整理自CSE 444 Database Internals, Spring 2019 的课程Lectures,课程地址:https://courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse444/19sp/
Lecture 7 Query Execution and Operator Algorithms(part 1)
Next Lectures
How to answer queries efficiently!
- Physical query plans and operator algorithms
How to automatically find good query plans
- How to compute the cost of a complete plan
- How to pick a good query plan for a query
- i.e., Query optimization
Query Execution Bottom Line
SQL query transformed into physical plan
- Access path selection for each relation
- Implementation choice for each operator
- Scheduling decisions for operators:Single-threaded or parallel, pipelined or with materialization, etc.
Execution of the physical plan is pull-based
Operators given a limited amount of memory
Pipelined Query Execution
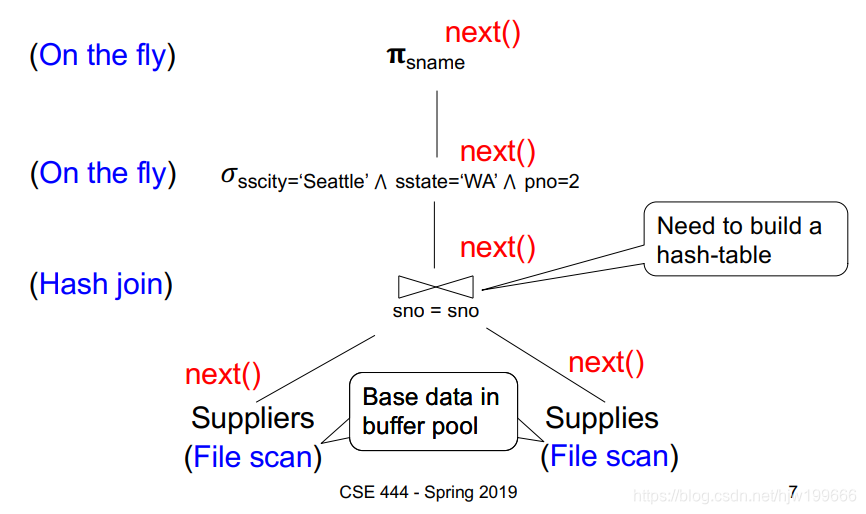
Memory Management
Each operator:
Pre-allocates heap space for input/output tuples
- Option 1: Array of pointers to base data in buffer pool
- Option 2: New tuples on the heap
Allocates memory for its internal state
- Either on heap or in buffer pool (depends on system)
DMBS limits how much memory each operator, or each query can use
Operator Algorithms
Design criteria
- Cost: IO, CPU, Network
- Memory utilization
- Load balance (for parallel operators)
Cost Parameters
Cost = total number of I/Os
- This is a simplification that ignores CPU, network
Parameters:
B(R) = # of blocks (i.e., pages) for relation R
T(R) = # of tuples in relation R
V(R, a) = # of distinct values of attribute a
- When a is a key, V(R,a) = T(R)
- When a is not a key, V(R,a) can be anything < T(R)
Convention
Cost = the cost of reading operands from disk
Cost of writing the final result to disk is not included; need to count it separately when applicable
Join Algorithms
- Hash join
- Nested loop join
- Sort-merge join





 本文探讨了数据库内部如何高效地执行SQL查询,包括物理查询计划的生成、操作符算法的设计,以及查询优化的自动选择过程。重点讲解了内存管理、成本参数、以及常见的连接算法如哈希连接、嵌套循环连接和排序-合并连接。
本文探讨了数据库内部如何高效地执行SQL查询,包括物理查询计划的生成、操作符算法的设计,以及查询优化的自动选择过程。重点讲解了内存管理、成本参数、以及常见的连接算法如哈希连接、嵌套循环连接和排序-合并连接。
















 518
518

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








