redis2.6开始在计算内存使用总量时,排除了如下
- slave的输出缓冲区
- aof缓冲区
- aof重写缓冲区
int freeMemoryIfNeeded(void) {
size_t mem_used, mem_tofree, mem_freed;
int slaves = listLength(server.slaves);
/* Remove the size of slaves output buffers and AOF buffer from the
* count of used memory. */
mem_used = zmalloc_used_memory();
if (slaves) {
listIter li;
listNode *ln;
listRewind(server.slaves,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
redisClient *slave = listNodeValue(ln);
unsigned long obuf_bytes = getClientOutputBufferMemoryUsage(slave);
if (obuf_bytes > mem_used)
mem_used = 0;
else
mem_used -= obuf_bytes;
}
}
if (server.aof_state != REDIS_AOF_OFF) {
mem_used -= sdslen(server.aof_buf);
mem_used -= aofRewriteBufferSize();
}
/* Check if we are over the memory limit. */
if (mem_used <= server.maxmemory) return REDIS_OK;
if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_NO_EVICTION)
return REDIS_ERR; /* We need to free memory, but policy forbids. */
/* Compute how much memory we need to free. */
mem_tofree = mem_used - server.maxmemory;
mem_freed = 0;
while (mem_freed < mem_tofree) {
int j, k, keys_freed = 0;
for (j = 0; j < server.dbnum; j++) {
...
}
if (!keys_freed) return REDIS_ERR; /* nothing to free... */
}
return REDIS_OK;
}
redis3.0.0开始对于lru的算法有所调整
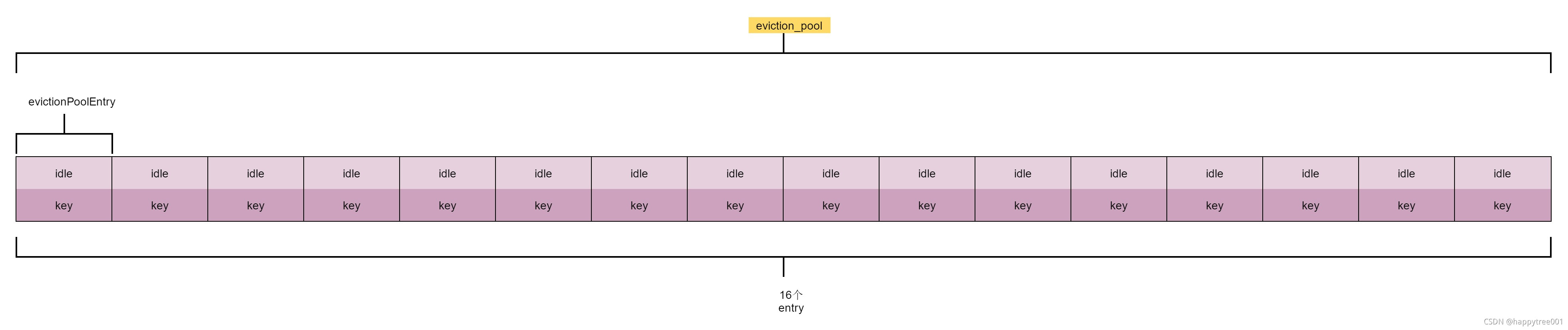
16个元素的淘汰池,每次随机筛选sample个元素到淘汰池中,然后从淘汰池中淘汰最近最近未访问的key
1. 结构增加evictionPoolEntry
#define REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE 16
struct evictionPoolEntry {
unsigned long long idle; /* Object idle time. */
sds key; /* Key name. */
};
/* Redis database representation. There are multiple databases identified
* by integers from 0 (the default database) up to the max configured
* database. The database number is the 'id' field in the structure. */
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP) */
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
struct evictionPoolEntry *eviction_pool; /* Eviction pool of keys */
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
} redisDb;
2. 初始化时建立淘汰池
void initServer(void) {
...
/* Create the Redis databases, and initialize other internal state. */
for (j = 0; j < server.dbnum; j++) {
server.db[j].dict = dictCreate(&dbDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].expires = dictCreate(&keyptrDictType,NULL);
...
server.db[j].eviction_pool = evictionPoolAlloc();
...
}
...
