原型模式(Prototype Pattern):就是从一个对象再创建另一个可定制对象的,而且不需要知道任何创建的细节。所谓原型模式,就是 Java 中的克隆技术,以某个对象为原型。复制出新的对象。显然新的对象具备原 型对象的特点,效率高(避免了重新执行构造过程步骤)。
所以当直接创建对象代价比较大的时候,推荐使用这种设计模式,例如对象在访问数据库操作之后被创建,那么可以缓存该对象,在下一个请求是返回它的克隆,这样可以减少对数据库的调用来提高性能。
在Spring中,把对象中配置的依赖关系,在每次使用对象之前,都会创建一个新的对象,并且会将依赖关系完整的赋值给这个行创建的对象。
在java中拷贝主要继承于Cloneable,直接实现的就是浅拷贝。
浅拷贝简单的理解就是当复制一个对象的时候,其实他的引用地址是不变的,那么当原对象更改了的话,复制的对象也会跟着更改。
而深拷贝则是,复制一个对象的时候,新的对象会重新申请新的内存空间,虽然结构和原对象是一样的,但是当拷贝完成之后,改变原对象的结构,并不会影响新的对象。
所以原型模式,也有对应的两种返回,即返回浅拷贝的对象和深拷贝的对象。
下面就是具体的实现了:
例子是一个比方,类MonkeyKing 继承于Monkey,然后它里面有浅拷贝方法clone()和深拷贝方法copy()(一般来说只需要一个,实际使用中如果需要深拷贝,一般是重写clone()方法)。
首先设计类图:
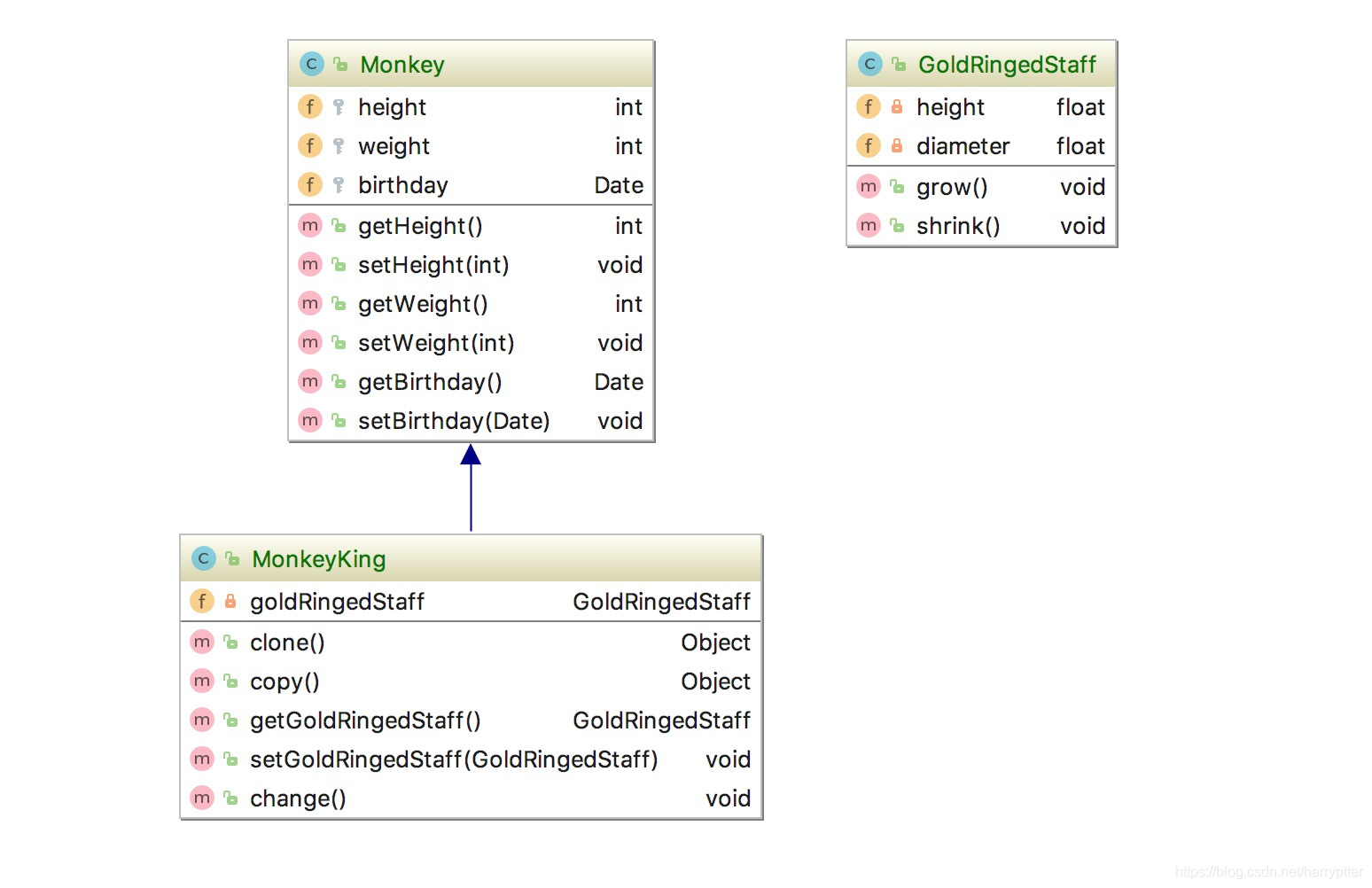 Monkey类的实现
Monkey类的实现
package ProtoType;
import java.util.Date;
//猴子
public class Monkey {
//身高
protected int height;//基本
//体重
protected int weight;
//生日
protected Date birthday;//不是基本类型
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
}
GoldRingStaff实现
package ProtoType;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* 金箍棒
*
*/
public class GoldRingedStaff implements Serializable {
private float height = 100; //长度
private float diameter = 10;//直径
/**
* 金箍棒长大
*/
public void grow(){
this.diameter *= 2;
this.height *= 2;
}
/**
* 金箍棒缩小
*/
public void shrink(){
this.diameter /= 2;
this.height /= 2;
}
}
MonkeyKing 类实现
