目录
零、建表
1、学生表
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for student
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`Sname` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`sex` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`t_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 11 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Compact;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of student
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (1, '张三', '男', 18, 1);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (2, '李四', '女', 18, 1);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (3, '王五', '男', 18, 1);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (4, '小白', '女', 18, 1);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (5, '小黑', '男', 18, 1);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (6, '小红', '女', 20, 2);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (7, '小李', '男', 20, 2);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (8, '小张', '女', 20, 2);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (9, '小赵', '男', 20, 2);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (10, '小王', '女', 20, 2);
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;2、老师表
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for teacher
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `teacher`;
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`Tname` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 3 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Compact;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of teacher
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `teacher` VALUES (1, '张老师');
INSERT INTO `teacher` VALUES (2, '李老师');
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
一、多对一的关联映射
1、实体类、接口、mapper
Teacher类
package com.qcby.entity;
public class Teacher {
private Integer id;
private String Tname;
}Student类
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String Sname;
private String sex;
private Integer age;
private Integer t_id;
//这个是重点
private Teacher teacher;
}注意哈,Student类里有一个Teacher类
接口
public interface StudentDao
{
public List<Student> getStudentAndTeacher1();
public List<Student> getStudentAndTeacher2();
}Test
package com.qcby;
import com.qcby.dao.StudentDao;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class StudentTest {
private InputStream in = null;//输入流
private SqlSession session = null;//数据库会话
private StudentDao mapper = null;//mapper-->映射
@Before //前置通知, 在方法执行之前执行
public void init() throws IOException {
//加载主配置文件,目的是为了构建SqlSessionFactory对象
in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//创建SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
//通过SqlSessionFactory工厂对象创建SqlSesssion对象
session = factory.openSession();
//通过Session创建UserDao接口代理对象
mapper = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
}
@After //@After: 后置通知, 在方法执行之后执行 。
public void destory() throws IOException {
//释放资源
session.close();
in.close();
}
@Test
public void getStudentAndTeacher1(){
mapper.getStudentAndTeacher1();
}
@Test
public void getStudentAndTeacher2(){
mapper.getStudentAndTeacher2();
}
2、连表查询 注意看下column不同情况下作用
首先认识一下子标签:
resultMap与resultType只能存在一个,而resultmap是映射
在select写完后,下面写resultmap的标签 id要与select中的一致。
type映射类型
result返回标签,
property实体类的对象
columnn查询数据库所返回的标签
当在association里的时候是向下传参的意思
association用于处理特殊类型如实体类,集合的标签
collection处理集合
javaType java类后面是包名
上代码:
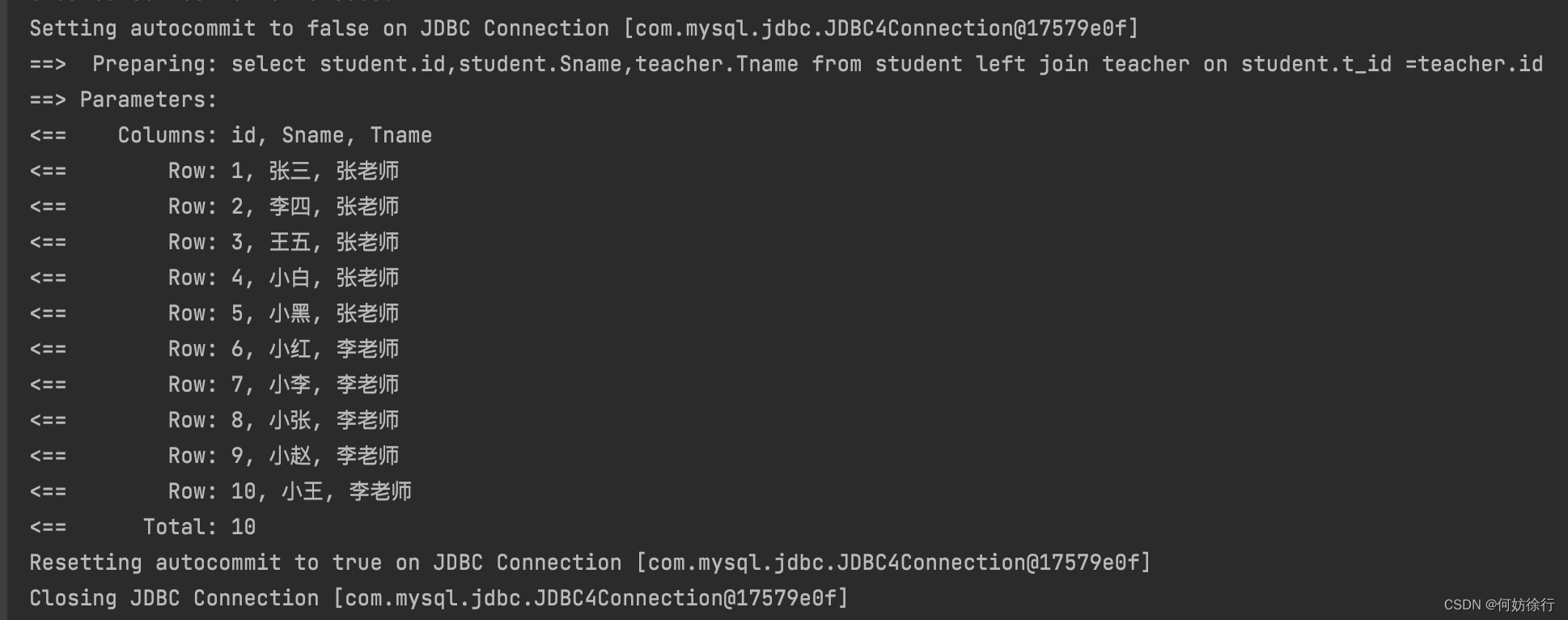
<select id="getStudentAndTeacher1" resultMap="StudentTeacher1">
select student.id,student.Sname,teacher.Tname
from student left join teacher
on student.t_id =teacher.id
</select>
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher1" type="com.qcby.entity.Student">
<!-- column:数据库查询返回的字段-->
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="Sname" column="Sname"/>
