基本类型原子类
- AtomicInteger
- AtomicBoolean
- AtomicLong
| 方法 | 说明 |
| public final int get() | 获取当前的值 |
| public final int getAndSet(int newValue) | 获得当前的值,并设置新的值 |
| public final int getAndIncrement() | 获得当前的值,并自增 |
| public final int getAndDecrement() | 获得当前的值,并自减 |
| public final getAndAdd(int delta) | 获取当前的值,并加上预期的值 |
| boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) | 如果输入的数值等于预期值,则以原子方式将设置为输入值(update) |
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
class MyNumber{
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0);
public void addPlusPlus() {
atomicInteger.getAndIncrement();
}
}
public class AtomicIntegerDemo {
public static final int SIZE = 50;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyNumber myNumber = new MyNumber();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(SIZE);
for (int i = 1; i <= SIZE; i++){
new Thread(()-> {
try{
for (int j = 1; j <= 1000; j++) {
myNumber.addPlusPlus();
}
}finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
// 等待上面 50 个线程 全部计算完成后,再去获得最终值
// try{ TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
// 优化
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "result:" + myNumber.atomicInteger.get());
}
}
数组类型原子类
- AtomicIntegerArray
- AtomicLongArray
- AtomicReferenceArray
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerArray;
public class AtomicIntegerArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// AtomicIntegerArray atomicIntegerArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[5]);
// AtomicIntegerArray atomicIntegerArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(5);
AtomicIntegerArray atomicIntegerArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[]{1,2,3,4,5});
for (int i = 0; i < atomicIntegerArray.length(); i++) {
System.out.println(atomicIntegerArray.get(i));
}
int tmpInt = 0;
tmpInt = atomicIntegerArray.getAndSet(0, 1122);
System.out.println(tmpInt +"\t" + atomicIntegerArray.get(0));
tmpInt = atomicIntegerArray.getAndIncrement(0);
System.out.println(tmpInt +"\t" + atomicIntegerArray.get(0));
}
}
引用类型原子类
- AtomicReference
- AtomicStampedReference(版本号 + 1)
- AtomicMarkableReference(状态戳简化为 treu | false)
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicMarkableReference;
public class AtomicMarkableReferenceDemo {
static AtomicMarkableReference markableReference = new AtomicMarkableReference(100, false);
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()-> {
boolean marked = markableReference.isMarked();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "默认标识:" + marked);
try{ TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
markableReference.compareAndSet(100, 1000, marked, !marked);
},"t1").start();
new Thread(()-> {
boolean marked = markableReference.isMarked();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "默认标识:" + marked);
try{ TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
boolean b = markableReference.compareAndSet(100, 2000, marked, !marked);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "t2 线程 CAS result:" + b);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + markableReference.getReference());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + markableReference.isMarked());
},"t2").start();
}
}
对象的属性修改原子类
- AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater
- AtomicLongFieldUpdater
- AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater
使用目的:
- 以一种线程安全的方式操作非线程安全对象内的某些字段
使用要求:
- 更新的对象属性必须使用 public volatile 修饰符
- 因为对象的属性修改类型原子类都是抽象类,所以每次使用都必须使用静态方法 newUpdater() 创建一个更新器, 并且需要设置想要更新的类和属性
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater:
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater;
class BankAccount{
String bankName = "CCB";
public volatile int money = 0;
public synchronized void add() {
money ++;
