ServletContext
0.ServletContext介绍及用法
0.1介绍
ServletContext官方叫servlet上下文。服务器会为每一个工程创建一个对象,这个对象就是ServletContext对象。这个对象全局唯一,而且工程内部的所有servlet都共享这个对象。所以叫全局应用程序共享对象。
0.2作用
-
是一个域对象
-
可以读取全局配置参数
-
可以搜索当前工程目录下面的资源文件
-
可以获取当前工程名字(了解)
0.2.1 servletContext是一个域对象
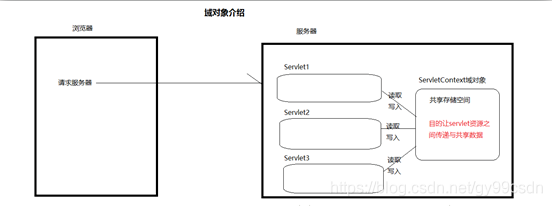
0.2.1.1 域对象介绍
域对象是服务器在内存上创建的存储空间,用于在不同动态资源(servlet)之间传递与共享数据。
0.2.1.2 域对象方法
凡是域对象都有如下3个方法:
| 项目 | Value |
|---|---|
| setAttribute(name,value);name是String类型,value是Object类型; | 往域对象里面添加数据,添加时以key-value形式添加 |
| getAttribute(name); | 根据指定的key读取域对象里面的数据 |
| removeAttribute(name); | 根据指定的key从域对象里面删除数据 |
0.2.1.2 域对象功能代码
域对象存储数据AddDataServlet代码
publicvoid doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {
//往serlvetContext里面存数据
//1.获取ServletContext对象
//getServletContext()
//2.往对象里面设置数据
getServletContext().setAttribute("username","admin");
response.getOutputStream().write("用户名写入到servletContext成功".getBytes());
}
获取域对象数据GetDataServlet代码
publicvoid doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取ServletContext里面的用户名数据
Object valueObject =getServletContext().getAttribute("username");
if(valueObject!=null){
response.getOutputStream().write(("从servletContext读取到的用户名据:"+valueObject.toString()).getBytes());
}
}
servletContext存储数据特点:
- 全局共享,里面的数据所有动态资源都可以写入和获取
- 服务器启动的时候创建,服务器关闭的时候销毁,因为这是全局应用程序对象,全局共享对象
0.2.2 可以读取全局配置参数
0.2.2.1 servletContext读取全局参数核心方法
getServletContext().getInitParameter(name);//根据指定的参数名获取参数值
getServletContext().getInitParameterNames();//获取所有参数名称列表
0.2.2.2 实现步骤:
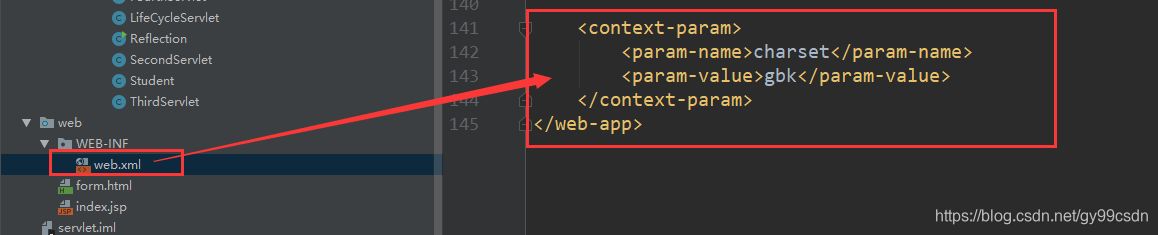
- 在web.xml中配置全局参数
<!-- 全局配置参数,因为不属于任何一个servlet,但是所有的servlet都可以通过servletContext读取这个数据 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>param1</param-name>
<param-value>value1</param-value>
</context-param>
<context-param>
<param-name>param2</param-name>
<param-value>value2</param-value>
</context-param>
- 在动态资源servlet里面使用servletcontext读取全局参数代码
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {
//使用servletContext读取全局配置参数数据
//核心方法 /*getServletContext().getInitParameter(name);//根据指定的参数名获取参数值
getServletContext().getInitParameterNames();//获取所有参数名称列表*/
//打印所有参数
//1.先获取所有全局配置参数名称
Enumeration<String> enumeration = getServletContext().getInitParameterNames();
//2.遍历迭代器
while(enumeration.hasMoreElements()){
//获取每个元素的参数名字
String parameName = enumeration.nextElement();
//根据参数名字获取参数值
String parameValue =getServletContext().getInitParameter(parameName);
//打印
System.out.println(parameName+"="+parameValue);
}
}
0.2.2.3 可以搜索当前工程目录下面的资源文件
核心方法:
getServletContext().getRealPath(path),根据相对路径获取服务器上资源的绝对路径
getServletContext().getResourceAsStream(path),根据相对路径获取服务器上资源的输入字节流
0.2.2.4 可以获取当前工程名字
核心方法: getServletContext().getContextPath();
作用:获取当前工程名字
publicvoid doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取工程名字,getServletContext().getContextPath()
response.getOutputStream().write(("工程名字:"+getServletContext().getContextPath()).getBytes());
}
1.获取全局性的初始化参数(了解)
使用场景:
web.xml中有如下标签
可不可以将这个键值对也封装到一个map中
ServletContext对象中有一个map
map.put(param-name,param-value);
getInitParameter(String name){
return map.get(name);
}
@WebServlet("/context1")
