数据结构优化
HashMap
简介
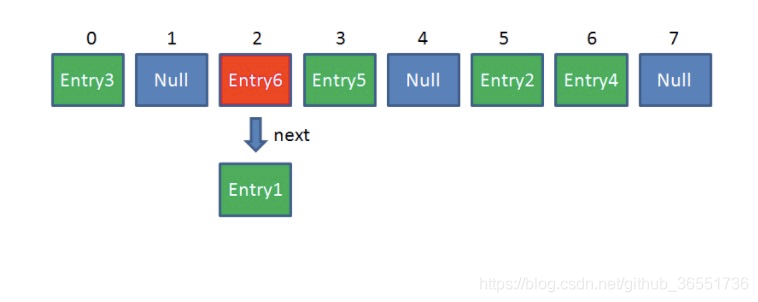
java中的常用集合,底层使用数组+链表的数据格式存储键值对。数组为主干,元素为键值对组成的Entry
源码分析
关键元素
// 默认初始容量-必须为2的幂
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
// 最大容量
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 阀值 当前容量的75%
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 当链表长度大于8时转换为红黑树 当红黑树长度小于6时转换为链表
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
put
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
//声明了一个局部变量 tab,局部变量 Node 类型的数据 p,int 类型 n,i
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
/*首先将当前 hashmap 中的 table(哈希表)赋值给当前的局部变量 tab,然后判断tab
是不是空或者长度是不是 0,实际上就是判断当前 hashmap 中的哈希表是不是空或者长度等于 0
**/
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
//如果是空的或者长度等于0,代表现在还没哈希表,所以需要创建新的哈希表,
//默认就是创建了一个长度为 16 的哈希表
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//将当前哈希表中与要插入的数据位置对应的数据取出来,(n - 1) & hash])就是
//找当前要插入的数据应该在哈希表中的位置,如果没找到,代表哈希表中当前的位置是空的,否则就代表找到数据了, 并赋值给变量 p
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null){
//创建一个新的数据,这个数据没有下一条,并将数据放到当前这个位置
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);}
else {
//代表要插入的数据所在的位置是有内容的
//声明了一个节点 e, 一个 key k
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//如果当前位置上的那个数据的 hash 和我们要插入的 hash 是一样,代表没有放错位置
//如果当前这个数据的 key 和我们要放的 key 是一样的,实际操作应该是就替换值
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))){
//将当前的节点赋值给局部变量 e
e = p;
//如果当前节点的 key 和要插入的 key 不一样,
//然后要判断当前节点是不是一个红黑色类型的节点
}else if (p instanceof TreeNode){
//如果是就创建一个新的树节点,并把数据放进去
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
}else {
//如果不是树节点,代表当前是一个链表,那么就遍历链表
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
//如果当前节点的下一个是空的,就代表没有后面的数据了
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
//创建一个新的节点数据并放到当前遍历的节点的后面
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 重新计算当前链表的长度是不是超出了限制
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) {
/*超出了之后就将当前链表转换为树,注意转换树的时候,
如果当前数组的长度小于MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(默认 64),会触发扩容,
我个人感觉可能是因为觉得一个节点下面的数据都超过8 了,
说明 hash寻址重复的厉害(比如数组长度为 16 ,
hash 值刚好是 0或者 16 的倍数,导致都去同一个位置),需要重新扩容重新 hash**/
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
}
break;
}
//如果当前遍历到的数据和要插入的数据的 key 是一样,和上面之前的一样,赋值给变量 e,下面替换内容
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { //如果当前的节点不等于空,
V oldValue = e.value;//将当前节点的值赋值给 oldvalue
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value; //将当前要插入的 value 替换当前的节点里面值
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;//增加长度
if (++size > threshold){
/*
如果当前的 hash表的长度已经超过了当前 hash 需要扩容的长度,
重新扩容,条件是 haspmap 中存放的数据超过了临界值(经过测试),
而不是数组中被使用的下标
**/
resize();
}
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
get
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K, V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final HashMap.Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
//定义变量
HashMap.Node<K,V>[] tab; HashMap.Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
//查看数据需要满足一下条件
//1)数组不为空
//2)数组长度>0
//3)通过hash计算出该元素在数组中存放位置的索引,而且该索引处数据不为空null
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
//判断该数组索引位置处第一个是否为我们要找的元素 判断条件需要满足hash 和 key 相同
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
//如果第一个就是我们要找的,直接返回即可
return first;
//如果第一个不是,我们需要循环遍历,然后找数据
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
//如果第1个的元素是红黑树类型的节点