}
/* Create a new eviction pool. */
struct evictionPoolEntry *evictionPoolAlloc(void) {
struct evictionPoolEntry *ep;
int j;
ep = zmalloc(sizeof(*ep)*REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE);
for (j = 0; j < REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE; j++) {
ep[j].idle = 0;
ep[j].key = NULL;
}
return ep;
}
3. 更新淘汰池
3.1 筛选samples个key
和随机有一点不同,找到一个有数据的槽时,取当前槽下的所有节点,并且移动到下一个节点继续,当连续空的槽个数大于等于5个并且大于需要筛选的个数时,才进行下一次的随机
unsigned int dictGetSomeKeys(dict *d, dictEntry **des, unsigned int count) {
unsigned int j; /* internal hash table id, 0 or 1. */
unsigned int tables; /* 1 or 2 tables? */
unsigned int stored = 0, maxsizemask;
unsigned int maxsteps;
if (dictSize(d) < count) count = dictSize(d);
maxsteps = count*10;
/* Try to do a rehashing work proportional to 'count'. */
for (j = 0; j < count; j++) {
if (dictIsRehashing(d))
_dictRehashStep(d);
else
break;
}
tables = dictIsRehashing(d) ? 2 : 1;
maxsizemask = d->ht[0].sizemask;
if (tables > 1 && maxsizemask < d->ht[1].sizemask)
maxsizemask = d->ht[1].sizemask;
/* Pick a random point inside the larger table. */
unsigned int i = random() & maxsizemask;
unsigned int emptylen = 0; /* Continuous empty entries so far. */
while(stored < count && maxsteps--) {
for (j = 0; j < tables; j++) {
/* Invariant of the dict.c rehashing: up to the indexes already
* visited in ht[0] during the rehashing, there are no populated
* buckets, so we can skip ht[0] for indexes between 0 and idx-1. */
if (tables == 2 && j == 0 && i < (unsigned int) d->rehashidx) {
/* Moreover, if we are currently out of range in the second
* table, there will be no elements in both tables up to
* the current rehashing index, so we jump if possible.
* (this happens when going from big to small table). */
if (i >= d->ht[1].size) i = d->rehashidx;
continue;
}
if (i >= d->ht[j].size) continue; /* Out of range for this table. */
