用好标准库的模块

errno
通过系统errno精准捕获异常内容
>>> import os
>>> os.kill(12345, 0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ProcessLookupError: [Errno 3] No such process
>>> os.errno(3)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: module 'os' has no attribute 'errno'
>>> os.strerror(3)
'No such process'
>>> os.strerror(1)
'Operation not permitted'
>>> os.strerror(0)
'Success'
>>> os.strerror(2)
'No such file or directory'
>>> os.strerror(3)
'No such process'
>>> os.strerror(4)
'Interrupted system call'
>>> os.strerror(5)
'Input/output error'
>>>
>>> os.strerror(6)
'No such device or address'
# coding=utf-8
import os
import errno
def listdir(dirname):
try:
os.listdir(dirname)
except OSError as e:
error = e.errno
if error == errno.ENOENT:
print('No such file or directory')
elif error == errno.EACCES:
print('Prmission denied')
elif error == errno.ENOSPC:
print('No space left on device')
else:
print(e.strerror)
else:
print('No error!')
for filename in ['/no/such/dir', '/root', '/home/vagrant']:
listdir(filename)
subprocess
>>> import subprocess
>>>
>>> 1 call
>>> subprocess.call("ls -al /tmp/ddd", shell=True)
ls: cannot access /tmp/ddd: No such file or directory
2
>>> subprocess.call("systemctl show-environment", shell=True)
LANG=en_US.UTF-8
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
0
>>> res =subprocess.call("systemctl show-environment", shell=True)
LANG=en_US.UTF-8
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
>>> res
0
>>>
>>>
>>> 安全起见,不要直接使用shell=True
>>> import shlex
>>> subprocess.call(shlex.split("systemctl show-environment"), shell=False)
LANG=en_US.UTF-8
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
0
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>> subprocess.call(shlex.split("systemctl show-environmen"), shell=False)
Unknown operation 'show-environmen'.
1
>>> 2 check_call可以执行call的返回值不为0时,会抛出异常
>>> subprocess.check_call(shlex.split("systemctl show-environmen"), shell=False)
Unknown operation 'show-environmen'.
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/usr/local/python3/lib/python3.7/subprocess.py", line 347, in check_call
raise CalledProcessError(retcode, cmd)
subprocess.CalledProcessError: Command '['systemctl', 'show-environmen']' returned non-zero exit status 1.
>>>
>>> 3 Popen,用来执行子进程的类,通过commuicate获取返回结果
>>> from subprocess import Popen, PIPE
>>> proc = Popen(shlex.split("systemctl show-environment"), stdout=PIPE)
>>> print(proc.communicate())
(b'LANG=en_US.UTF-8\nPATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin\n', None)
>>>
>>> Popen实现shell管道
>>> proc = Popen(shlex.split("ps -ef"), stdout=PIPE)
>>> proc2 = Popen(shlex.split("grep gunic"), stdin=proc.stdout, stdout=PIPE)
>>> print(proc2.communicate())
(b'root 7374 1 0 06:12 ? 00:00:00 /srv/vpp_agent_venv3.7/bin/python3 /srv/vpp_agent_venv3.7/bin/gunicorn -c gunicorn\nroot 7377 7374 1 06:12 ? 00:00:25 /srv/vpp_agent_venv3.7/bin/python3 /srv/vpp_agent_venv3.7/bin/gunicorn -c gunicorn\nroot 7378 7374 1 06:12 ? 00:00:25 /srv/vpp_agent_venv3.7/bin/python3 /srv/vpp_agent_venv3.7/bin/gunicorn -c gunicorn\nroot 7379 7374 1 06:12 ? 00:00:25 /srv/vpp_agent_venv3.7/bin/python3 /srv/vpp_agent_venv3.7/bin/gunicorn -c gunicorn\n', None)
>>>
>>> 4 check_put是比Popen更简单的获取执行结果的方式
>>> subprocess.check_output(shlex.split("systemctl show-environment"))
b'LANG=en_US.UTF-8\nPATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin\n'
>>> res = subprocess.check_output(shlex.split("systemctl show-environment"))
>>> res
b'LANG=en_US.UTF-8\nPATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin\n'
>>> res = subprocess.check_output(shlex.split("systemctl show-environments"))
>>> 如果执行返回值不为0,会抛出异常
Unknown operation 'show-environments'.
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/usr/local/python3/lib/python3.7/subprocess.py", line 395, in check_output
**kwargs).stdout
File "/usr/local/python3/lib/python3.7/subprocess.py", line 487, in run
output=stdout, stderr=stderr)
subprocess.CalledProcessError: Command '['systemctl', 'show-environments']' returned non-zero exit status 1.
>>>
实例:
@bp.route("/exec_system_cmd")
@Validate.validate_exec_system_cmd
@log_execution_time
@use_cache(timeout=10)
@Count
def exec_system_cmd():
data = request.get_json()
cmd = data.get("cmd", None)
if not cmd:
return err_resp_json_make(extra_errmsg="exec_system_cmd fail", result="cmd cant be null")
try:
res = subprocess.check_output(shlex.split(cmd))
# res_list = res.decode().split("\n")
res = "\r\n".join(res.decode().split("\n"))
except (subprocess.CalledProcessError, ) as e:
res = "exec cmd error: {}".format(str(e))
return succ_resp_json_make("exec_system_cmd ok", res)
contextlib

