一.配置文件
1.applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p">
<!--三种实例化bean的方式-->
<!--1. 使用类构造器实例化(默认无参数)-->
<bean id="mathMethods" class="test.spring.Service.Impl.MathMethodImpl"></bean>
<!--2. 使用静态工厂方法实例化(简单工厂模式):节省内存消耗-->
<bean id="person" class="test.spring.Service.Impl.PersonServiceFactory" factory-method="createPerson"></bean>
<!--3. 使用实例工厂方法实例化(工厂方法模式)-->
<bean id="personFactory" class="test.spring.Service.Impl.PersonServiceFactory" scope="prototype"></bean>
<bean id="per" factory-bean="personFactory" factory-method="newPerson"></bean>
</beans>
2.web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1">
<!-- 初始化spring容器,上下文的位置 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
</web-app>
二、Bean
1. 使用类构造器实例化(默认无参数)-MathMethodImpl
package test.spring.Service.Impl;
import test.spring.Service.MathMethodService;
public class MathMethodImpl implements MathMethodService {
public int getCalc(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
}
2.PersonImpl
package test.spring.Service.Impl;
public class PersonImpl {
public void sayHi(){
System.out.println("Hi");
}
}
3. 使用静态工厂方法实例化(简单工厂模式)-PersonServiceFactory
package test.spring.Service.Impl;
public class PersonServiceFactory {
public static PersonImpl createPerson(){
return new PersonImpl();
}
}
4.使用实例工厂方法实例化(工厂方法模式)-PersonServiceFactory
package test.spring.Service.Impl;
public class PersonServiceFactory {
public PersonImpl newPerson() {
return new PersonImpl();
}
}
三、测试
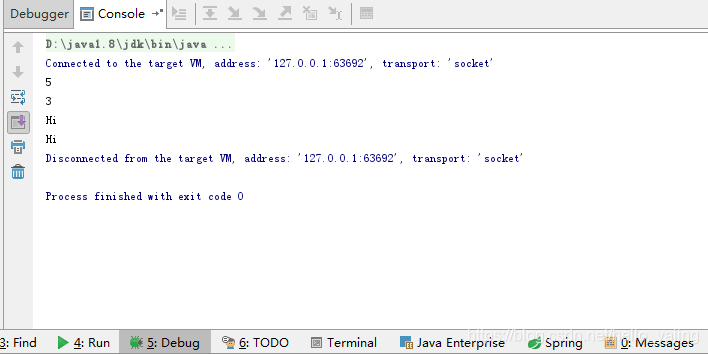
public class MathMethodController {
public static void main(String[] args){
//法一:普通实现方法
MathMethodService math = new MathMethodImpl();
System.out.println(math.getCalc(2,3));
//法二:spring实现方法(实例化bean三种方式):区别在xml中。
//1.类构造器实例化,无参
/* 第一步:初始化spring容器*/
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
/*第二步:从容器中获取service对象*/
MathMethodService methodService = (MathMethodService)applicationContext.getBean("mathMethods");
/*第三步:使用对象的方法*/
System.out.println(methodService.getCalc(1,2));
//2.静态工厂方法实例化
PersonImpl person = (PersonImpl)applicationContext.getBean("person");
person.sayHi();
//3.使用实例工厂方法实例化
PersonImpl per = (PersonImpl)applicationContext.getBean("per");
per.sayHi();
}
}





















 2306
2306

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