dictEntry *he = d->ht[j].table[i];
/* Count contiguous empty buckets, and jump to other
* locations if they reach 'count' (with a minimum of 5). */
if (he == NULL) {
emptylen++;
if (emptylen >= 5 && emptylen > count) {
i = random() & maxsizemask;
emptylen = 0;
}
} else {
emptylen = 0;
while (he) {
/* Collect all the elements of the buckets found non
* empty while iterating. */
*des = he;
des++;
he = he->next;
stored++;
if (stored == count) return stored;
}
}
}
i = (i+1) & maxsizemask;
}
return stored;
}
比如需要筛选5个元素,并且整个数据如下结构(忽略了hash正在重建的过程)
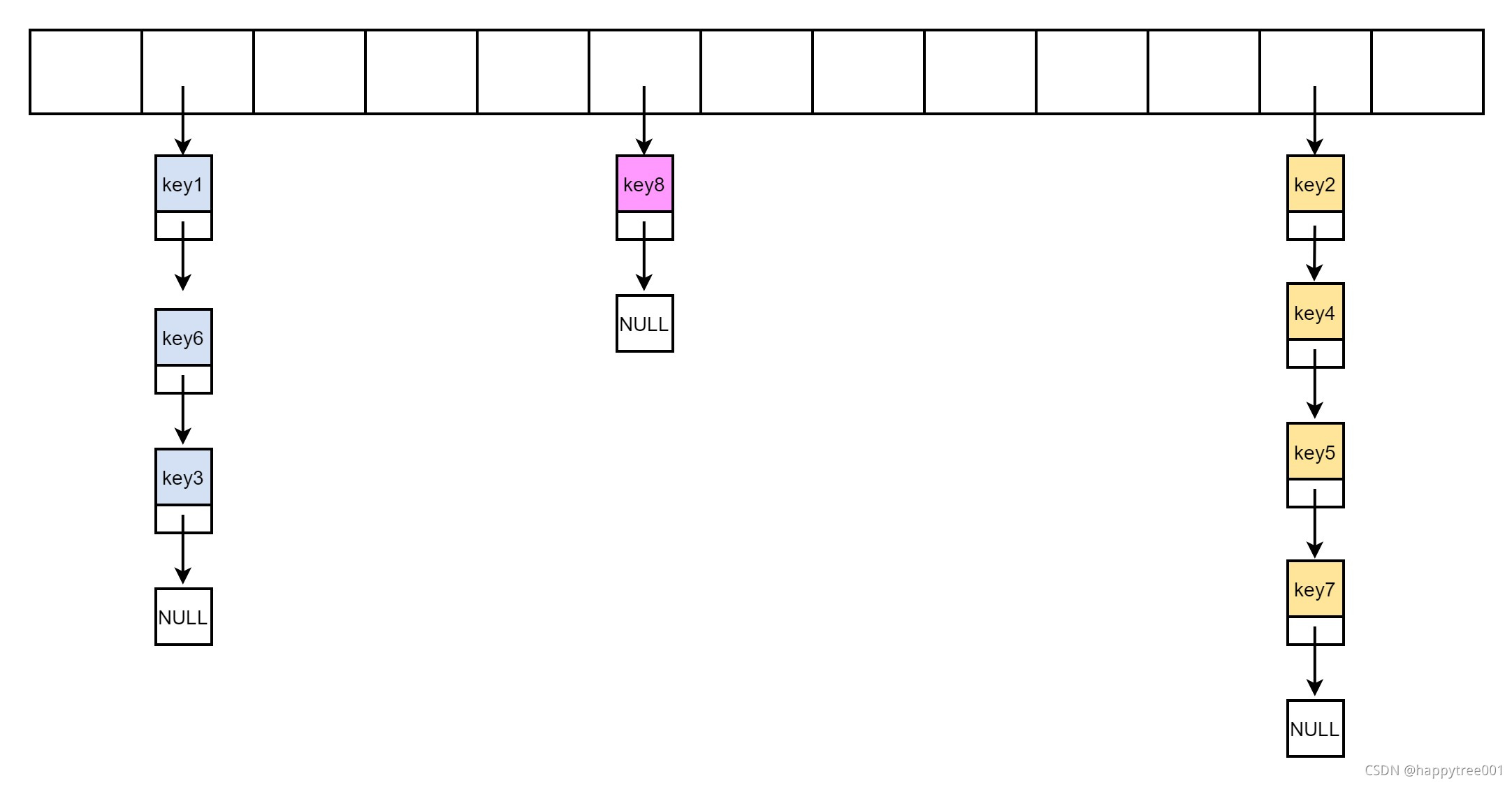
- 首选随机一个起始位置
...
unsigned int i = random() & maxsizemask;
...
比如i=1
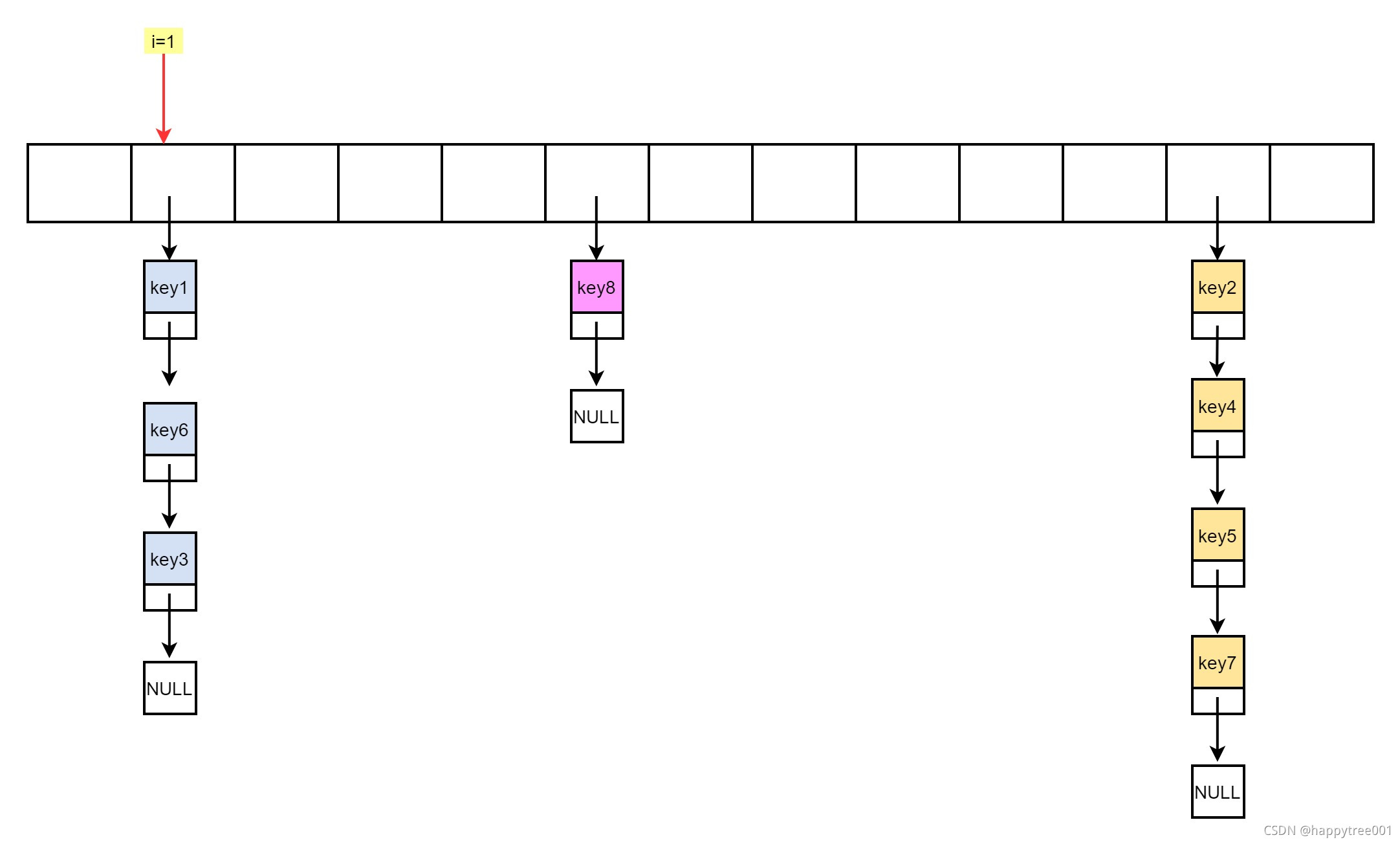
- 判断当前槽下是否有元素
当前i=1的槽下有元素,则将当前下所有的节点(在sample个数以内)- 取key1, key6,key3, stored=3
- 依然不够5个,继续
- 位置向下移一个位置
i = (i+1) & maxsizemask;- i = 2 无元素 , emptylen=1
- 继续
- 位置向下移一个位置
i = (i+1) & maxsizemask;- i = 3 无元素, emptylen=2