实例:
python chapter14/section1/contextlib_example.py
通过contextmanager实现多个子context函数的聚合功能
# coding=utf-8
import threading
from contextlib import contextmanager
class LockContext(object):
def __init__(self):
print('__init__')
self.lock = threading.Lock()
def __enter__(self):
print('__enter__')
self.lock.acquire()
return self
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
print('__exit_')
self.lock.release()
with LockContext():
print('In the context')
class OpenContext(object):
def __init__(self, filename, mode):
print('OpenContext __init__')
self.fp = open(filename, mode)
def __enter__(self):
print('OpenContext __enter__')
return self.fp
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
print('OpenContext __exit__')
self.fp.close()
with OpenContext('/tmp/a', 'a') as f:
f.write('hello world')
print("write ok")
@contextmanager
def make_open_context(filename, mode):
print("in make_open_context")
fp = open(filename, mode)
try:
print("before yield make_open_context")
yield fp
print("after yield make_open_context")
finally:
print("finally make_open_context")
fp.close()
with make_open_context('/tmp/a', 'a') as f:
print("write before")
f.write('hello world\n')
print("write after")
"""@contextmanager decorator.
Typical usage:
@contextmanager
def some_generator(<arguments>):
<setup>
try:
yield <value>
finally:
<cleanup>
This makes this:
with some_generator(<arguments>) as <variable>:
<body>
equivalent to this:
<setup>
try:
<variable> = <value>
<body>
finally:
<cleanup>
"""
@contextmanager
def make_context(*args):
print(args)
yield args
with make_context(1, 2) as A:
with make_context(3, 4) as B:
print('In the context')
with make_context(1, 2) as A, make_context(3, 4) as B:
print('In the context')
# with nested(make_context(1, 2), make_context(3, 4)) as (A, B):
# print('In the context')
@contextmanager
def sqaure_context(*args):
res = (i*i for i in args)
yield res
@contextmanager
def plus_one_context(*args):
res = (i+i for i in args[0])
yield res
def handler(*args):
with sqaure_context(*args) as A:
with plus_one_context(A) as B:
return B
res = handler(1,2,3)
for i in res:
print(i)
python chapter14/section3/context_lib.py
# coding=utf-8
import os
import sys
from functools import partial
from contextlib import contextmanager
@contextmanager
def suppress(*exceptions):
try:
yield
except OSError as e:
print(str(e))
except exceptions:
pass
with suppress(OSError):
os.remove('/no/such/file')
with open('help.txt', 'w') as f:
oldstdout = sys.stdout
sys.stdout = f
try:
help(int)
finally:
sys.stdout = oldstdout
@contextmanager
def redirect_stdout(fileobj, std_type='stdout'):
oldstdout = getattr(sys, std_type)
setattr(sys, std_type, fileobj)
try:
yield fileobj
finally:
setattr(sys, std_type, oldstdout)
redirect_stderr = partial(redirect_stdout, std_type='stderr')
with open('help_out.txt', 'w') as out, open('help_err.txt', 'w') as err:
with redirect_stdout(out), redirect_stderr(err):
msg = 'Test'
sys.stdout.write('(stdout) A: {!r}\n'.format(msg))
sys.stderr.write('(stderr) A: {!r}\n'.format(msg))
functools
partial