}
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<BankAccount> fieldUpdater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(BankAccount.class, "money");
public void transMoney(BankAccount bankAccount) {
fieldUpdater.getAndIncrement(bankAccount);
}
}
public class AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterDemo {
final static Integer SIZE = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BankAccount bankAccount = new BankAccount();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(SIZE);
for (int i = 1; i <= SIZE; i++){
new Thread(()-> {
try{
for (int j = 1; j <= 1000; j++) {
bankAccount.transMoney(bankAccount);
}
}finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "result:" + bankAccount.money);
}
}
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater:
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater;
class MyVar{
public volatile Boolean isInit = Boolean.FALSE;
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<MyVar, Boolean> referenceFieldUpdater = AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(MyVar.class, Boolean.class, "isInit");
public void init(MyVar myVar) {
if (referenceFieldUpdater.compareAndSet(myVar, Boolean.FALSE, Boolean.TRUE)) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "----- start init, need 2 seconds");
try{ TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "----- over init");
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "----- 已经有线程在进行初始化工作....");
}
}
}
public class AtomicReferenceFieldUpdaterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyVar myVar = new MyVar();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
myVar.init(myVar);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
原子操作增强类原理深度解析
- DoubleAccumulator:
- DoubleAdder
- LongAccumulator
- LongAdder
| 方法名 | 说明 |
| void add(long x) | 将 当前的 value 加x |
| void increment() | 将当前的value 加 1 |
| void decrement() | 将当前的 value 减 1 |
| long sum() | 返回当前值,注意,在没有并发更新 value的情况下,sum 会返回一个精确值,在存在并发的情况下, sum 不保证返回精确值 |
| void reset() | 将 value 重置为0, 用用于替代重新 new 一个 LongAdder, 但是此方法只可以在没有并发更新的情况下使用 |
| long sumThenReset() | 获取当前 value, 并将 value 重置为 0 |
简单API 使用:
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAccumulator;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder;
import java.util.function.LongBinaryOperator;
public class LongAdderAPIDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// LongAdder 只能用来计算加法, 且从零开始计算
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
longAdder.increment();
longAdder.increment();
longAdder.increment();
System.out.println(longAdder.sum());
// 提供了自定义的函数操作
//LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x,y)-> x + y, 0);
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator(new LongBinaryOperator() {
@Override
public long applyAsLong(long left, long right) {
return left + right;
}
},0);
longAccumulator.accumulate(1);
longAccumulator.accumulate(3);
System.out.println(longAccumulator.get());
}
}
高并发下性能比较:
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAccumulator;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder;
class ClickNumber{
int number = 0;
public synchronized void clickBySynchronized() {
number++;
}
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(0);
public void clickByAtomicLong() {
atomicLong.getAndIncrement();
}
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
public void clickByLongAdder() {
longAdder.increment();
}
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x,y) -> x + y,0);
public void clickByLongAccumulator(){
longAccumulator.accumulate(1);
}
}
public class AccmulatorCompareDemo {
public static final int _1W = 10000;
public static final int threadNumber = 50;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ClickNumber clickNumber = new ClickNumber();
