Decorator 是一种结构型设计模式,它动态地给对象添加额外的职责,相比继承更加灵活。装饰器模式通过创建包装对象来实现功能的扩展。
核心思想
-
运行时扩展:在不修改原有类的情况下动态添加功能
-
组合优于继承:通过对象组合而非继承实现功能扩展
-
透明性:装饰后的对象与原对象具有相同的接口
主要角色
-
Component(抽象组件):定义对象的接口
-
ConcreteComponent(具体组件):实现基本功能
-
Decorator(抽象装饰器):继承/实现Component,并持有Component引用
-
ConcreteDecorator(具体装饰器):实现具体的装饰功能
经典案例:咖啡加料系统
1. 基础实现
// 2. 具体组件
class SimpleCoffee implements Coffee {
@Override
public double getCost() {
return 1.0;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return "普通咖啡";
}
}
// 3. 抽象装饰器
abstract class CoffeeDecorator implements Coffee {
protected final Coffee decoratedCoffee;
public CoffeeDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
this.decoratedCoffee = coffee;
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return decoratedCoffee.getCost();
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return decoratedCoffee.getDescription();
}
}
// 1. 抽象组件
interface Coffee {
double getCost();
String getDescription();
}
// 4. 具体装饰器
class MilkDecorator extends CoffeeDecorator {
public MilkDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return super.getCost() + 0.5;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return super.getDescription() + ",加牛奶";
}
}
class SugarDecorator extends CoffeeDecorator {
public SugarDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return super.getCost() + 0.2;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return super.getDescription() + ",加糖";
}
}
// 客户端
public class DecoratorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Coffee coffee = new SimpleCoffee();
System.out.println(coffee.getDescription() + " ¥" + coffee.getCost());
coffee = new MilkDecorator(coffee);
System.out.println(coffee.getDescription() + " ¥" + coffee.getCost());
coffee = new SugarDecorator(coffee);
System.out.println(coffee.getDescription() + " ¥" + coffee.getCost());
}
}
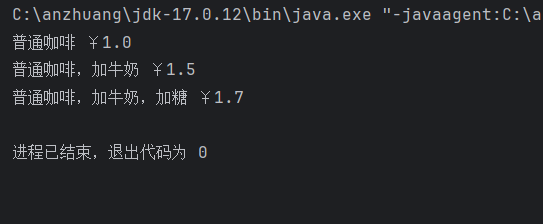
输出结果:
2. 简化实现(Java I/O风格)
Java I/O 流是装饰器模式的经典应用:
// 模拟InputStream
abstract class InputStream {
public abstract int read();
}
class FileInputStream extends InputStream {
@Override
public int read() {
System.out.println("读取文件字节");
return 0;
}
}
// 装饰器基类
class FilterInputStream extends InputStream {
protected InputStream in;
protected FilterInputStream(InputStream in) {
this.in = in;
}
@Override
public int read() {
return in.read();
}
}
// 具体装饰器
class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {
super(in);
}
@Override
public int read() {
System.out.println("缓冲读取");
return super.read();
}
}
class DataInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
public DataInputStream(InputStream in) {
super(in);
}
@Override
public int read() {
System.out.println("按数据类型读取");
return super.read();
}
}
// 客户端
public class IoStyleDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream in = new FileInputStream();
in = new BufferedInputStream(in);
in = new DataInputStream(in);
in.read(); // 组合功能
}
}
输出结果:

装饰器模式 vs 继承
| 特性 | 装饰器模式 | 继承 |
|---|---|---|
| 扩展方式 | 动态组合 | 静态编译时确定 |
| 功能组合 | 灵活的多层组合 | 单一继承链 |
| 类数量 | 大量小装饰器类 | 需要创建多个子类 |
| 运行时影响 | 可以动态添加/移除功能 | 编译时固定 |
实际应用场景
-
Java I/O 流:
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream("test.txt")); -
GUI组件装饰:
-
滚动条装饰基础组件
-
边框装饰可视化组件
-
-
Web开发:
// Servlet API示例 HttpServletRequest wrappedRequest = new RequestWrapper(originalRequest); -
Spring Security:
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext(); Authentication auth = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(...); context.setAuthentication(auth);
最佳实践建议
-
适用场景:
-
需要动态、透明地添加职责
-
不适合用子类扩展的情况(如需要大量组合)
-
-
注意事项:
-
装饰器接口必须与组件接口一致
-
避免创建过多小对象(可能影响性能)
-
与代理模式区别:装饰器侧重功能增强,代理侧重访问控制
-
-
Java实现技巧:
// 使用lambda简化装饰器(Java8+) Function<Coffee, Coffee> decorator = coffee -> { System.out.println("添加装饰"); return new Coffee() { public double getCost() { return coffee.getCost() + 0.3; } public String getDescription() { return coffee.getDescription() + "+装饰"; } }; };
装饰器模式通过灵活的运行时组合,完美实现了开闭原则(对扩展开放,对修改关闭),是面向对象设计中功能扩展的重要手段。




















 67
67

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