public class ContextServlet1 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.先拿到ServletContext对象
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
//2.调用getInitParameter
String charset = servletContext.getInitParameter("charset");
System.out.println(charset);
}
}
2.context域(非常重要)
例一:
DomainServlet1.java
@WebServlet("/domain1")
public class DomainServlet1 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//context域
//进行了一些操作,得到一个值,list、string、对象
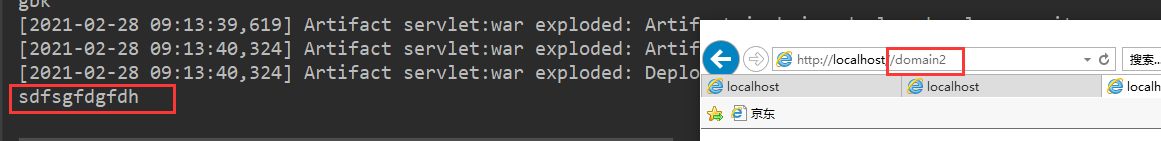
String name = "sdfsgfdgfdh";
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
//这个API相当于去给这个servletContext对象里面的map进行赋值
servletContext.setAttribute("username", name);
}
}
DomainServlet2.java
@WebServlet("/domain2")
public class DomainServlet2 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
String username = (String) servletContext.getAttribute("username");
System.out.println(username);
}
}
例二:
IndexServlet.java
@WebServlet(value = "/index",loadOnStartup = 1)//loadOnStartup启动优先级
public class IndexServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
//init()随着应用的加载直接执行
public void init() throws ServletException {
//运算,得到一个结果;或者去查询数据库、或者配置文件 IO
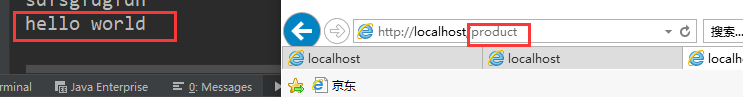
String content = "hello world";
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("content", content);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
}
ProductServlet.java
@WebServlet("/product")
public class ProductServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
String content = (String) servletContext.getAttribute("content");
System.out.println(content);
}
}
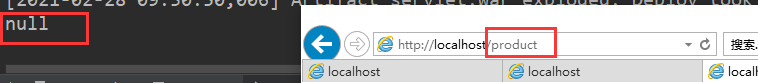
结果:
如果IndexServlet.java中没有写(loadOnStartup = 1)
3.获取绝对路径
为什么要有这个API?
获取应用根目录的绝对路径。
每个应用其实有两个属性,path叫做应用名,一个叫做docBase是当前应用的绝对路径。docBase就是我们应用的部署根目录。
接下来只需要提供一个相对部署根目录的相对路径,那么拼上前面docBase是不是就可以拿到绝对路径了。
PathServlet.java
@WebServlet("/path")
public class PathServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
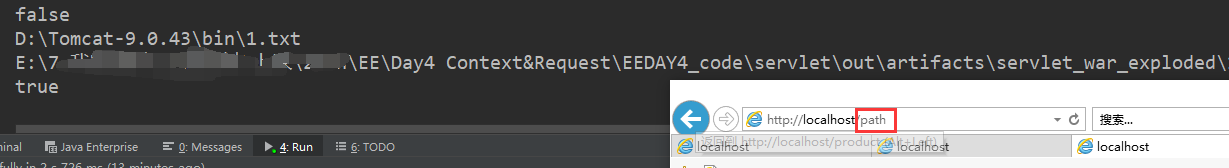
//希望可以拿到部署根目录下面的1.txt的absolutePath----file----inputStream
File file = new File("1.txt");
System.out.println(file.exists());
// 为什么再EE项目里调用相对路径,发现相对的是tomcat的bin目录?
// 工作目录其实是tomcat的bin目录,再哪个目录下调用了jvm
//实际上是再bin目录下调用了jvm
//从本质上去看EE项目:tomcat是一个java程序,调用我们写的代码片段
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
//获取部署根目录下面1.txt文件的绝对路径 -----file
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
//可以输入一个空字符串,那么它回给你返回当前部署根目录的绝对路径
//也可以输入一个相对路径,那么它回给你返回部署根目录的绝对路径+提供的相对路径
//比如你提供了一个1.html docBase + /1.html
//如果你希望获取应用下面的任何一个文件的绝对路径,
// 那么只需要给它传入一个相对部署根目录的一个相对路径即可
String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("1.html");
System.out.println(realPath);
//WEB-INF用来屏蔽浏览器的直接访问
String realPath1 = servletContext.getRealPath("WEB-INF/2.txt");
boolean exists = new File(realPath1).exists();
System.out.println(exists);
}
}
结果:







 本文详细介绍了ServletContext的概念、作用及其在Servlet中的具体应用。主要内容包括如何作为域对象进行数据存储和共享、读取全局配置参数、获取资源文件及工程名字等。
本文详细介绍了ServletContext的概念、作用及其在Servlet中的具体应用。主要内容包括如何作为域对象进行数据存储和共享、读取全局配置参数、获取资源文件及工程名字等。
















 1538
1538

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








