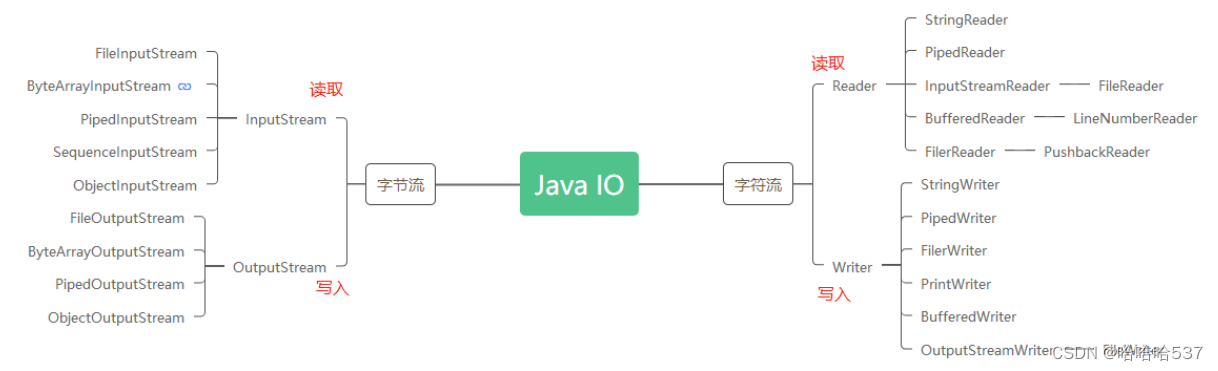
java io
i/o
I:input:输入,读,数据从哪里来
三种情况:1. 内存来,2. 文件来,3.网络来
O:output:输出,写,数据到哪里去
三种情况:1. 内存,2。文件里,3.网络中
IO流又叫输入输出流 ,输入和输出均是以内存作为参照物。
字节流
可以操作字符型和字节型。
复制文件内容
一,
public class IODemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IODemo ioDemo = new IODemo();
ioDemo.copay("F:\\小程序\\test01\\weather2\\project.config.json", "copay.json");
}
public void copay(String oldFilePath, String newFilePath) {
try (FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(oldFilePath);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(newFilePath)) {
byte[] count = new byte[1];
while ((fileInputStream.read(count)) != -1) {//每次读取byte.length个字节,这里每次读取1个所以速度很慢。
fileOutputStream.write(count);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
二,
public class IODemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IODemo ioDemo = new IODemo();
ioDemo.copay("F:\\小程序\\test01\\weather2\\project.config.json", "copay.json");
}
public void copay(String oldFilePath, String newFilePath) {
try (FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(oldFilePath);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(newFilePath)) {
byte[] count = new byte[20];
while ((fileInputStream.read(count)) != -1) {//每次读取byte.length个字节,这里每次读取20个所以速度很快。
fileOutputStream.write(count);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
但是因为fileInputStream.read()是读取数据覆盖上一次while循环读取的内容,所以读取的内容会有一些重复
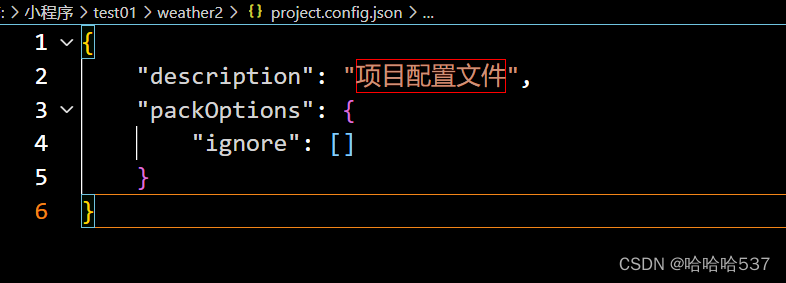
源文件:
复制后的文件:
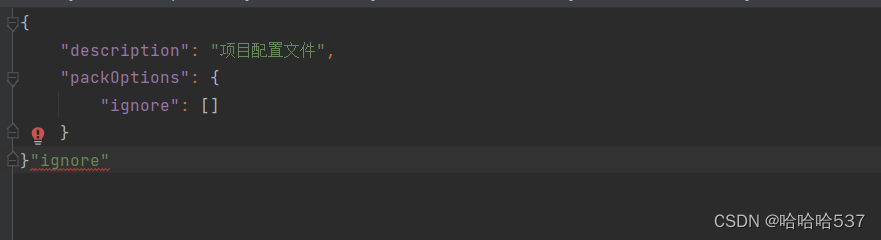
这里多出了 “ “ignore” ”这些字符
三,
public class IODemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IODemo ioDemo = new IODemo();
ioDemo.copay("F:\\小程序\\test01\\weather2\\project.config.json", "copay.json");
}
public void copay(String oldFilePath, String newFilePath) {
try (FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(oldFilePath);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(newFilePath)) {
byte[] count = new byte[1024];
int length = 0;
while ((length =fileInputStream.read(count)) != -1) {//每次读取1024个,并把不为空的字节数赋值给length变量。
fileOutputStream.write(count, 0, length);//每次循环都将内容从count变量写到copay.json文件并且每次都是从第0个开始,第length个结束。这样就解决了读写慢或者内容重复的问题。
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
try-with-resources
JDK1.7以后try有一个新的用法叫 try-with-resources。解决流的关闭问题。
try()里可以有多个临时流对象,无论是出现异常还是程序执行完毕,都会自动关闭流。可以用在流、数据库连接等。
字符流
只能处理字符型
public void charEncodingUTF8() {
String value = "你";
try(FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("value.txt")) {
//能写入成功,文件里可以显示 你
fileOutputStream.write(value.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void charEncodingISO() {
String value = "你";
try(FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("value.txt")) {
// 写入不成功个,文件里显示乱码
fileOutputStream.write(value.getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Buffer流
java.io.BufferedInputStream 与 java.io.BufferedOutputStream 可以为InputStream、OutputStream 增加缓冲区功能。
BufferedInputStream的默认缓冲区大小是8192,当读取数据时BufferedInputStream会把这个缓冲区填满,当使用read() 方法时,实际上是从缓冲区读取数据,而不是直接读取源数据。当缓冲区数据不足时,BufferedInputStream 才会操作給定的 InputStream 的read() 方法读取数据到缓冲区。
BufferedOutputStream的缓存区默认是8192,数据会先写入到buf,当buf区装满后或close()、flush()时把缓存数据写到目标(磁盘或其它目标)。





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