if (first instanceof HashMap.TreeNode)
//那我们需要调用红黑树的方法查找节点
return ((HashMap.TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
//如果不是,则该为链表,需要遍历查找
do {
//循环判断下一个节点的hash和key是否相同
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
//更新e为下一个
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
//没找到返回Null
return null;
}
SparseArray
简介
integer到Object的映射。与其他Array不同的是,他的index可以是不连续的。比HashMap更节省内存,因为它避免了auto-boxing keys并且他的数据结构中的每个映射关系不依赖一个额外的入口对象。使用数组 数据结构来存储映射,使用二分查找法 查找key。不适用于存储大量的数据,通常他比传统的HashMap慢,因为查找需要通过二分搜索,而且增加和删除需要在Array中插入和删除条目。对于存储量几百的容器来说,性能的差异不是很大,少于50%.为了提高性能,这个容器对于移除key有一个优化:它保留那些被移除的条目并给它们一个deleted标志而不是直接删除并压缩数组。这个条目可以在以后被同样的键值重用或者在之后的垃圾回收时一起进行回收。垃圾回收会在任何一个数组需要增长或者映射的size或者条目的值被获取的时间被执行。
可以通过keyAt(int)方法和valueAt(int)方法遍历容器中的item。
优点:
避免了基本数据类型的装箱操作
不需要额外的结构体,单个元素的存储成本更低
数据量小的情况下,随机访问的效率更高
缺点:
插入操作需要复制数组,增删效率降低
数据量巨大时,复制数组成本巨大,gc()成本也巨大
数据量巨大时,查询效率也会明显下降
源码分析
关键元素
// 删除元素后的标志
private static final Object DELETED = new Object();
// 是否存在垃圾,当调用delete remove 等方法时标记为true
private boolean mGarbage = false;
// 存储key的数组
private int[] mKeys;
// 存储value的数组
private Object[] mValues;
// 当前集合的大小
private int mSize;
binarySearch
class ContainerHelpers {
/**
* 通过二分查找获取value值在当前数组中的位置
* @param array
* @param size
* @param value
* @return 如果存在value则返回该元素的索引,如果不存在当前元素则返回~(比该元素小的前一个元素的索引) ~ 非运算
* ~1 = -2 ~-1 = 0
* 即如果存在则返回正整数或0 不存在则返回负整数
*/
static int binarySearch(int[] array, int size, int value) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = size - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
final int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
final int midVal = array[mid];
if (midVal < value) {
lo = mid + 1;
} else if (midVal > value) {
hi = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid; // value found
}
}
return ~lo; // value not present
}
static int binarySearch(long[] array, int size, long value) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = size - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
final int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
final long midVal = array[mid];
if (midVal < value) {
lo = mid + 1;
} else if (midVal > value) {
hi = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid; // value found
}
}
return ~lo; // value not present
}
}
put
public void put(int key, E value) {
// 使用二分查找查询当前key存在的索引
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
//如果i >= 0 证明元素存在 直接覆盖 value数组中对应索引的值
if (i >= 0) {
mValues[i] = value;
} else {
// i<0 证明不存在 i是比当前元素小的最近的元素
// 如待插入元素为15, 存在数组[10,13,14,16,44] 则应该插入14与16之间 返回~(14的索引)即 ~2 等于 -3;
// i = ~i (~-3 等于 2) //获取 14的正确索引值
i = ~i;
//如果索引小于当前长度,且value数组中当前索引的值被删除标记为deleted 那么就覆盖keys数组以及value数组中当前索引对应的值
if (i < mSize && mValues[i] == DELETED) {
mKeys[i] = key;
mValues[i] = value;
return;
}
//如果 当前 集合中存在垃圾(被删除过),并且当前集合长度>= key数组的长度 则进行垃圾回收
if (mGarbage && mSize >= mKeys.length) {
gc();
// Search again because indices may have changed.
i = ~ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
}
// 将 key 跟value插入数组中对应位置
mKeys = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mKeys, mSize, i, key);
mValues = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mValues, mSize, i, value);
mSize++;
}
}
get
/**
* Gets the Object mapped from the specified key, or <code>null</code>
* if no such mapping has been made.