wraps
class Validate():
@classmethod
def validate_exec_system_cmd(cls, f):
@wraps(f)
def decorated_function(*args, **kwargs):
json_data = request.get_json()
schema = Schema({
Required('cmd'): All(str),
})
try:
schema(json_data)
print("valiate ok")
# raise AssertionError('MultipleInvalid not raised')
except (MultipleInvalid, ) as e:
print(str(e))
return err_resp_json_make(errcode=FAIL, extra_errmsg=str(e), result='')
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return decorated_function
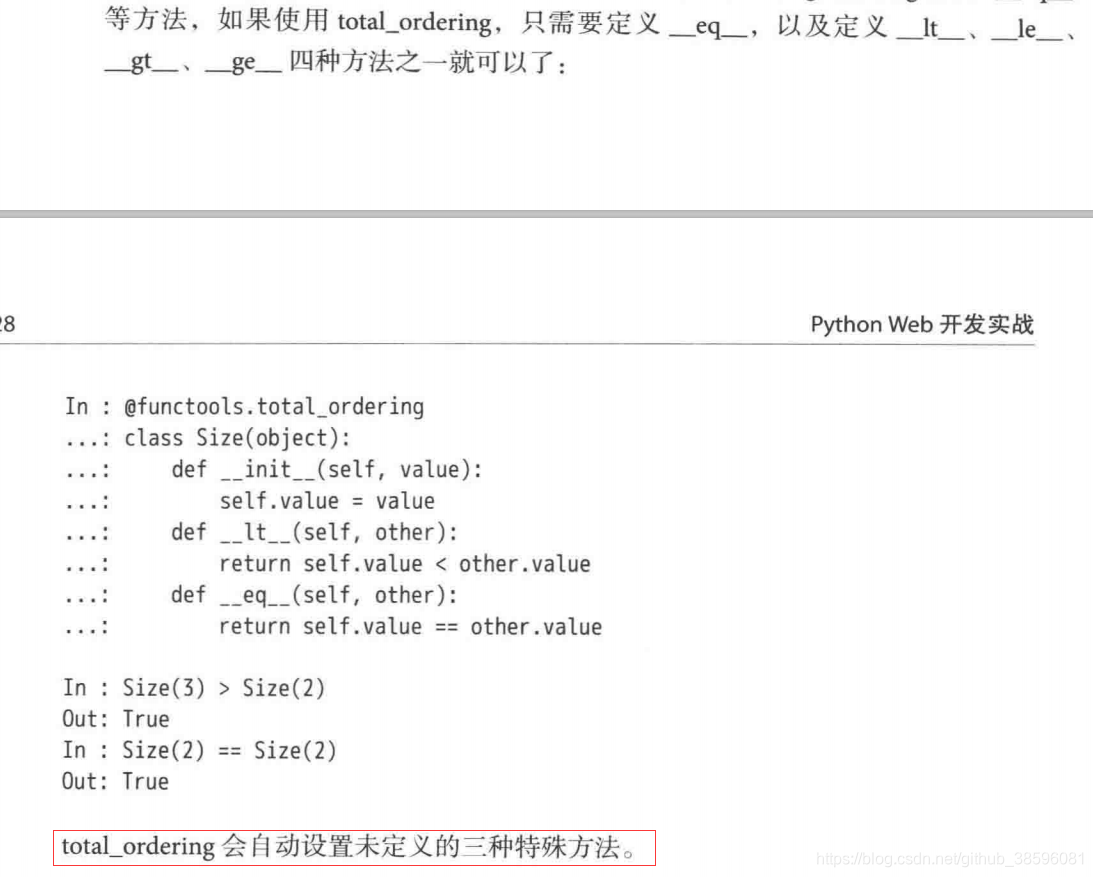
total_ordering
glob

