绍了树的基本概念,包括定义、实现、遍历方法以及树的深度和高度等。特别聚焦于二叉查找树,阐述了其性质、递归实现方式,以及查找、插入、删除操作的具体算法。
本文详细介绍了树的基本概念,包括定义、实现、遍历方法以及树的深度和高度等。特别聚焦于二叉查找树,阐述了其性质、递归实现方式,以及查找、插入、删除操作的具体算法。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