package ProtoType;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Date;
import ProtoType.GoldRingedStaff;
public class MonkeyKing extends Monkey implements Cloneable,Serializable {
private GoldRingedStaff goldRingedStaff;
public MonkeyKing(){
this.goldRingedStaff = new GoldRingedStaff();
this.birthday = new Date();
this.height = 150;
this.weight = 324;
System.out.println("------------");
}
public Object clone(){
//浅克隆
try {
return super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
//深克隆 需要通过序列化操作
public Object copy() {
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
ByteArrayInputStream bis = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try{
//序列化
bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(this);
//反序列化
bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
MonkeyKing copy = (MonkeyKing)ois.readObject();
copy.birthday = new Date();
return copy;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}finally {
try {
bos.close();
oos.close();
bis.close();
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public GoldRingedStaff getGoldRingedStaff() {
return goldRingedStaff;
}
public void setGoldRingedStaff(GoldRingedStaff goldRingedStaff) {
this.goldRingedStaff = goldRingedStaff;
}
public void change(){
MonkeyKing origin = new MonkeyKing();
MonkeyKing monkeyKingClone = (MonkeyKing)origin.clone();
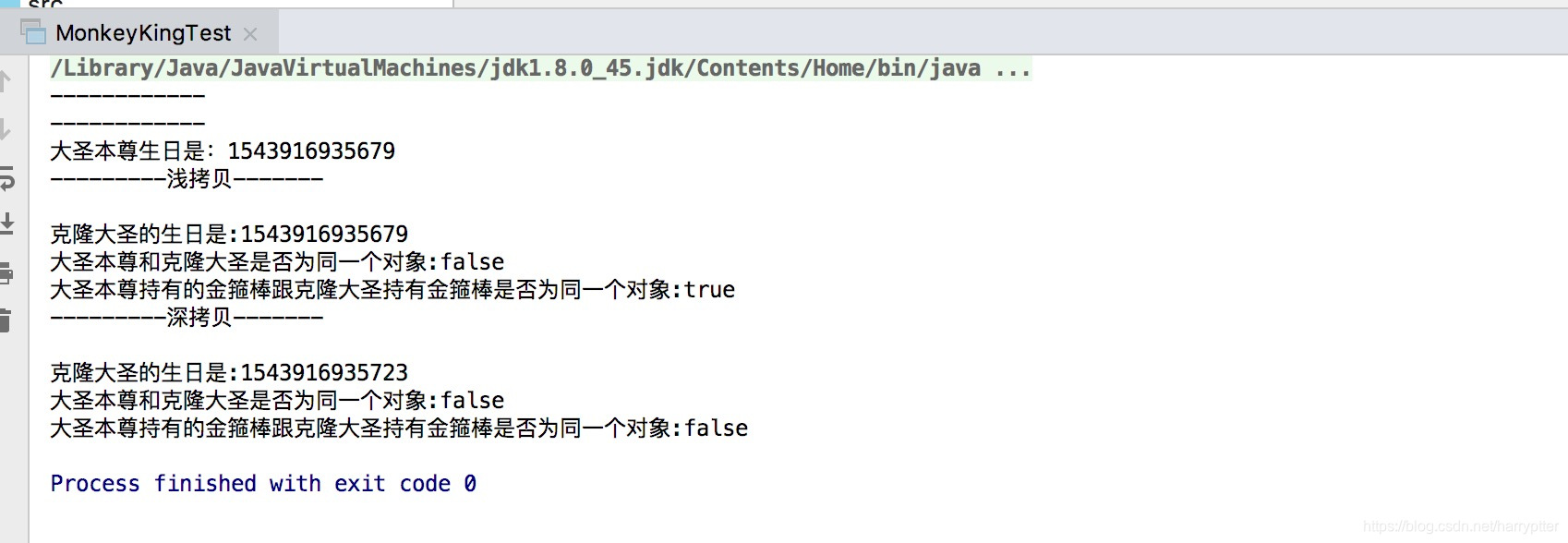
System.out.println("大圣本尊生日是:" + origin.getBirthday().getTime());
System.out.println("---------浅拷贝-------\n");
System.out.println("克隆大圣的生日是:" + monkeyKingClone.getBirthday().getTime());
System.out.println("大圣本尊和克隆大圣是否为同一个对象:" + (origin == monkeyKingClone));
System.out.println("大圣本尊持有的金箍棒跟克隆大圣持有金箍棒是否为同一个对象:" + (origin.getGoldRingedStaff() == monkeyKingClone.getGoldRingedStaff()));
MonkeyKing monkeyKingCopy = (MonkeyKing)copy();
System.out.println("---------深拷贝-------\n");
System.out.println("克隆大圣的生日是:" + monkeyKingCopy.getBirthday().getTime());
System.out.println("大圣本尊和克隆大圣是否为同一个对象:" + (origin == monkeyKingCopy));
System.out.println("大圣本尊持有的金箍棒跟克隆大圣持有金箍棒是否为同一个对象:" + (origin.getGoldRingedStaff() == monkeyKingCopy.getGoldRingedStaff()));
}
}
创建一个测试类:
package ProtoType;
public class MonkeyKingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MonkeyKing monkeyKing = new MonkeyKing();
monkeyKing.change();
}
}
执行,测试类,返回结果:







 本文深入解析Java中的原型模式,一种用于高效复制对象的设计模式,尤其适用于对象创建成本较高的场景。通过实例演示浅拷贝与深拷贝的区别,以及如何在MonkeyKing类中实现这两种拷贝方式。
本文深入解析Java中的原型模式,一种用于高效复制对象的设计模式,尤其适用于对象创建成本较高的场景。通过实例演示浅拷贝与深拷贝的区别,以及如何在MonkeyKing类中实现这两种拷贝方式。
















 270
270

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