partialmethod
python chapter14/section3/glorous_python.py
#获取第一个能被4整除的数
a = -1
for i in range(1,10):
if not i%4:
a = i
break
a = next((i for i in range(1,10) if not i % 4), -1)
#
# print(a)
res = ""
with open("./help.txt", "r") as f:
while True:
buff = f.read(32)
if buff == "": break
res += buff
# print(res)
import os
from functools import partial
here = os.path.dirname(__file__)
res = ""
with open(os.path.join(here, "help.txt"), "r") as f:
for buff in iter(partial(f.read, 32), ""):
res += buff
# print(res)
def find(seq, target):
found = False
for i, value in enumerate(seq):
if value == target:
found = True
break
return found
def find2(seq, target):
for i, value in enumerate(seq):
if value == target:
# found = True
break
else:
return -1
return i
print("find2--> {}".format(find2(["1","1","1","1","1","1"], "1")))
import urllib
from functools import wraps
def cache(func):
saved = {}
@wraps(func)
def deco(*args, **kwargs):
if not saved[args]: saved[args] = func(*args, **kwargs)
return saved[args]
return deco
@cache
def web_lookup(url):
return urllib.request.urlopen(url).read()
from functools import partialmethod
def get_name(self):
return self._name
class Cell(object):
def __init__(self):
self._alive = False
self._name = self.__class__
@property
def status(self):
return self._alive
def set_state(self, state):
self._alive = bool(state)
#partialmethod就是作用于类方法的partial
set_alive = partialmethod(set_state, True)
set_dead = partialmethod(set_state, False)
get_name = partialmethod(get_name)
cell = Cell()
print(cell.status)
cell.set_alive()
print(cell.status)
cell.set_dead()
print(cell.status)
# print(cell.get_name())
import requests
class Request(object):
default_url = "www.baidu.com"
def request(self, method, url, params=None, data=None):
print("execute request {} method {}".format(url, method))
# return self.METHOD_MAP.get(method)
get = partialmethod(request,"GET")
post = partialmethod(request,"POST")
put = partialmethod(request,"PUT")
delete = partialmethod(request,"DELETE")
get_default_url = partialmethod(get, default_url)
r = Request()
r.get_default_url()
r.get("shen.com")
r.put("xian.com")
operator
import operator
from functools import reduce
res = reduce(operator.mul, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
print(res)
res = map(lambda x: x**3, [10, 20, 30])
print(list(res))
for r in res:
print(r)
def f(op, *args):
return {
"+": operator.add,
"-": operator.sub,
"*": operator.mul,
"/": operator.floordiv,
"%": operator.mod
}[op](*args)
res = f("/", f("-", 1, 2), 3)
print(res)
res = map(lambda x, y: x + y, [1, 3, 5, 7, 9], [2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
print(list(res))
l = [1,2,3,4,5]
res = operator.itemgetter(l[1])(l)
print(res)
res = operator.itemgetter(1,3,4)(l)
print(res)
objs= [("a",2),("b",1),("c",3)]
res = sorted(objs,key=operator.itemgetter(0))
print(res)
# 获取对象属性值
import sys
print(sys.platform)
res = operator.attrgetter('platform')(sys)
print(res)
# 调用对象方法
attr = "a"
res = operator.methodcaller('isdigit')(attr)
print(res)
functools&collections
python chapter14/section3/functools\&collections.py
import functools
def f(a, b=3):
return a+b
f2 = functools.partial(f,1)
# f2()
print(f2())
print(f2(5))
@functools.total_ordering
class Size(object):
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
def __le__(self, other):
return self.value <= other.value
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.value == other.value
print(Size(2) > Size(3))
print(Size(2) < Size(3))
print(Size(3) == Size(3))
def numeric_compare(x, y):
print(x, y)
return x[1] - y[1]
# print(sorted())
import collections
words = ["a", "b", "b", "b", "c", "d", "c"]
cnt = collections.Counter(words)
#統計出現次數最多的前2個
print(cnt.most_common(2))
class Str():
def __init__(self, value):
self._value = value
@property
def value(self):
return self._value
def __repr__(self):
return "<Str (val: {})>".format(self._value)
#双端队列
d = collections.deque((Str(1),Str(2)))
print(d.append(Str(3)))
print(d.appendleft(Str(4)))
print(d.popleft())
d.extend((Str(4),))
print(d)
d.extendleft((Str(9),Str(10)))
print(d)
# d = {}
d = collections.defaultdict(int)
words = ["a","b","a","c","d","c"]
for w in words: d[w] += 1
print(d)
d2 = collections.defaultdict(str)
words = ["a","b","a","c","d","c"]
for w in words: d2[w] += "1"
print(d2)
print("-"*20)
# dir(list)
import bisect
class BisectList(list):
def insort(self, arr):
bisect.insort_right(self, arr)
d = collections.defaultdict(BisectList)
d["l"].insort(1)
d["l"].insort(9)
d["l"].insort(3)
print(d)
d = collections.defaultdict(lambda x=10: x)
print(d["a"])
d["a"] += 1
print(d["a"])
print("-"*20)
od = collections.OrderedDict([("a", 1),("b", 3),("c", 2)])
print(od)
class User():
def __init__(self, name, age, location, phone):
self._name = name
self._age = age
self._location = location
self._phone = phone
User = collections.namedtuple("User", "name age location phone")
user = User("shen", 23, "chongqing", "1111")
print(user.age)
print(user._asdict())
print(user._asdict()["location"])
python语法最佳实践


