该题目来源于Robert Sedgewick 的《算法》。
1.1.31 Random connections. Write a program that takes as command-line arguments an integer N and a double value p (between 0 and 1), plots N equally spaced dots of size .05 on the circumference of a circle,and then, with probability p for each pair of points, draws a gray line connecting them.
1.1.31 随机连接。写一个程序从命令行获取一个int类型的参数N和一个double类型的参数p(在0到1之间),在一个圆的圆周上
画出N个大小为0.05且间距相等的点,每对点相连的概率为p,用灰色的线连接它们。
思路:
1、根据“在一个圆周上画出N个大小为0.05且间距相等的点”,可以算出圆周的周长,进而算出圆周的半径:
// N个大小为0.05且间距相等的点,因此可以算出圆周的周长
double circumferenceLen = spaceSize * N;
// 圆周的半径
double radius = circumferenceLen / Math.PI / 2;
2、将一个圆平分成N分,分份的角度为:
// 将圆平分成N份,每一份的角度为
double angle = 360.0 / N;
3、圆上N个点的坐标,可以根据余弦和正弦公式算出:
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
points[i] = new Point(radius + radius * Math.cos(i * angle * Math.PI / 180),
radius + radius * Math.sin(i * angle * Math.PI / 180));
}
4、然后利用StdDraw来画圆、画点、画线
5、使用StdRandom中的bernoulli方法来判断哪两对点可以相连
核心代码如下(详细代码在git上):
/**
* exercise 1.1.31 的解决方案
* @param spaceSize
* @param N
* @param p
*/
public static void randomConnectionSolution(double spaceSize, int N, double p) {
// N个大小为0.05且间距相等的点,因此可以算出圆周的周长
double circumferenceLen = spaceSize * N;
// 圆周的半径
double radius = circumferenceLen / Math.PI / 2;
// 画出坐标系
StdDraw.setXscale(0, radius * 2);
StdDraw.setYscale(0, radius * 2);
// 画一个以(radius,radius) 为圆心,以radius为半径的圆
StdDraw.circle(radius, radius, radius);
// 将圆平分成N份,每一份的角度为
double angle = 360.0 / N;
// 圆上N个点的坐标,放在一个对象数组中
Point[] points = new Point[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
points[i] = new Point(radius + radius * Math.cos(i * angle * Math.PI / 180),
radius + radius * Math.sin(i * angle * Math.PI / 180));
System.out.println("radius:" + radius + "x: "+ Math.cos(i * angle * Math.PI / 180));
// 在圆周上画点
StdDraw.point(points[i].x, points[i].y);
}
// 遍历点,连接线,画点
for (int i = 0; i < N-1; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < N; j++) {
if(StdRandom.bernoulli(p)){
StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.GRAY);
StdDraw.line(points[i].x, points[i].y, points[j].x, points[j].y);
}
}
}
}运行之后,展示出来的结果如下:
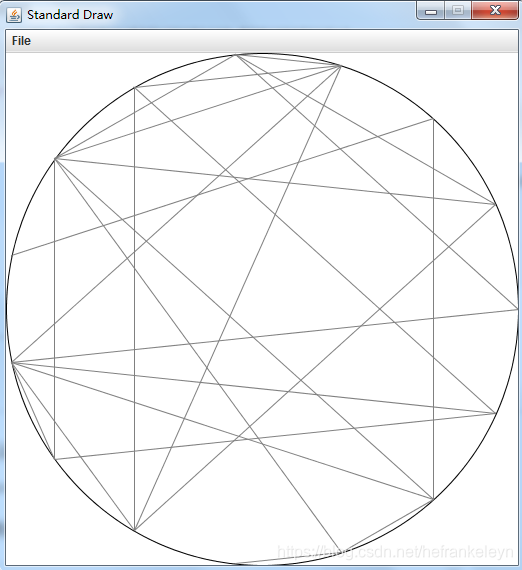





 本文介绍了一种基于Robert Sedgewick《算法》一书的1.1.31题目的解决方案,通过绘制圆周上的N个等距点,并以概率p随机连接这些点,生成随机的灰线网络。
本文介绍了一种基于Robert Sedgewick《算法》一书的1.1.31题目的解决方案,通过绘制圆周上的N个等距点,并以概率p随机连接这些点,生成随机的灰线网络。

















 595
595

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








