了解网站部署
1.nginx小试牛刀
yum install nginx -y
2.简单了解,给你的机器,配置一个软件仓库(360软件大师,点点点,下载各种工具,它的软件,还携带了一堆广告)
配置阿里云的软件仓库
https://developer.aliyun.com/mirror/
下载资源,且指定到某一个路径下
centos7源
#第一种方法
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
#第二种方法
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
epel源
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
3.既然机器有了软件仓库,即可下载各种应用了
yum install nginx -y
4. 就可以启动该应用
systemctl start nginx
5.程序运行了,如何判断他运行?
windows
任务管理器
查看进程,就是一个个运行中的软件,在消耗系统的资源
linux
任务管理器
查看进程
查看nginx这个程序的进程
执行ps命令
仅仅查看这个机器上的 nginx进程信息,是否存在
ps -ef | grep nginx
6. 一个网站的运行,默认端口是 http的80端口
用你的客户端,浏览器去访问,
10.96.0.134:80即可 (虚拟机的网卡地址 + 端口)
7.注意关闭服务器的防火墙
iptables -F
setenforce 0
*8.停止这个网站服务,思路是?
systemctl stop nginx
重启nginx服务
systemctl restart nginx
8.可以修改该软件的配置了,比如网站首页的内容
完成1分钟,做一个dnf官网
下载该网址的首页html文件
wget https://dnf.qq.com/main.shtml
移动,拷贝该文件,到你的nginx网站目录下, 它会自动识别
移动 /opt/main.shtml 到/usr/share/nginx/html/ 目录下,且重命名为index.html
[root@localhost opt]# mv /opt/main.shtml /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
mv: overwrite ‘/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html’? y
9.当你修改了网站的前端页面,无须重启,网站自动更新
http://10.96.0.134/
文件管理篇命令二
cat命令
1.cat 适合读取小文件,不能读取大文件,一次性将文件内容全部读取到内存中,且输出到屏幕上
查看nginx软件的配置文件(前提是你安装了该软件,linux默认安装的软件,配置文件会自动写到/etc目录下)
[root@localhost opt]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
查看系统的用户信息有哪些
[root@localhost opt]# cat /etc/passwd
2.cat 添加一个功能参数 -n 显示行号
[root@localhost opt]# cat -n /etc/passwd
3. cat不适合读取大文件,显示也不友好
cat /var/log/messages
4. 还可以连续读取多个文件,并且显示三文件一共有多少行
[root@localhost opt]# cat -n doupo.txt hehe.txt hello_python.txt
5. 结合重定向符号使用
> 重定向覆盖输出符 ,数据从左边,覆盖写入到右边
< 重定向覆盖输入符,数据从右边,覆盖写入到左边
>> 重定向追加输出符, ,数据从左边,追加写入到右边
<< 重定向覆盖输入符,数据从右边,追加写入到左边
cat doupo.txt hehe.txt hello_python.txt > ./three_files.txt