命名


使用join连接字符串

EAFP vs LBYL
python的风格更倾向于EAFP,但如果你的预期操作在逻辑上概率超过50%,应该使用LBYL

 定义类的__str__和__repr__
定义类的__str__和__repr__


优美的python
charpter14/section3/glorious_python.py
#获取第一个能被4整除的数
a = -1
for i in range(1,10):
if not i%4:
a = i
break
a = next((i for i in range(1,10) if not i % 4), -1)
#
# print(a)
res = ""
with open("./help.txt", "r") as f:
while True:
buff = f.read(32)
if buff == "": break
res += buff
# print(res)
import os
from functools import partial
here = os.path.dirname(__file__)
res = ""
with open(os.path.join(here, "help.txt"), "r") as f:
for buff in iter(partial(f.read, 32), ""):
res += buff
# print(res)
def find(seq, target):
found = False
for i, value in enumerate(seq):
if value == target:
found = True
break
return found
def find2(seq, target):
for i, value in enumerate(seq):
if value == target:
# found = True
break
else:
return -1
return i
print("find2--> {}".format(find2(["1","1","1","1","1","1"], "1")))
import urllib
from functools import wraps
def cache(func):
saved = {}
@wraps(func)
def deco(*args, **kwargs):
if not saved[args]: saved[args] = func(*args, **kwargs)
return saved[args]
return deco
@cache
def web_lookup(url):
return urllib.request.urlopen(url).read()
from functools import partialmethod
def get_name(self):
return self._name
class Cell(object):
def __init__(self):
self._alive = False
self._name = self.__class__
@property
def status(self):
return self._alive
def set_state(self, state):
self._alive = bool(state)
#partialmethod就是作用于类方法的partial
set_alive = partialmethod(set_state, True)
set_dead = partialmethod(set_state, False)
get_name = partialmethod(get_name)
cell = Cell()
print(cell.status)
cell.set_alive()
print(cell.status)
cell.set_dead()
print(cell.status)
# print(cell.get_name())
import requests
class Request(object):
default_url = "www.baidu.com"
def request(self, method, url, params=None, data=None):
print("execute request {} method {}".format(url, method))
# return self.METHOD_MAP.get(method)
get = partialmethod(request,"GET")
post = partialmethod(request,"POST")
put = partialmethod(request,"PUT")
delete = partialmethod(request,"DELETE")
get_default_url = partialmethod(get, default_url)
r = Request()
r.get_default_url()
r.get("shen.com")
r.put("xian.com")
singedispatch
3.7要手动安装singedispatch
(vpp_agent_venv3.7) [root@localhost source]# pip install singledispatch
实例:
charpter14/section3/json_singledispatch.py
# coding=utf-8
import json
from datetime import date, datetime
from singledispatch import singledispatch
from functools import update_wrapper
def methdispatch(func):
dispatcher = singledispatch(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kw):
return dispatcher.dispatch(args[1].__class__)(*args, **kw)
wrapper.register = dispatcher.register
update_wrapper(wrapper, func)
return wrapper
def json_serial(obj):
if isinstance(obj, datetime):
serial = obj.isoformat()
return serial
TypeError(repr(obj) + ' is not JSON serializable')
class Board(object):
def __init__(self, id, name, create_at=None):
self.id = id
self.name = name
if create_at is None:
create_at = datetime.now()
self.create_at = create_at
def to_dict(self):
return {'id': self.id, 'name': self.name,
'create_at': self.create_at}
@methdispatch
def get(self, arg):
return getattr(self, arg, None)
@get.register(list)
def _(self, arg):
return [self.get(x) for x in arg]
@singledispatch
def json_encoder(obj):
raise TypeError(repr(obj) + ' is not JSON serializable')
@json_encoder.register(date)
@json_encoder.register(datetime)
def encode_date_time(obj):
return obj.isoformat()
board = Board(1, 'board_1')
try:
print(json.dumps(board))
except (TypeError, ) as e:
print(str(e))
print(json.dumps(board.to_dict(), default=json_encoder))
print(board.get('name'))
print(board.get(['id', 'create_at']))
suppress

redirect_stdout和redirect_stderr







 本文深入探讨了Python标准库的使用,包括errno模块用于精确异常处理,subprocess进行进程控制,contextlib实现上下文管理器以聚合功能,以及functools、glob、operator等模块的实用技巧。此外,还讨论了Python的编程风格EAFP与LBYL的选择,以及类的__str__和__repr__方法。文章提供了多个示例代码,帮助读者掌握这些高级Python特性。
本文深入探讨了Python标准库的使用,包括errno模块用于精确异常处理,subprocess进行进程控制,contextlib实现上下文管理器以聚合功能,以及functools、glob、operator等模块的实用技巧。此外,还讨论了Python的编程风格EAFP与LBYL的选择,以及类的__str__和__repr__方法。文章提供了多个示例代码,帮助读者掌握这些高级Python特性。
















 1066
1066

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








