1、数组的watch
data() {
return {
winChips: new Array(11).fill(0)
}
},
watch: {
winChips: {
handler(newValue, oldValue) {
for (let i = 0; i < newValue.length; i++) {
if (oldValue[i] != newValue[i]) {
console.log(newValue)
}
}
},
deep: true
}
}2、对象的watch
data() {
return {
bet: {
pokerState: 53,
pokerHistory: 'local'
}
}
},
watch: {
bet: {
handler(newValue, oldValue) {
console.log(newValue)
},
deep: true
}
}tips: 只要bet中的属性发生变化(可被监测到的),便会执行handler函数;
如果想监测具体的属性变化,如pokerHistory变化时,才执行handler函数,则可以利用计算属性computed做中间层。
事例如下:
data() {
return {
bet: {
pokerState: 53,
pokerHistory: 'local'
}
}
},
computed: {
pokerHistory() {
return this.bet.pokerHistory
}
},
watch: {
pokerHistory(newValue, oldValue) {
console.log(newValue)
}
}或者:
data() {
return {
bet: {
pokerState: 53,
pokerHistory: 'local'
}
}
},
watch: {
'bet.pokerHistory'(newValue, oldValue) {
console.log(newValue)
}
}上面代码块确定不能监测 数组中某个属性值得变化,利用computed做中间层则没有这个限制
也可以利用vm.$watch(fn,fn,{}) 来监测更复杂的表达式。例如:
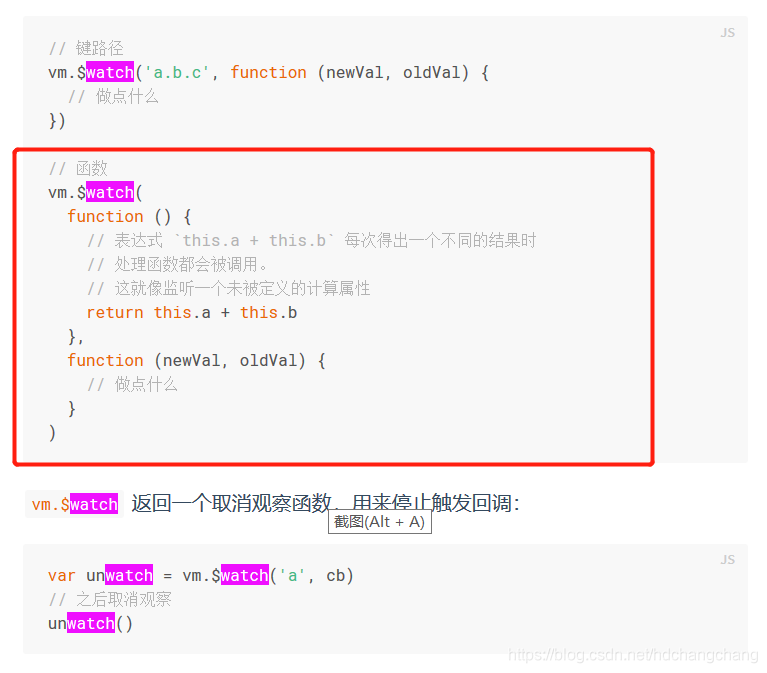
参见 vue 官网:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#vm-watch





 本文探讨了Vue中watch的使用,特别是针对数组和对象的深度监听。通过实例说明了如何监测数组中某个属性的变化,以及如何通过使用computed属性或vm.$watch方法来监控更复杂的表达式,确保在数据变化时能够及时响应。
本文探讨了Vue中watch的使用,特别是针对数组和对象的深度监听。通过实例说明了如何监测数组中某个属性的变化,以及如何通过使用computed属性或vm.$watch方法来监控更复杂的表达式,确保在数据变化时能够及时响应。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