- 继续
- 位置向下移一个位置
i = (i+1) & maxsizemask;- i = 4 无元素, emptylen=3
- 继续
- 位置向下移一个位置
i = (i+1) & maxsizemask;- i = 5 有元素, emptylen=0
- 取 key8, stored=4
- 还不够5个继续
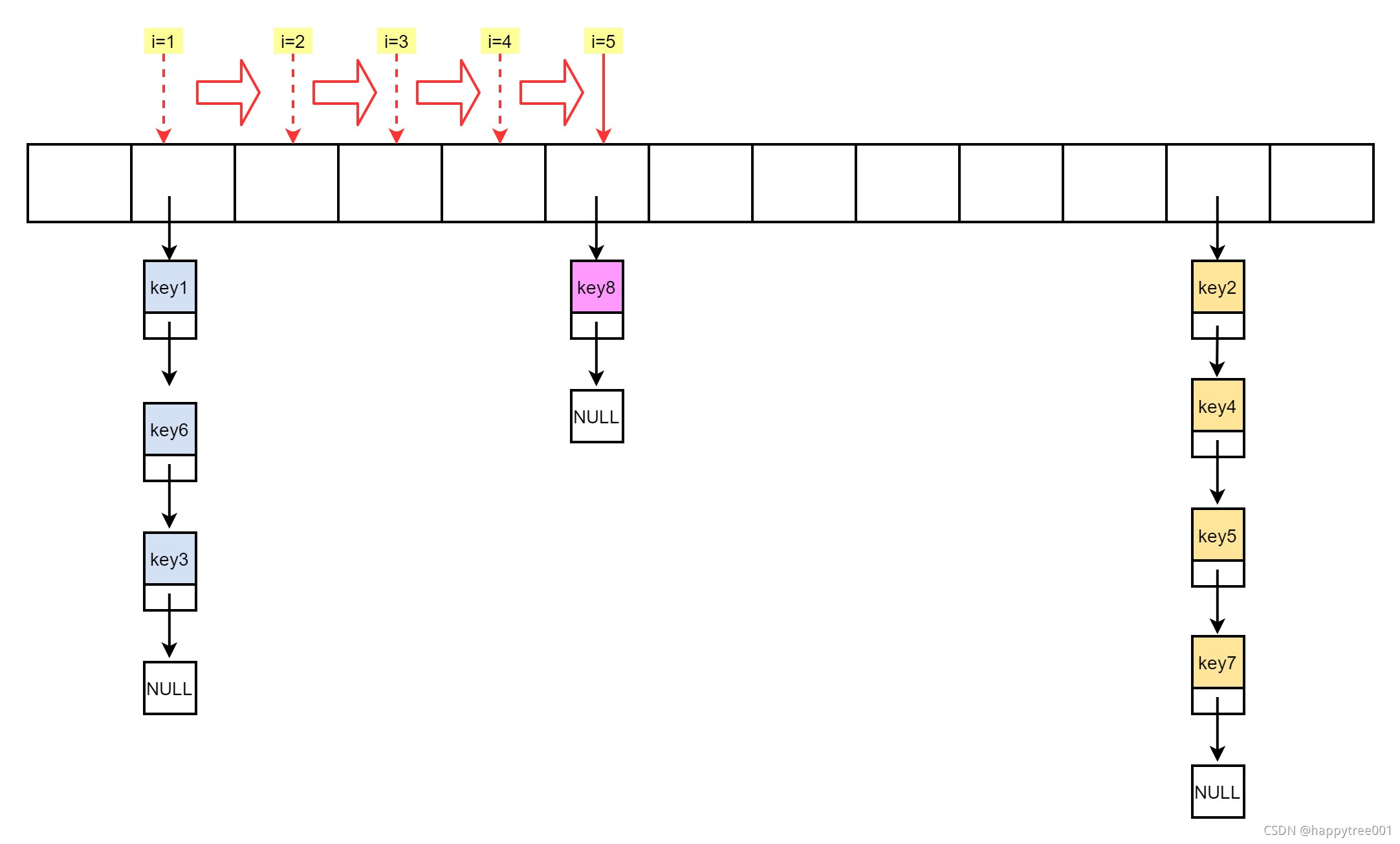
- 位置向下移一个位置
i = (i+1) & maxsizemask;- i = 6 无元素, emptylen=1
- 继续
- 位置向下移一个位置
i = (i+1) & maxsizemask;- i = 7 无元素, emptylen=2
- 继续
- 位置向下移一个位置
i = (i+1) & maxsizemask;- i = 8 无元素, emptylen=3
- 继续
- 位置向下移一个位置
- i = 9 无元素, emptylen=4
- 继续
- 位置向下移一个位置
i = (i+1) & maxsizemask;- i = 10 无元素, emptylen=5
- 重写随机位置, i = 4, emptylen=0
i = random() & maxsizemask;
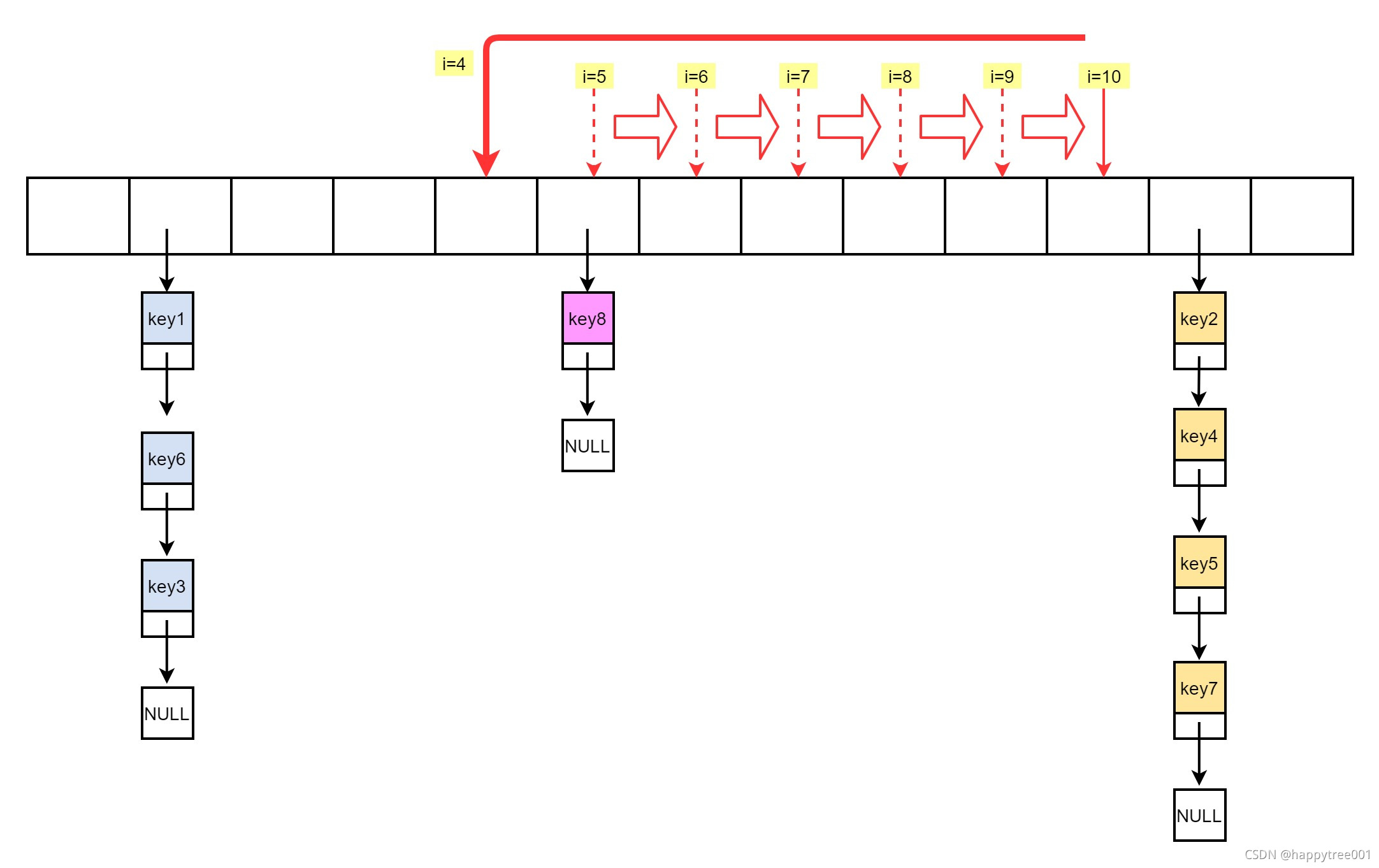
- 位置向下移一个位置
i = (i+1) & maxsizemask;- i = 5, 有元素
- 取key8, stored=5, 取够了,退出
最终取到的元素有key1,key6,key3,key8,key8
此函数:
不保证不重复不保证个数一定是sample个,while循环还有maxsteps控制(count*10)- 比dictGetRandomKey函数更快
3.2 将筛选的key加入淘汰池中
淘汰池中按照lru值的大小升序排序,每次淘汰最后一个元素则可。
#define EVICTION_SAMPLES_ARRAY_SIZE 16
void evictionPoolPopulate(dict *sampledict, dict *keydict, struct evictionPoolEntry *pool) {
int j, k, count;
dictEntry *_samples[EVICTION_SAMPLES_ARRAY_SIZE];
dictEntry **samples;
/* Try to use a static buffer: this function is a big hit...
* Note: it was actually measured that this helps. */
if (server.maxmemory_samples <= EVICTION_SAMPLES_ARRAY_SIZE) {
samples = _samples;
} else {
samples = zmalloc(sizeof(samples[0])*server.maxmemory_samples);
}
count = dictGetSomeKeys(sampledict,samples,server.maxmemory_samples);
for (j = 0; j < count; j++) {
unsigned long long idle;
sds key;
robj *o;
dictEntry *de;
de = samples[j];
key = dictGetKey(de);
/* If the dictionary we are sampling from is not the main
* dictionary (but the expires one) we need to lookup the key
* again in the key dictionary to obtain the value object. */
if (sampledict != keydict) de = dictFind(keydict, key);
o = dictGetVal(de);
idle = estimateObjectIdleTime(o);
/* Insert the element inside the pool.