long startTime;
long endTime;
CountDownLatch countDownLatch1 = new CountDownLatch(threadNumber);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch2 = new CountDownLatch(threadNumber);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch3 = new CountDownLatch(threadNumber);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch4 = new CountDownLatch(threadNumber);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <= threadNumber; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try{
for (int j = 1; j <= 100* _1W; j++) {
clickNumber.clickBySynchronized();
}
}finally {
countDownLatch1.countDown();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch1.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("---- costTime:" + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒:" + "\t clickBySynchronized:" + clickNumber.number);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <= threadNumber; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try{
for (int j = 1; j <= 100* _1W; j++) {
clickNumber.clickByAtomicLong();
}
}finally {
countDownLatch2.countDown();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch2.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("---- costTime:" + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒:" + "\t clickByAtomicLong:" + clickNumber.number);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <= threadNumber; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try{
for (int j = 1; j <= 100* _1W; j++) {
clickNumber.clickByLongAdder();
}
}finally {
countDownLatch3.countDown();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch3.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("---- costTime:" + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒:" + "\t clickByLongAdder:" + clickNumber.number);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <= threadNumber; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try{
for (int j = 1; j <= 100* _1W; j++) {
clickNumber.clickByLongAccumulator();
}
}finally {
countDownLatch4.countDown();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch4.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("---- costTime:" + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒:" + "\t clickByLongAccumulator:" + clickNumber.number);
}
}
LongAdder
- LongAdder 是 Striped64的子类
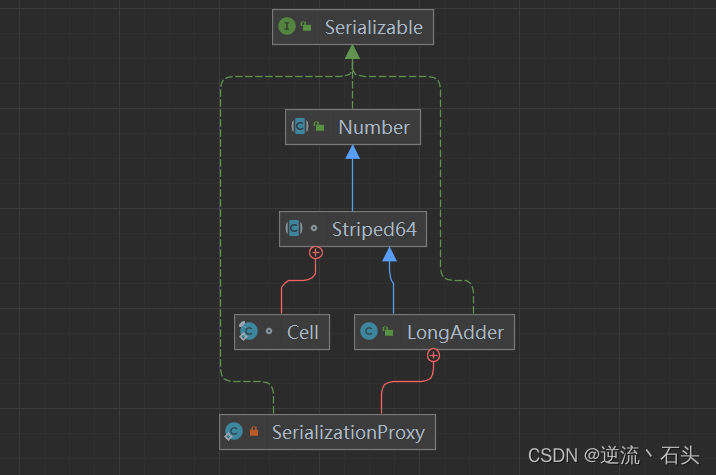
Striped64 一些变量或方法定义:
| 变量或方法 | 说明 |
| base | 类似于 AtomicLong 中全局的 value。在没有竞争情况下数据直接累加到base 上,或者 cells 扩容时,也需要将数据写入到 base 上 |
| collide | 表示扩容意向, false 一定不会扩容, true 可能会扩容 |
| cellsBusy | 初始化 cells 或者 扩容 cells 需要获取锁, 0:表示无锁装固态 1: 表示其他线程已经持有了锁 |
| casCellsBusy() | 通过 CAS 操作修改 cellsBusy 的值, CAS 成功代表获取锁, 返回 true |
| NCPU | 当前计算机 CPU 数量, Cell 数组扩容时使用到 |
| getProbe() | 获取当前线程的 hash 值 |
| advanceProbe() | 重置当前线程的 hash值 |
LongAdder 基本思想:
- 基本思想就是分散热点,将 value 值分散到一个 Cell 数组中,不同线程会命中到数组的不同槽中,各个线程只对自己槽中的那个值进行 CAS 操作,这样热点就被分散了,冲突的概率就小很多。如果要获取真正的 long 值,只要将各个槽中的变量值累加返回。
- sum() 会将所有 Cell 数组中的 value 和 base 累加作为返回值,核心思想就是将之前的 AtomicLong 一个 value 的更新压力分散到多个 value 中去。
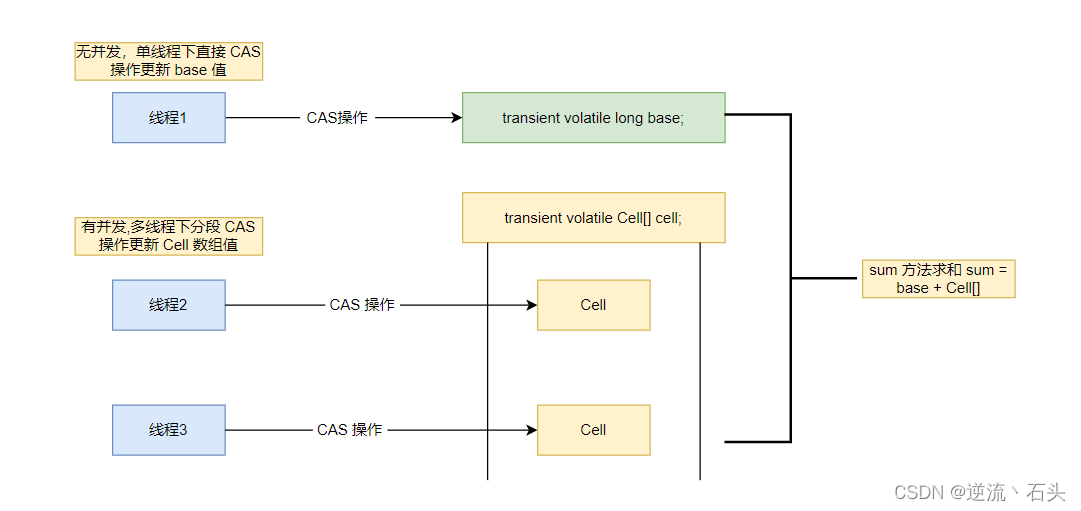
LongAdder 源码分析:
LongAdder 在无竞争的情况,跟 AtomicLong 一样,对同一个 Base 进行操作,当出现竞争关系时是采用化整为零分散热点的做法,用空间换时间, 用一个数组 cells, 将一个 value 拆分进这个数组 cells。 多个线程需要同时对 value 进行操作时候,可以对线程 ID 进行 hash 得到 hash 值,再根据 hash 值映射到这个数组 cells 的某个下标,再对该下标所对应的值进行自增操作。当所有线程操作完毕,将数组 cells 的所有值 和 base 都加起来作为最终结果。
add(long x):
- 最初无竞争时只更新 base
- 如果更新 base 失败后,首次新建一个 Cell[] 数组
- 当多个线程竞争同一个 Cell 比较激烈时, 可能就要对 Cell[] 扩容
public void add(long x) {
// as 表示 cells 引用, b 表示获取的 base 值, v 表示 期望值, m 表示 cells 数组的长度 a 表示 当前线程命中的 cell 单元格
Cell[] as; long b, v; int m; Cell a;
// 首次线程一定是false, 此时走 casBase 方法,以 CAS的方法更新 base 值,且只有当 CAS 失败时,才会走到 if 中
// 条件1 cells 不为空
// 条件2 cas 操作 base 失败, 说明其它线程先一步修改了 base 正在出现竞争
if ((as = cells) != null || !casBase(b = base, b + x)) {