<result property="sex" column="sex"/>
<result property="age" column="age"/>
<result property="t_id" column="t_id"/>
<association property="teacher" javaType="com.qcby.entity.Teacher">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="Tname" column="Tname"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<!-- 复杂属性 对象:association 集合:collection -->
<!-- property="teacher" student类当中的关联字段 -->
<!-- javaType="com.javen.model.Teacher" 为复杂属性设置类类型-->
<!-- 此处的column向下传参-->我们为什么要在association下有两个result呢?这是为了查询到sql语句中的teacher表的内容
3、分步查询
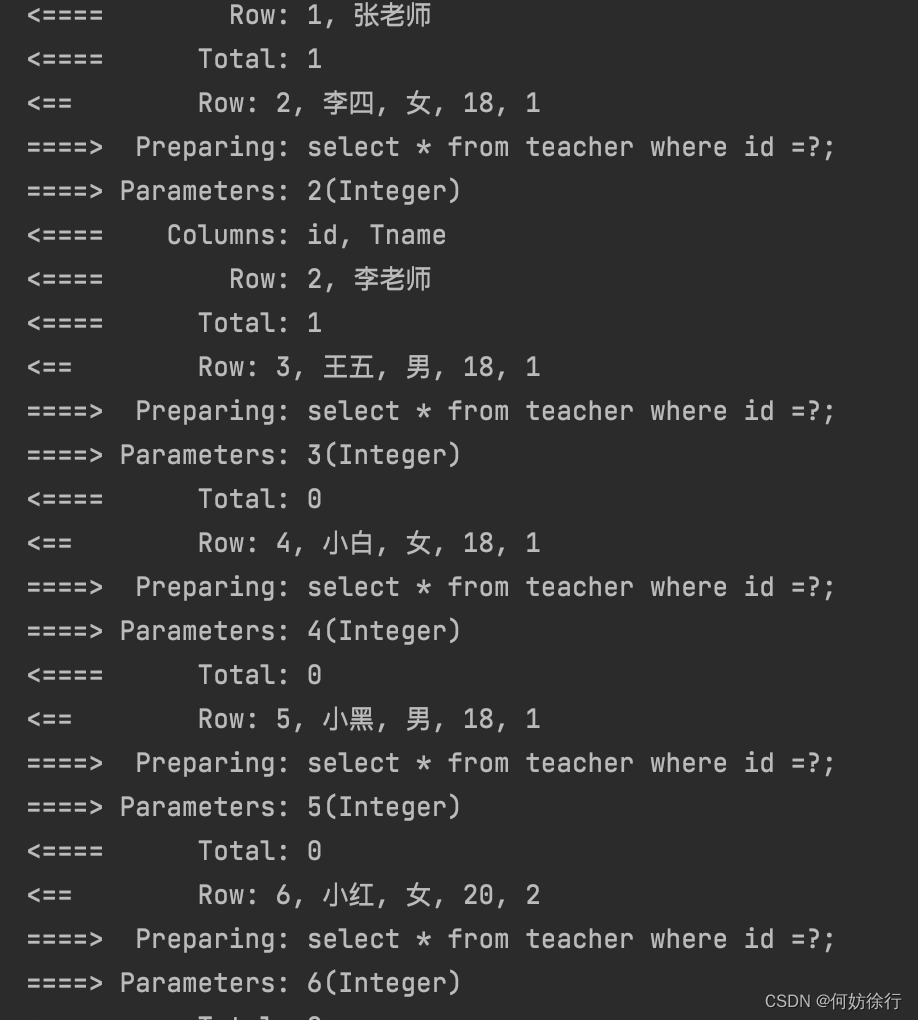
<select id="getStudentAndTeacher2" resultMap="st">
select * from student
</select>
<resultMap id="st" type="com.qcby.entity.Student">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="Sname" column="Sname"/>
<result property="sex" column="sex"/>
<result property="age" column="age"/>
<result property="t_id" column="t_id"/>
<association property="teacher" column="t_id" select="chaxun" javaType="com.qcby.entity.Teacher">
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="chaxun" resultType="com.qcby.entity.Teacher">
select * from teacher where id =#{suibian};
</select>对比一下分布查询和连表查询代码的区别。
运行流程:查表往下走直到teacher类,调用select,把t_id传到下面的select,select#{}随便填。反正是接受上面的内容
如果对向下传参有疑惑,那就把t_id改为id
现在懂了吧。
二、一对多的关联映射
1、实体类、接口、mapper
Student
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String Sname;
private String sex;
private Integer age;
private Integer t_id;
}
Teacher
public class Teacher {
private Integer id;
private String Tname;
private List<Student> students;
}
我们删除了Student类的Teacher而是在Teacher中加一个Student集合
每个类有自己该有的。
2、连表查询
<!--按照结果进行查询-->
<select id="getTeacher" resultMap="TeacherStudent">
SELECT teacher.id,teacher.Tname,student.Sname FROM teacher
LEFT JOIN student on student.t_id = teacher.id
</select>
<resultMap id="TeacherStudent" type="com.qcby.entity.Teacher">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="Tname" column="Tname"/>