* First, find the first empty bucket or the first populated
* bucket that has an idle time smaller than our idle time. */
k = 0;
while (k < REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE &&
pool[k].key &&
pool[k].idle < idle) k++;
if (k == 0 && pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1].key != NULL) {
/* Can't insert if the element is < the worst element we have
* and there are no empty buckets. */
continue;
} else if (k < REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE && pool[k].key == NULL) {
/* Inserting into empty position. No setup needed before insert. */
} else {
/* Inserting in the middle. Now k points to the first element
* greater than the element to insert. */
if (pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1].key == NULL) {
/* Free space on the right? Insert at k shifting
* all the elements from k to end to the right. */
memmove(pool+k+1,pool+k,
sizeof(pool[0])*(REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-k-1));
} else {
/* No free space on right? Insert at k-1 */
k--;
/* Shift all elements on the left of k (included) to the
* left, so we discard the element with smaller idle time. */
sdsfree(pool[0].key);
memmove(pool,pool+1,sizeof(pool[0])*k);
}
}
pool[k].key = sdsdup(key);
pool[k].idle = idle;
}
if (samples != _samples) zfree(samples);
}
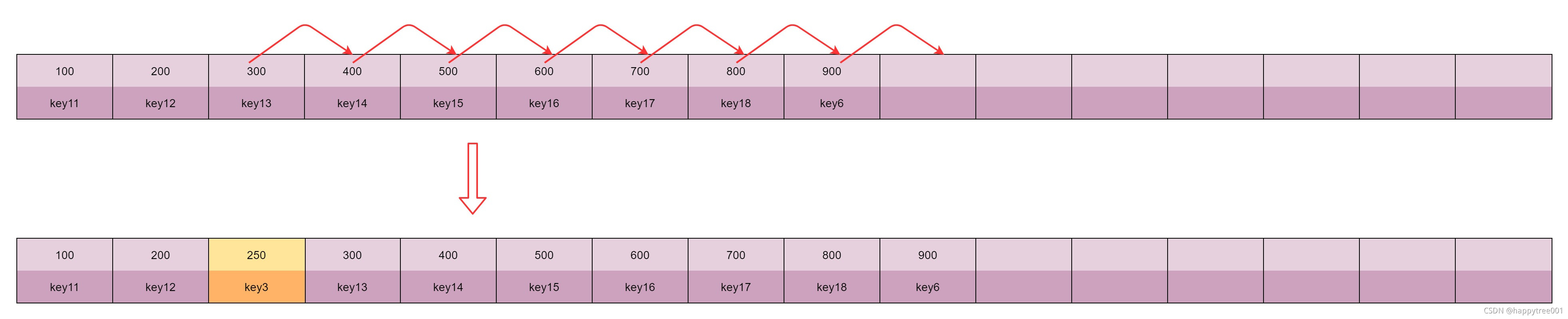
筛选出来的key的lru值和当前淘汰池中的lru值有三种关系
-
比最小值还小
不加入淘汰池, 比如key1的lru值为50,比最小的100还小

-
最大的值,并且淘汰池未满(即插入的是一个空位置)
直接插入,比如key6计算的lru为900

-
插入在已有数据的中间位置,并且淘汰池未满
将插入位置后的所有数据往后移动,以腾出插入位置, 比如key3的lru为250
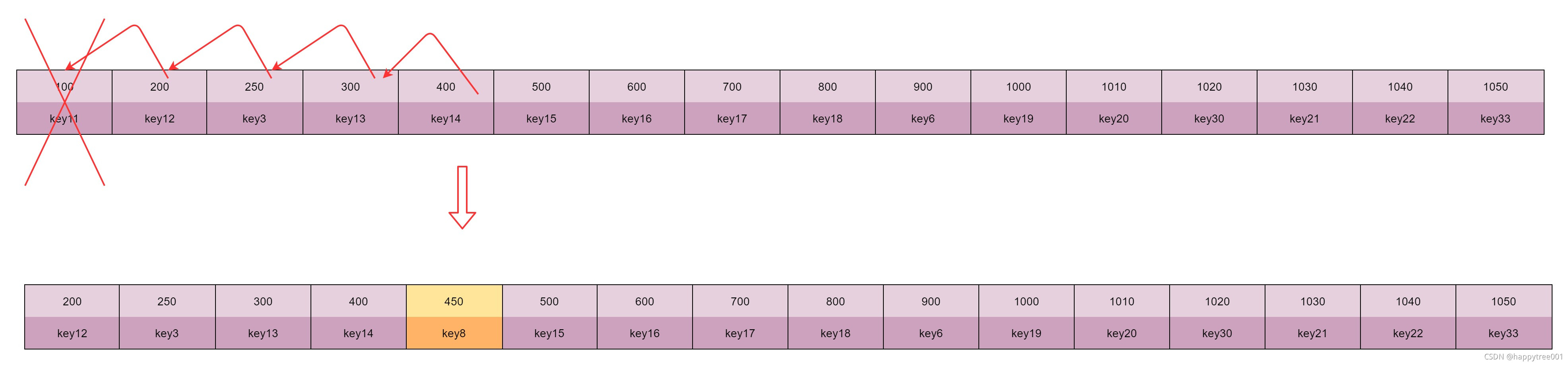
-
插入在已有数据的中间位置,并且淘汰池已经满了
将淘汰池中的第一个元素删除,将插入位置以前的数据向前移动,以腾出插入位置
比如key8的lru值为450,并且此时的16个位置都满了
3.3 从淘汰池中获取一个淘汰元素
从后向前遍历,后面的lru值越大,未访问的时间就越长
/* Go backward from best to worst element to evict. */
for (k = REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1; k >= 0; k--) {
if (pool[k].key == NULL) continue;
de = dictFind(dict,pool[k].key);
/* Remove the entry from the pool. */
sdsfree(pool[k].key);
/* Shift all elements on its right to left. */
memmove(pool+k,pool+k+1,
sizeof(pool[0])*(REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-k-1));
/* Clear the element on the right which is empty
* since we shifted one position to the left. */
pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1].key = NULL;
pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1].idle = 0;
/* If the key exists, is our pick. Otherwise it is
* a ghost and we need to try the next element. */
if (de) {
bestkey = dictGetKey(de);
break;
} else {
/* Ghost... */
continue;
}
}
在从淘汰池中取一个元素后,将会判断此key是否存在,因为整个淘汰池在整个redis运行过程中都存在,可能其中某些值已经被删除了
3.4 删除淘汰元素
/* Finally remove the selected key. */
if (bestkey) {
long long delta;
robj *keyobj = createStringObject(bestkey,sdslen(bestkey));
propagateExpire(db,keyobj);
/* We compute the amount of memory freed by dbDelete() alone.
* It is possible that actually the memory needed to propagate
* the DEL in AOF and replication link is greater than the one
* we are freeing removing the key, but we can't account for
* that otherwise we would never exit the loop.
*
* AOF and Output buffer memory will be freed eventually so
* we only care about memory used by the key space. */
delta = (long long) zmalloc_used_memory();
latencyStartMonitor(eviction_latency);
dbDelete(db,keyobj);
latencyEndMonitor(eviction_latency);
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("eviction-del",eviction_latency);
latencyRemoveNestedEvent(latency,eviction_latency);
delta -= (long long) zmalloc_used_memory();
mem_freed += delta;
server.stat_evictedkeys++;
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_EVICTED, "evicted",
keyobj, db->id);
decrRefCount(keyobj);
keys_freed++;
/* When the memory to free starts to be big enough, we may
* start spending so much time here that is impossible to
* deliver data to the slaves fast enough, so we force the
* transmission here inside the loop. */
if (slaves) flushSlavesOutputBuffers();
}
在删除操作中也比原先多了很多工作
- 计算了删除过程中执行的时间
- 增加执行时间监控,如果配置了阈值,并且超过了,则会发送一个事件
- 调用 notifyKeyspaceEvent
- 给slaves发送数据(如果有的话)





 本文详细介绍了Redis从2.6版本开始的内存管理机制,包括如何计算内存使用量,以及如何在超过最大内存限制时执行淘汰策略。在3.0版本中,Redis引入了一种新的LRU算法,通过16个元素的淘汰池选择待淘汰的键,根据键的最近未访问时间(lru值)进行淘汰。淘汰池的更新和淘汰过程涉及对键的随机采样和按照lru值排序。此外,文章还讨论了在删除淘汰元素时的额外操作,如计算内存释放量、通知键空间事件和向从服务器发送数据。
本文详细介绍了Redis从2.6版本开始的内存管理机制,包括如何计算内存使用量,以及如何在超过最大内存限制时执行淘汰策略。在3.0版本中,Redis引入了一种新的LRU算法,通过16个元素的淘汰池选择待淘汰的键,根据键的最近未访问时间(lru值)进行淘汰。淘汰池的更新和淘汰过程涉及对键的随机采样和按照lru值排序。此外,文章还讨论了在删除淘汰元素时的额外操作,如计算内存释放量、通知键空间事件和向从服务器发送数据。
















 1318
1318

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