6.追加古诗
[root@localhost opt]# echo 春晓 > 春晓.txt
[root@localhost opt]# echo 春眠不觉晓 >> 春晓.txt
[root@localhost opt]# echo 处处蚊子咬>> 春晓.txt
[root@localhost opt]# echo 越来讽喻诗>> 春晓.txt
[root@localhost opt]# echo 滑落至多为>> 春晓.txt
[root@localhost opt]# cat 春晓.txt
春晓
春眠不觉晓
处处蚊子咬
越来讽喻诗
滑落至多为
7.写入多行数据
[root@localhost opt]# cat >>古诗2.txt <<EOF
> 嗯嗯嗯
> 呃呃呃,曲项向天歌
> 白毛浮绿水
> 红掌拨清波
> EOF
[root@localhost opt]# cat 古诗2.txt
嗯嗯嗯
呃呃呃,曲项向天歌
白毛浮绿水
红掌拨清波
注意:如果后面写进的文档没有会自动创建
8.cat证明文件存在空行的办法
-b 只会对有内容的行,显示其行号,空行不显示
-E 在linux文件中,每一行的结束,默认会添加一个你看不到的,特殊符号 '$' ,表示是该行的结尾
#查看文件的字符数量有多少
[root@localhost opt]# cat -b doupo.txt
tac命令
将文件从后,向前,倒着查看
[root@localhost opt]# cat -n hehe.txt
1 yuchao
2 yejingyang
3 chenliangliang
[root@localhost opt]#
[root@localhost opt]#
[root@localhost opt]# tac hehe.txt
chenliangliang
yejingyang
yuchao
ls和sl
ls 查看文件夹下内容
安装这个sl命令
yum install sl -ysl是一个小火车命令
more和less命令
more和cat都是一次性读取所有内容到内存,不适合读取大文件,占资源
less命令是显示多少文本,消耗多少内存,省资源。
空格--------翻篇
回车--------下一行
head和tail命令
head
作用:查看文件的默认前n行
查看文件的默认前10行
[root@localhost opt]# head doupo.txt
[root@localhost opt]# head -5 文件 # 查看文件的前5行
tail 命令
作用:查看文件的默认后n行
查看文件的后默认10行
tail -5 文件 #表示查看文件的后5行
tail -f
tail有一个重点命令,叫做实时刷新文件内容
-f 跟踪文件内容变化,但是需要文件正常退出后,可见,最常用的也就是小写的f,检测程序的日志变化(程序代码,追加新内容到文件中的)

结合tail和上午安装的nginx练习日志查看
1.用tail 检测nginx的访问日志
[root@localhost opt]# tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log
2.用浏览器,访问nginx的页面即可,不断刷新,不断出现新的
tail -F
能够对文件进行刷新读取,即使该文件不存在,也可以检测
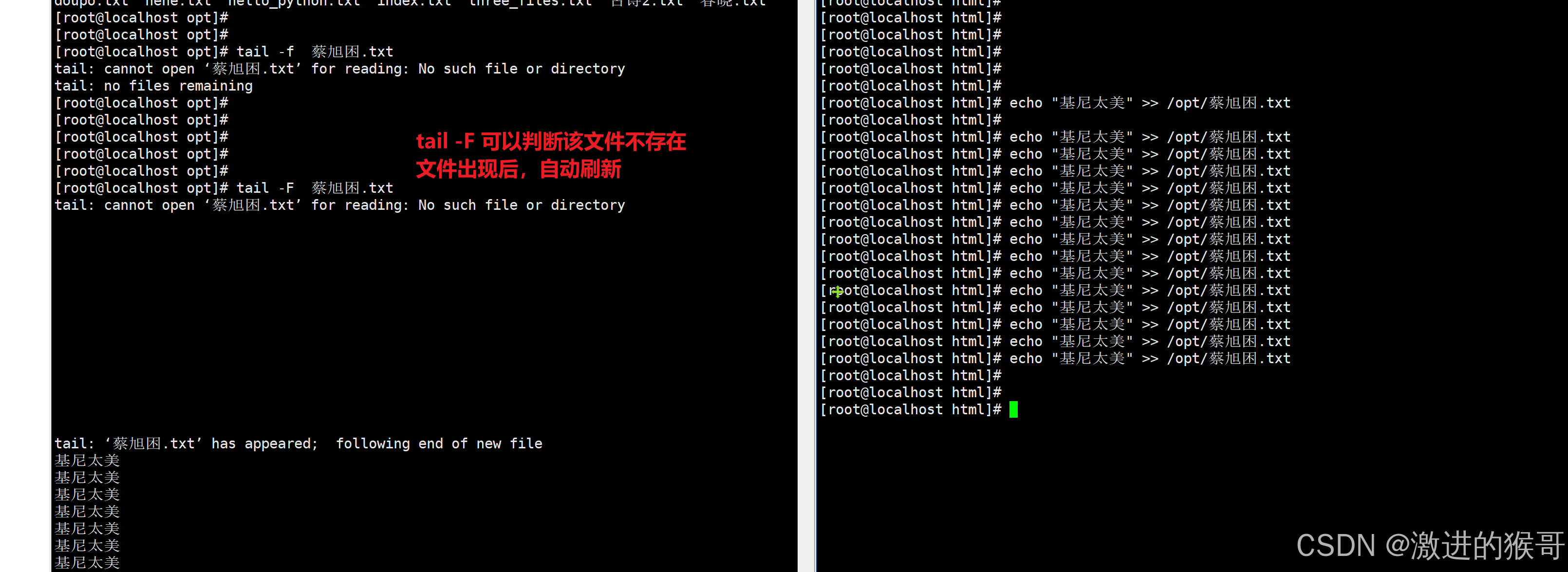
wc命令
统计文件的行
1.wc命令,统计文件内有多少行,有一个回车,是一个空行
[root@localhost opt]# wc -l doupo.txt
32 doupo.txt
[root@localhost opt]# ll
2. wc -w 统计文件内的单词数
[root@localhost opt]# wc -w hehe.txt
11 hehe.txt
du命令
作用:查看文件或目录(会递归显示子目录)占用磁盘空间大小
语法:du [参数选项] 文件名或目录名
参数:
-s :summaries,只显示汇总的大小,统计文件夹的大小
[root@localhost opt]# du -s .