<!-- 复杂的属性我么需要单独去处理 对象:association 集合:collection
在集合中的泛型信息,我们使用ofType获取
-->
<collection property="students" ofType="com.qcby.entity.Student">
<result property="Sname" column="Sname"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>因为是集合类型,所以不用association而是用collection 类型是ofType类型
注意这点即可。
3、分步查询
<!--按照查询嵌套处理-->
<select id="getTeacher" resultMap="TeacherStudent2">
select * from teacher
</select>
<resultMap id="TeacherStudent2" type="com.qcby.entity.Teacher">
<collection property="students" column="id" javaType="ArrayList"
ofType="com.qcby.entity.Student" select="getStudentByTeacherId" />
</resultMap>
<select id="getStudentByTeacherId" resultType="com.qcby.entity.Student">
select * from student where t_id = #{t_id}
</select>上面懂了 这个也就懂了。
三、真正的分布查询
不知道你有没有注意到分布查询查询teahcer的语句放入student类里,查询student同理。
这样其实还不算分布查询
我们应该讲查询老师的语句放在老师的mapper里。
现在我们来修改下多对一的
studentDao.xml
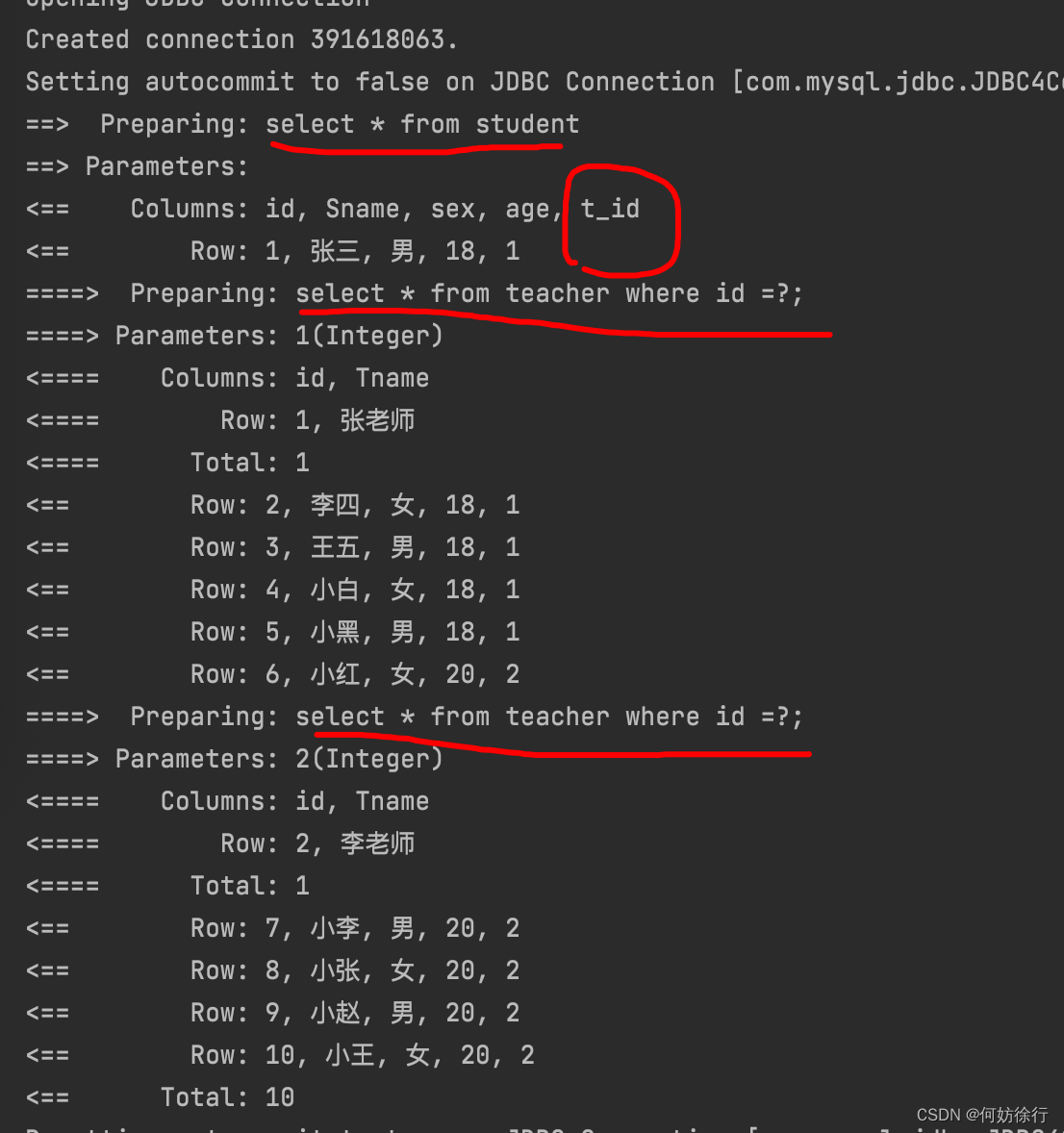
<select id = "getStudent" resultMap="StudentTeacher">
select * from student;
</select>
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher" type="com.qcby.entity.Student">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="Sname" column="Sname"/>
<result property="sex" column="sex"/>
<result property="age" column="age"/>
<result property="t_id" column="t_id"/>
<association property="teacher" column="t_id" javaType="com.qcby.entity.Teacher"
select="com.qcby.dao.TeacherDao.getTeacher" />
</resultMap>TeacherDao.xml
<select id="getTeacher" resultType="com.qcby.entity.Teacher" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
select * from teacher where id = #{t_id};
</select>TeacherDao
Teacher getTeacher(Integer id);
可能出现的错误:
主配置文件没有对应mapper

调用select方法名与select的id不一致
自己完成真正的一对多的分布查询知之后,可以接着这个学习延迟加载
MyBatis延迟加载策略(看了就会)_何妨徐行的博客-优快云博客
之后你就会了解我们为什么要使用分布查询以及如何设置延迟加载





















 895
895

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








