ThreadLocal 的使用
变量值的共享可以使用 public static 变量的形式,所有的线程都使用同一个 public static 变量。如果想实现每一个线程都有自己的共享变量该如何解决?JDK 中提供的类 ThreadLocal 正是为了解决这样的问题。
类 Thread Local 主要为了解决的就是每个线程绑定自己的值,可以将 ThreadLocal 类比喻成全局存放数据的盒子,盒子中可以存储每个线程的私有数据
方法 get() 和 null
public class ThreadLocal_Demo1 {
public static ThreadLocal t1 = new ThreadLocal();
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(t1.get() == null){
System.out.println("从未放过值");
t1.set((int)(Math.random()*10));
}
System.out.println(t1.get());
System.out.println(t1.get());
}
}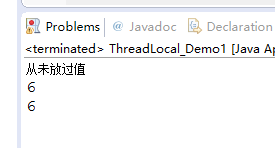
从上图中可以看到,第一次调用 t1 对象的 get() 方法时返回值是 null,通过调用 set() 方法赋值将值打印在控制台上。类 ThreadLocal 解决的是变量在不同线程间的隔离性,也就是不同的线程拥有自己的值,不同线程中的值是可以放入 ThreadLocal 中进行保存的。
验证线程隔离性
创建测试用的项目 ThreadLocalTest,类 Tools.java 代码如下
Tools 代码
public class Tools {
public static ThreadLocal t1 = new ThreadLocal();
}ThreadA 代码
public class ThreadA extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Tools.t1.set("ThreadA "+i);
System.out.println("Thread A get Value "+ Tools.t1.get());
Thread.sleep(200);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}ThreadB 代码
public class ThreadB extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Tools.t1.set("ThreadB "+i);
System.out.println("Thread B get Value "+ Tools.t1.get());
Thread.sleep(200);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}主线程代码
public class mainThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Thread A = new ThreadA();
Thread B = new ThreadB();
A.start();
B.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Tools.t1.set("main "+ i);
System.out.println("Main get Value = " + Tools.t1.get());
Thread.sleep(200);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
程序运行结果如上所示。
虽然 3 个线程都向 t1 对象中 set() 数据值,但每个线程还是能够取出自己的数据。
创建新的项目,我们重新验证一次数据的隔离性
Tools 代码
import java.util.Date;
public class Tools {
public static ThreadLocal<Date> t1 = new ThreadLocal<Date>();
}ThreadA 代码
import java.util.Date;
public class ThreadA extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if(Tools.t1.get() == null){
Tools.t1.set(new Date());
}
System.out.println("Thread A get Value "+ Tools.t1.get());
Thread.sleep(200);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}ThreadB 代码
import java.util.Date;
public class ThreadB extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if(Tools.t1.get() == null){
Tools.t1.set(new Date());
}
System.out.println("Thread B get Value "+ Tools.t1.get());
Thread.sleep(200);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}main 线程代码
public class mainThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Thread A = new ThreadA();
Thread B = new ThreadB();
A.start();
B.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if(Tools.t1.get() == null){
Tools.t1.set(new Date());
}
System.out.println("Main get Value = " + Tools.t1.get());
Thread.sleep(200);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}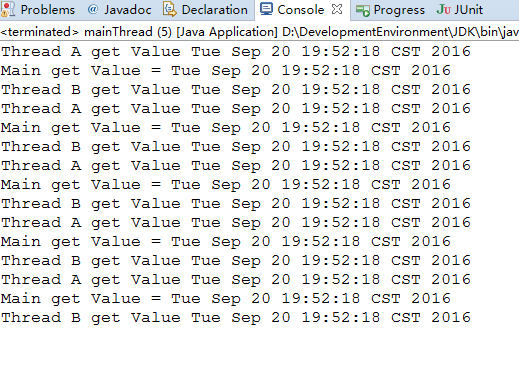
如上所示,虽然数据隔离性方面没有问题,但是每一次设置值的时候都要进行非空判定是一件令人烦恼的事情,那么我们要如何解决呢?
解决 get() 返回 null 问题
创建名称为 ThreadLcoal4 的项目,继承 ThreadLocal 类产生的 ThreadLocalExt 类
ThreadLocalExt 代码
public class ThreadLocalExt extends ThreadLocal {
public static ThreadLocal<Date> t1 = new ThreadLocal<Date>();
protected Object initialValue() {
return "我是默认值,第一次 get 的时候不再为空";
}
}main 线程代码
public class mainThread {
public static ThreadLocalExt t1 = new ThreadLocalExt();
public static void main(String[] args) {
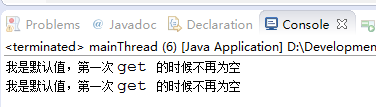
if(t1.get() == null){
System.out.println("从未放过值");
}
System.out.println(t1.get());
System.out.println(t1.get());
}
}
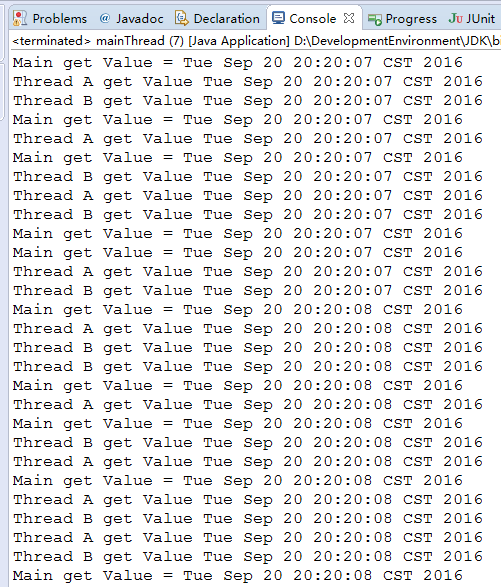
再次验证线程变量的隔离性
ThreadLocalExt
public class ThreadLocalExt extends ThreadLocal {
public static ThreadLocal<Date> t1 = new ThreadLocal<Date>();
protected Object initialValue() {
return new Date().getTime();
}
}Tools
public class ThreadLocalExt extends ThreadLocal {
public static ThreadLocal<Date> t1 = new ThreadLocal<Date>();
protected Object initialValue() {
return new Date().getTime();
}
}ThreadA
public class ThreadA extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Tools.t1.set(new Date());
System.out.println("Thread A get Value " + Tools.t1.get());
Thread.sleep(200);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}ThreadB
public class ThreadB extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Tools.t1.set(new Date());
System.out.println("Thread B get Value " + Tools.t1.get());
Thread.sleep(200);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}mainThread
public class mainThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Thread A = new ThreadA();
Thread B = new ThreadB();
A.start();
B.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Tools.t1.set(new Date());
System.out.println("Main get Value = " + Tools.t1.get());
Thread.sleep(200);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}





 本文详细介绍了ThreadLocal类在Java中的使用方法,包括解决线程间变量隔离的问题,避免共享变量冲突,以及如何设置默认值来避免get方法返回null等问题。
本文详细介绍了ThreadLocal类在Java中的使用方法,包括解决线程间变量隔离的问题,避免共享变量冲突,以及如何设置默认值来避免get方法返回null等问题。
















 680
680

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