105072KB
-h:表示以高可读性的形式进行显示,如果不写-h,默认以KB的形式显示文件大小
linux的文件系统,对文件最小管理单位是4kb算起。
[root@localhost opt]# du -h *
4.0K doupo.txt
4.0K hehe.txt
4.0K hello_python.txt
4.0K index.txt
4.0K three_files.txt
26M xixi
26M xixi1
26M xixi2
26M xixi3
4.0K 古诗2.txt
4.0K 呵呵.txt
4.0K 春晓.txt
4.0K 蔡旭困.txt
2.显示文件夹的大小
[root@localhost /]# du -h /opt
103M /opt
3.发现机器磁盘空间不够了,你领导让你看看日志目录是不是太大了
du -sh /var/log
4.查看nginx软件的日志目录,容量是多少
[root@localhost log]# du -sh /var/log/nginx
32K /var/log/nginx
find命令
windows下的强大搜索工具
everything工具
linux的工具是谁?---find命令。
find是递归查找
语法:
find 从哪找 -name "你要找什么"
[root@localhost ~]# find / -name 'doupo.txt'
/opt/doupo.txt
缩小搜索范围,从/opt开始找
[root@localhost ~]# find /opt -name 'doupo.txt'
/opt/doupo.txt
找到机器上所有的 doupo.txt
[root@localhost ~]# find / -name 'doupo.txt'
/etc/doupo.txt
/tmp/doupo.txt
/usr/local/doupo.txt
/home/doupo.txt
/opt/doupo.txt
[root@localhost ~]#
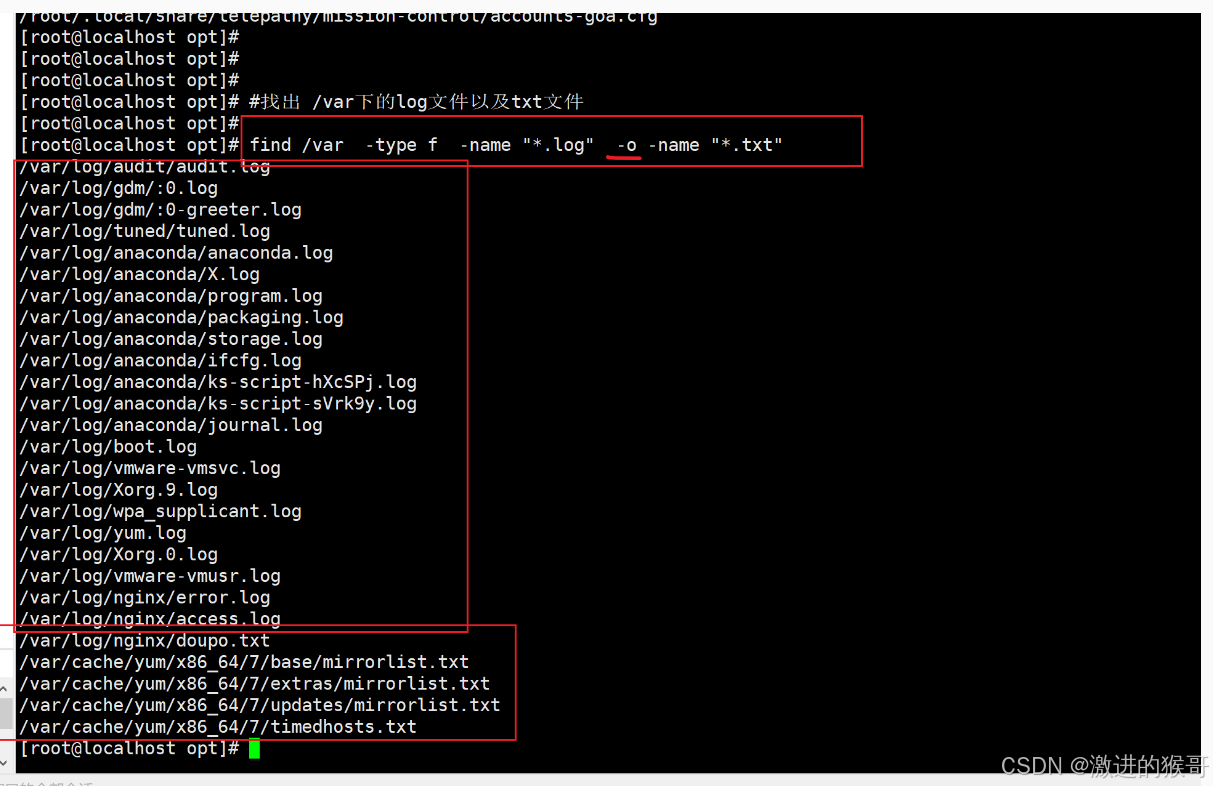
模糊查找,找出/var下所有的log文件 nginx.log mysql.log yuchao.log *.log
[root@localhost ~]# find /var -name '*.log'
这是限制查找文件类型的:
# -type f 找到文本类型的数据
# -type d 找到文件夹类型的数据
找出机器上所有的 doupo.txt 【文件,文本文件,可以被cat的文件】
find / -type f -name 'doupo.txt'
找出系统上超过20M的压缩包(自行查阅)
[root@server ~]#find / -type f -size 20M -name "*.tar.gz"
-o # 找出多种类型的文件






















 986
986

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