// true 无竞争, false 表示竞争激烈, 多个线程 hash到同一个 Cell, 可能要扩充
boolean uncontended = true;
// 条件1: cells 为空
// 条件2: 应该不会出现
// 条件3: 当前线程所在的 Cell 为空,说明当前线程还没有更新过 Cell,应该初始化 Cell
// 条件4: 当更新当前线程所在的 Cell 失败,说明现在竞争很激烈,多个线程 hash 到同一个 Cell,应扩容
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
// getProbe 返回当线程中的 threadLocalRandomProbe 字段
// 它是通过随机数生成一个值, 对于一个确定的线程这个值是固定的(除非刻意修改它)
(a = as[getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended = a.cas(v = a.value, v + x)))
// 调用stringped64 中的方法处理
longAccumulate(x, null, uncontended);
}
}
longAccumulate:
final void longAccumulate(long x, LongBinaryOperator fn,
boolean wasUncontended) {
int h;
if ((h = getProbe()) == 0) {
ThreadLocalRandom.current(); // force initialization
h = getProbe();
wasUncontended = true;
}
boolean collide = false; // True if last slot nonempty
for (;;) {
Cell[] as; Cell a; int n; long v;
if ((as = cells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) {
if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) { // 当前线程的 hash 值 运算后映射得到的 Cell 单元为 Null, 说明该 Cell 没有被使用
if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Cell[] 数组没有正在扩容
Cell r = new Cell(x); // 创建了一个 Cell 单元
if (cellsBusy == 0 && casCellsBusy()) { // 尝试加锁, 成功后cellsBusy == 1
boolean created = false;
try { // 在有锁的情况下再检测一遍之前的判断
Cell[] rs; int m, j; // 将Cell 单元附到 Cell[] 数组上
if ((rs = cells) != null &&
(m = rs.length) > 0 &&
rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) {
rs[j] = r;
created = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (created)
break;
continue; // Slot is now non-empty
}
}
collide = false;
}
else if (!wasUncontended)
wasUncontended = true; // 只是重新设置了这个值为 true,紧接着执行 advanceProbe(h) 重置当前线程的 hash, 重新循环
else if (a.cas(v = a.value, ((fn == null) ? v + x :
fn.applyAsLong(v, x)))) // 说明当前线程对应的数组中有了数据,也重置过 hash 值, 这时通过 cas 操作尝试对当前数组中的 value 值进行累加 x 的操作, x 默认为1, 如果 CAS 成功则直接跳出循环
break;
else if (n >= NCPU || cells != as)
collide = false; // 如果 n 大于 CPU 最大数量,不可扩容, 并通过下面的 h = advanceProbe(h) 方法修改线程的 probe 再重新尝试
else if (!collide)
collide = true; // 如果扩容意向的 colide 是 false 则修改它为 true, 然后重新计算当前线程的 hash 值继续循环
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && casCellsBusy()) {
// 当前的cells 数组和最新赋值的 as 是同一个, 代表没有被其他线程扩容过
try {
if (cells == as) { // Expand table unless stale
// * 2
Cell[] rs = new Cell[n << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
rs[i] = as[i]; // 拷贝
cells = rs;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
collide = false;
continue; // Retry with expanded table
}
h = advanceProbe(h);
}
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && cells == as && casCellsBusy()) {
boolean init = false;
try { // Initialize table
if (cells == as) {
// 扩充是 2^n
Cell[] rs = new Cell[2];
rs[h & 1] = new Cell(x);
cells = rs;
init = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (init)
break;
}
else if (casBase(v = base, ((fn == null) ? v + x :
fn.applyAsLong(v, x))))
break; // Fall back on using base
}
}
sum():
- 将所有 Cell 数组中的 value 和 base 累加作为返回值
- 将之前的 AtomicLong 一个 value 的更新压力分散到多个 value 中去, 从而降级更新热点
- sum 执行时, 并没有限制 base 和 cells 的更新, 所以 LongAdder 不是强一致性, 是最终一致性
public long sum() {
Cell[] as = cells; Cell a;
long sum = base;
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
sum += a.value;
}
}
return sum;
}







 文章介绍了Java中的原子类,包括AtomicInteger、AtomicLong等基础类型原子类,AtomicIntegerArray等数组类型原子类,以及AtomicMarkableReference等引用类型原子类。通过示例代码展示了它们在并发环境下的使用,如线程安全的值更新。此外,还对比了LongAdder与其他原子类在高并发下的性能差异,指出LongAdder通过分散热点来提高性能。
文章介绍了Java中的原子类,包括AtomicInteger、AtomicLong等基础类型原子类,AtomicIntegerArray等数组类型原子类,以及AtomicMarkableReference等引用类型原子类。通过示例代码展示了它们在并发环境下的使用,如线程安全的值更新。此外,还对比了LongAdder与其他原子类在高并发下的性能差异,指出LongAdder通过分散热点来提高性能。
















 3784
3784

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