*/
public E get(int key) {
return get(key, null);
}
/**
* 含默认值重写方法
* @param key
* @param valueIfKeyNotFound 默认值
* @return value
*/
public E get(int key, E valueIfKeyNotFound) {
// 二分查找 key对应的索引值
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
// i < 0 或者 当前索引对应value 被删除时 返回默认值
if (i < 0 || mValues[i] == DELETED) {
return valueIfKeyNotFound;
} else {
return (E) mValues[i];
}
}
ArrayMap
简介
ArrayMap是一个<key,value>映射的数据结构,它设计上更多的是考虑内存的优化,内部是使用两个数组进行数据存储,一个数组记录key的hash值,另外一个数组记录Value值,它和SparseArray一样,也会对key使用二分法进行从小到大排序,在添加、删除、查找数据的时候都是先使用二分查找法得到相应的index,然后通过index来进行添加、查找、删除等操作,所以,应用场景和SparseArray的一样,如果在数据量比较大的情况下,那么它的性能将退化至少50%。
源码分析
关键元素
put
public V put(K key, V value) {
final int osize = mSize;
// 1.计算 hash code 并获取 index
final int hash;
int index;
if (key == null) {
// 为空直接取 0
hash = 0;
index = indexOfNull();
} else {
// 否则取 Object.hashCode()
hash = mIdentityHashCode ? System.identityHashCode(key) : key.hashCode();
index = indexOf(key, hash);
}
// 2.如果 index 大于等于 0 ,说明之前存在相同的 hash code 且 key 也相同,则直接覆盖
if (index >= 0) {
index = (index<<1) + 1;
final V old = (V)mArray[index];
mArray[index] = value;
return old;
}
// 3.如果没有找到则上面的 indexOf() 或者 indexOfNull() 就会返回一个负数,而这个负数就是由将要插入的位置 index 取反得到的,所以这里再次取反就变成了将进行插入的位置
index = ~index;
// 4.判断是否需要扩容
if (osize >= mHashes.length) {
final int n = osize >= (BASE_SIZE*2) ? (osize+(osize>>1))
: (osize >= BASE_SIZE ? (BASE_SIZE*2) : BASE_SIZE);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: grow from " + mHashes.length + " to " + n);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
// 5.申请新的空间
allocArrays(n);
if (CONCURRENT_MODIFICATION_EXCEPTIONS && osize != mSize) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
if (mHashes.length > 0) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: copy 0-" + osize + " to 0");
// 将数据复制到新的数组中
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, ohashes.length);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, oarray.length);
}
// 6.释放旧的数组
freeArrays(ohashes, oarray, osize);
}
if (index < osize) {
// 7.如果 index 在当前 size 之内,则需要将 index 开始的数据移到 index + 1 处,以腾出 index 的位置
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: move " + index + "-" + (osize-index)
+ " to " + (index+1));
System.arraycopy(mHashes, index, mHashes, index + 1, osize - index);
System.arraycopy(mArray, index << 1, mArray, (index + 1) << 1, (mSize - index) << 1);
}
if (CONCURRENT_MODIFICATION_EXCEPTIONS) {
if (osize != mSize || index >= mHashes.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
// 8.然后根据计算得到的 index 分别插入 hash,key,以及 code
mHashes[index] = hash;
mArray[index<<1] = key;
mArray[(index<<1)+1] = value;
mSize++;
return null;
}
indexOf
/*
(1) 如果当前为空表,则直接返回 ~0,注意不是 0 ,而是最大的负数。
(2) 在 mHashs 数组中进行二分查找,找到 hash 的 index。
(3) 如果 index < 0,说明没有找到。
(4) 如果 index >= 0,且在 mArray 中对应的 index<<1 处的 key 与要找的 key 又相同,则认为是同一个 key,说明找到了。
(5) 如果 key 不相同,说明只是 hash code 相同,那么分别向后和向前进行搜索,如果找到了就返回。如果没找到,那么对 end 取反就是当前需要插入的 index 位置。
**/
int indexOf(Object key, int hash) {
final int N = mSize;
// Important fast case: if nothing is in here, nothing to look for.
if (N == 0) {
return ~0;
}
int index = binarySearchHashes(mHashes, N, hash);
// If the hash code wasn't found, then we have no entry for this key.
if (index < 0) {
return index;
}
// If the key at the returned index matches, that's what we want.
if (key.equals(mArray[index<<1])) {
return index;
}
// Search for a matching key after the index.
int end;
for (end = index + 1; end < N && mHashes[end] == hash; end++) {
if (key.equals(mArray[end << 1])) return end;
}
// Search for a matching key before the index.
for (int i = index - 1; i >= 0 && mHashes[i] == hash; i--) {
if (key.equals(mArray[i << 1])) return i;
}
// Key not found -- return negative value indicating where a
// new entry for this key should go. We use the end of the
// hash chain to reduce the number of array entries that will
// need to be copied when inserting.
return ~end;
}
get
public V get(Object key) {
final int index = indexOfKey(key);
return index >= 0 ? (V)mArray[(index<<1)+1] : null;
}





 本文深入剖析了Java中HashMap的数据结构、源码实现及其工作原理,包括put和get方法的关键流程,并对比SparseArray和ArrayMap的特点及应用场景。
本文深入剖析了Java中HashMap的数据结构、源码实现及其工作原理,包括put和get方法的关键流程,并对比SparseArray和ArrayMap的特点及应用场景。
















 3403
3403

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








